Steemian Friends,
Today, I will do homework for @kouba01 sir's lesson in Week 03 of Steemit Learning Challenge 23. This week's lesson is called SLC S23 Week 3 || Computer Repair-CPU (Processor). I learned about processors this week after computer motherboards. I hope everyone likes my homework.
.png)
Design By Canva
I have drawn the computer's block diagram and written the CPU's workings in short form below. The computer has two parts: input and output. Data is sent to the CPU through inputs. As input, we mostly use keyboards and mice. On the other hand, the CPU processes the data received from the input and sends it to us through the output. As output devices, we mostly use monitors and printers.
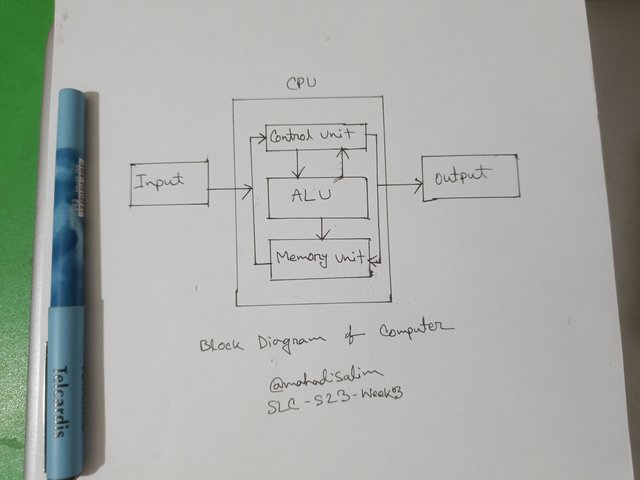
Computer Block Diagram
There are three main parts within the CPU. Control unit, ALU (Arithmetic Logical Unit) and memory with these three parts CPU. Here, the data exchange is shown in the block diagram. The control unit manages operations by passing instructions between the ALU and memory. The ALU unit sends the data to memory by completing logical operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Memory stores the data for some time and sends it to the output through the control unit. Many times, it stores data in memory. Thus, the CPU completes its work.
Today, I am sharing my experience with computer processors. I wrote about my computer usage in the previous week's lessons. I started using desktop computers in 2004. Then, the processors were not as updated as they are now. I remember the processors were Pentium processors. I have seen processor problems many times on my computer. I have had to change processors, especially over the years when processor update models came out. Then, I apply the processor update model to do graphics and other tasks. But to change the processor, we have to base it on the motherboard's model number, so later, we change the entire CPU and buy a new PC.
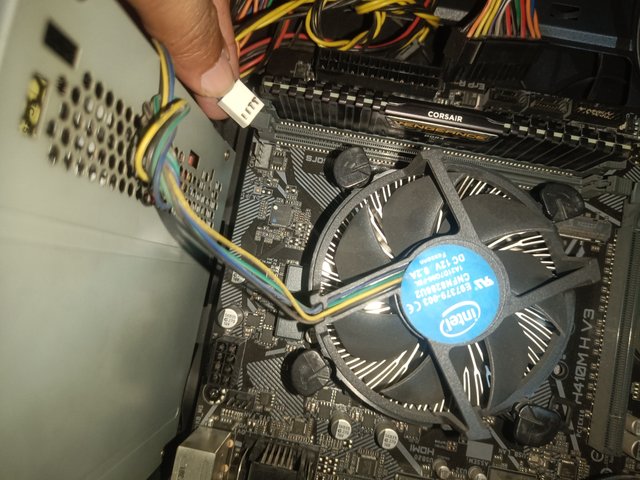
I will now discuss my problem with my first computer's processor. The name of the first processor of my computer is the Pentium processor of Intel company. I noticed a problem after about six months of using the computer. My computer keeps restarting suddenly. Then, I studied in my school dormitory. We are four friends staying in one room. Four of us had four computers. Then, I reinstalled Windows first. But my computer still has the problem. Then, I tried to open the CPU with a friend in my room. Then we all use new computers. After opening the CPU, I found that the processor fan was not spinning after powering the computer.
Then, I tried to unlock the processor fan from above the motherboard. I could not open the processor fan lock because I was using a new computer. Then, one of my friends suddenly managed to open the lock. Then, I saw the thermal paste on the processor drying up. Because the cooling fan was off and I tried to run it like this for a few days, the processor got hot, and the thermal paste dried out. Then we took the help of a senior brother to the computer servicing center. This is my first experience with processor issues.

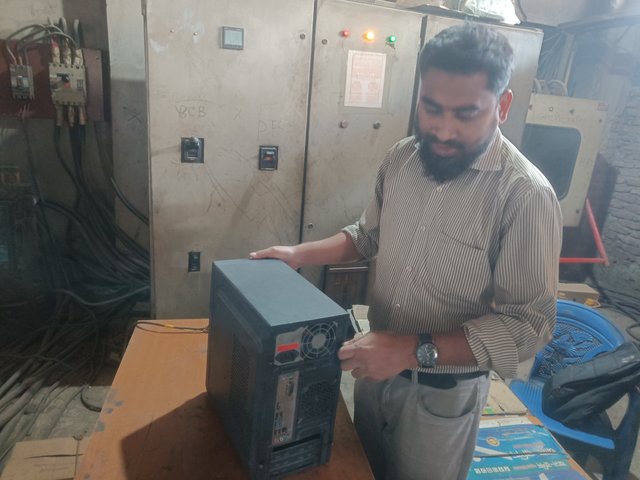
Today, I will reveal the processor of my office desktop computer. I first open the lock on one side of the CPU. Then, I tried to open the four locks inside the motherboard to open the processor cooling fan. I did not disconnect the cooling fan connector from the motherboard before opening the four locks on the cooling fan. I am careful while opening the four locks of the processor cooling fan because if one of the locks breaks while opening the lock, then I will be in trouble. So, I try to open the lock by looking at the symbol inside the processor fan lock. Then, I was able to detach the processor fan successfully.
 |  |  |
|---|
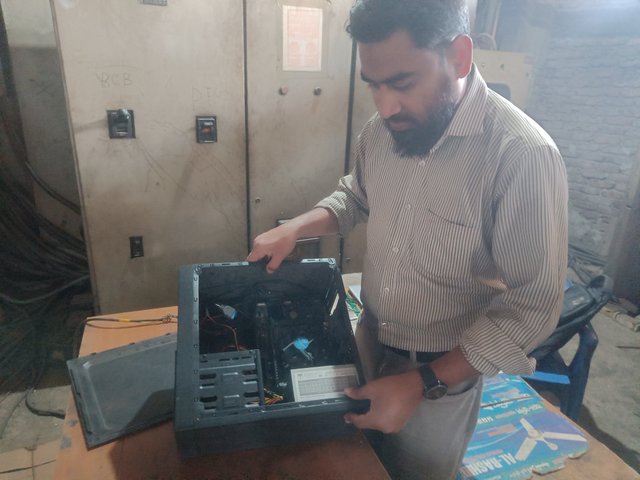
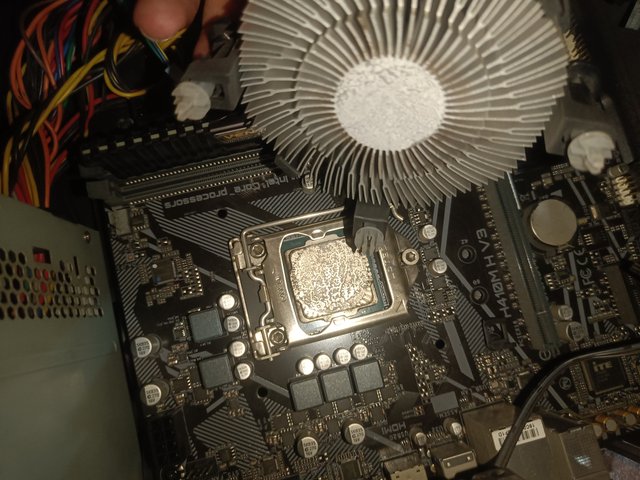
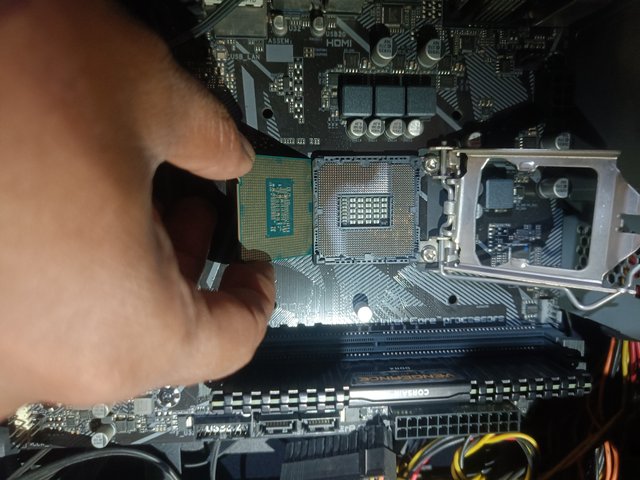
Now, I try to open the lock on top of the processor. But I am careful in this case that the thermal paste on the processor is not damaged. Looking at the quality of the thermal paste between the processor cooling fan and the processor surface, I will apply new thermal paste if necessary. There are pins and holes between the processor and the base. I carefully open the processor so as not to bend the pins.
 |  |  |  |
|---|
Main parts and features of a CPU:
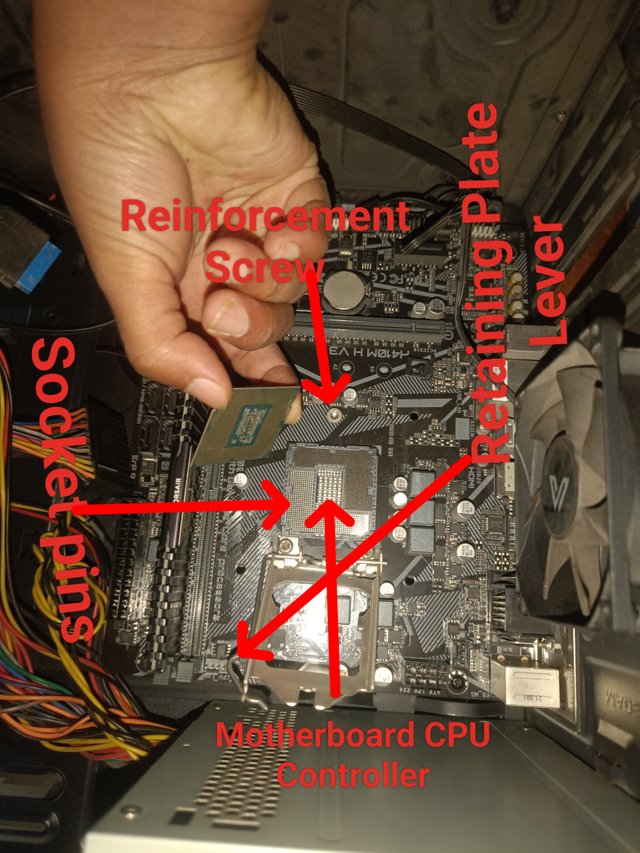


Socket type:
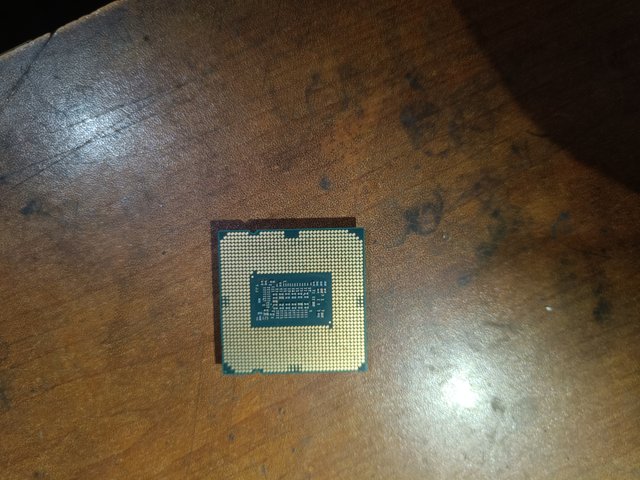
The part where the CPU sits on the motherboard is called the socket. There are different types of sockets on the motherboard, such as LGA(Land Grid Array), PGA(Pin Grid Array) and BGA(Ball Grid Array). The image I provided shows the LGA socket. The processor is placed through the socket and communicates with other parts of the motherboard. Intel uses the LGA-type socket. A PGA-type socket is used in the AMD series. BGA is used in specific devices such as laptops or embedded computers.
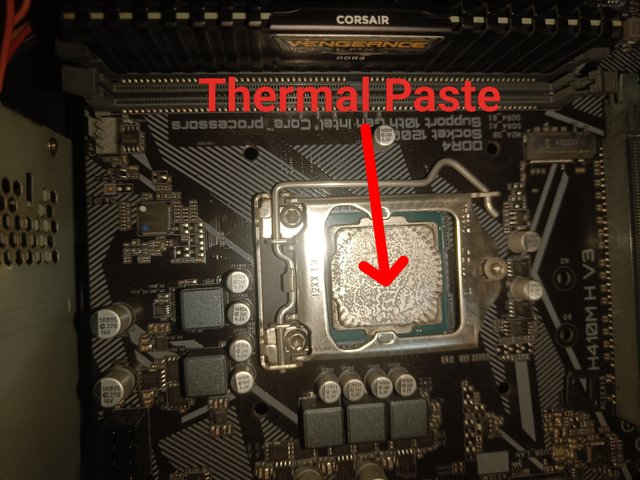
Thermal Interface:
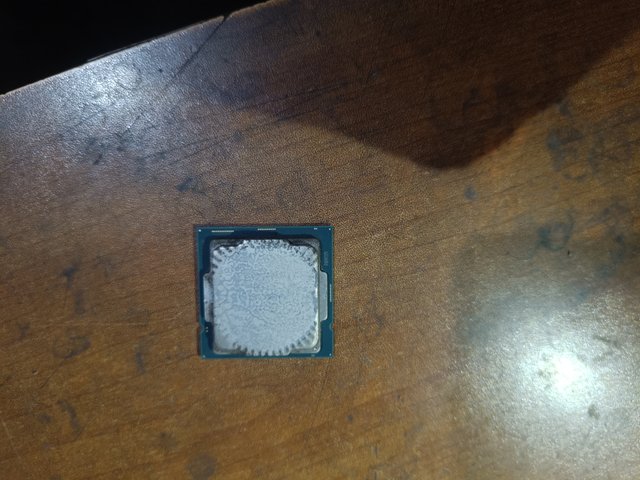
Thermal interface is a method of reducing the temperature of the processor. Thermal pastes of various colours are applied to the contact area of the processor with the cooling fan or heat sink. Through this, the temperature of the processor is kept under control.

Core:
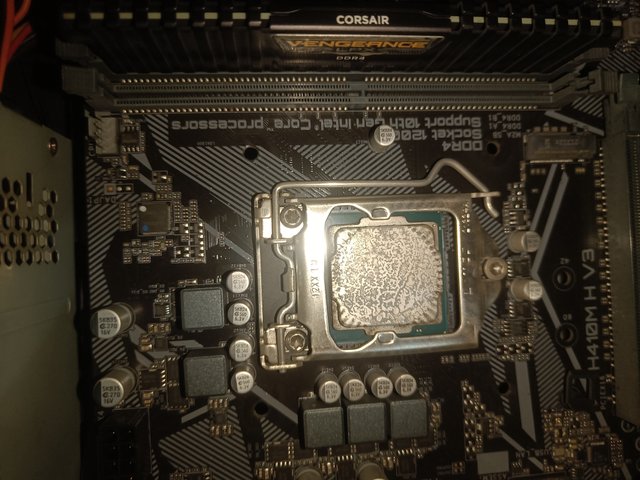
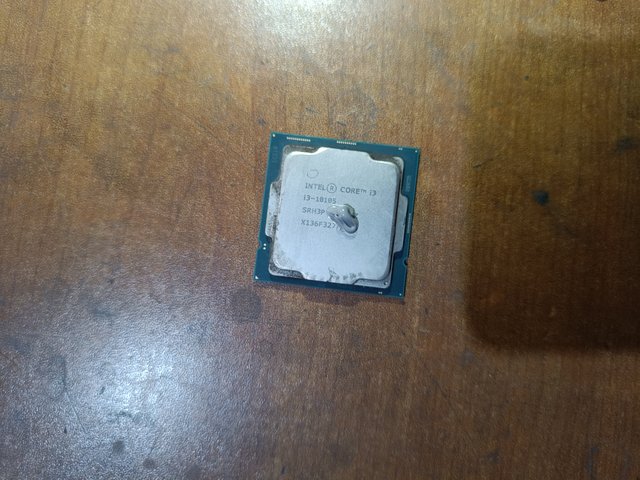
The core is the CPU's processing unit. Each core works differently. Currently, CPUs have 2,4,6,8 and 16 cores. The Intel Core I3 10105 model in the image I provided has four cores, which I have marked in the picture. The Intel Core I5 12400 model has six cores.
Cache Memory:
The CPU's own high-speed memory is the cache memory. Data can be stored repeatedly as needed in cache memory. The CPU has three types of cache memory: Level 1 (L1), Level 2 (L2), and Level 3 (L3). L1 is the smallest and fastest cache memory. L3 is relatively large but slightly slower.
Model and Brand:
The CPU has the model number and brand name. For example, the Intel Core I3 model number in the image I provided is 10105. Sometimes referred to as cache memory, it is marked in the picture.

CPU performance factor:
Clock speed (GHz):
Clock speed depends on how often the CPU can execute instructions per second. If the gigahertz is higher, the working speed is higher, and some other factors depend on it. But the speed depends on the clock speed.
Number of cores:
A CPU can do many tasks simultaneously if the number of cores is high. Each core can perform processing tasks separately. Currently, CPUs have 2,4,6,8 and 16 cores. The CPU I have shown is the Intel I3 10105 model. Its core number is 4.
Cache Size:
The CPU's cache memory is its fastest memory. Here, the required data is kept. If the cache memory is more, the data can be accessed quickly. The higher the cache memory, the better the CPU performance.
I have tabulated the specification differences between the two CPU Intel and AMD models below.
| Specification | Intel Core i9-13900K | AMD Ryzen 9 7950X |
|---|---|---|
| Clock Speed | Up to 5.8 GHz | Up to 5.7 GHz |
| Number of core | 24 | 16 |
| Cache Size | 36 MB L3 Cache | 64 MB L3 Cache |
Performance in various tasks:
Gaming:
The Intel Core i9-13900K model CPU is best for gaming. It has a high clock speed and a unique core design.
On the other hand, the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X model is for multi-threaded tasks such as video editing and 3D. It has more cache and core count.
AI workload:
The AMD model is good for machine learning training due to its large cache and multi-core performance, but Intel's hybrid architecture is better for AI inference.
Common CPU problems and solutions:
- CPU overheating:
Symptoms:
A) If the computer suddenly shuts down or restarts, we will see the CPU is faulty.
B) If the cooling fan noise increases abnormally, then we assume a CPU fault. Then, we will check the cooling fan.
C) CPU fault may also occur if CPU performance drops suddenly. We will check the CPU and other faults.
Reasons:
A) If there is not enough CPU cooling system, a CPU problem may occur. The CPU heats up, especially when we play high-performance games.
B) If the thermal paste dries out or is not applied properly.
C) Dust accumulation on the cooling fan or heat sink.
Solution:
A) The CPU cooler and heat sink should be cleaned regularly.
B) Apply good quality thermal paste and reinstall the cooler.
C) Use liquid cooling or air cooler if necessary.
D) If necessary, go to BIOS and correctly set the cooling fan settings.
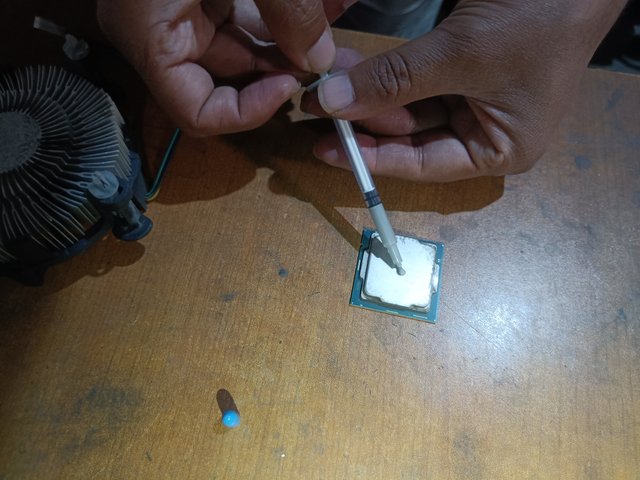

Good quality thermal paste should be applied
- CPU instability:
Symptoms:
A) CPU instability causes the computer to hang or show a blue screen (BSOD).
B) CPU instability can cause software to crash.
Reasons:
A) Wrong configuration while overclocking will cause a CPU instability fault.
B) The power supply unit problem causes CPU instability.
C) Compatibility with motherboard or RAM will cause CPU instability.
Solution:
A) Overclocking must be stopped from BIOS or Default setting must be done.
B) A good quality power supply that supports wattage should be used.
C) The RAM operation should be checked. If necessary, check by installing spare RAM.
- CPU Incompatibility:
Problem:
After setting up the new CPU of the computer, the computer does not turn on or work.
Reasons:
A) The socket of the CPU with the motherboard is not correct.
B) BIOS is old, so communication with the new CPU is not done.
Solution:
A) Check the connection of the CPU and socket again.
B) BIOS update should be given.
C) The connection of RAM and other devices should be checked.
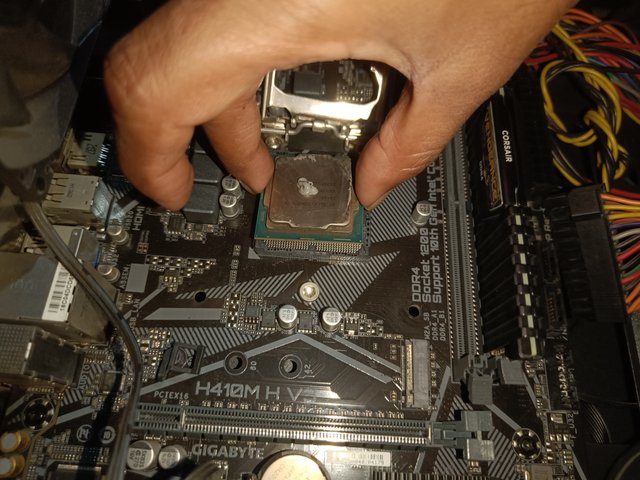

The placement of the CPU in the socket must be correct
Certain rules must be followed for a long life and good CPU performance. I have mentioned some of them below.
- Proper cooling system:
A) Air cooling:
Intel and AMD usually provide stock coolers for CPU use. But for high-performance work, it is better to use good-quality air coolers like Noctua or Cooler Master. Processors need good-quality air cooler systems for gaming and graphics work.
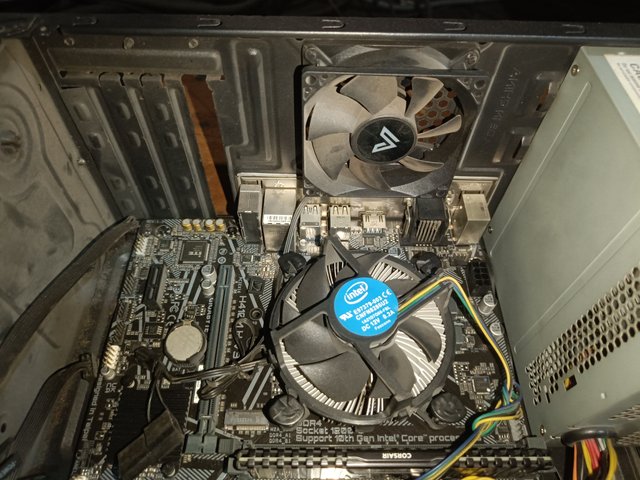

A good quality cooling fan should be installed
B) Liquid Cooling:
Liquid cooling systems provide good performance for high-end gaming and machine learning tasks. All-in-one (AIO) or custom liquid cooling systems are most effective. A cooling system will be good if our CPU is used for a long time.
C) Cable Management:
Tidying up the cables inside the computer case allows air to flow in and out, keeping the CPU cool and providing better performance. Keeping the cables organized using cable ties keeps the CPU cool.
Cables should be kept inside the casing with cable ties
- Correct use of thermal paste:
A) Good-quality thermal paste:
Arctic MX-4, Noctua NT-H1, or thermal Grizzly Kryonaut should be used. If low-quality thermal paste is used, it dries up after a few days and damages the processor.
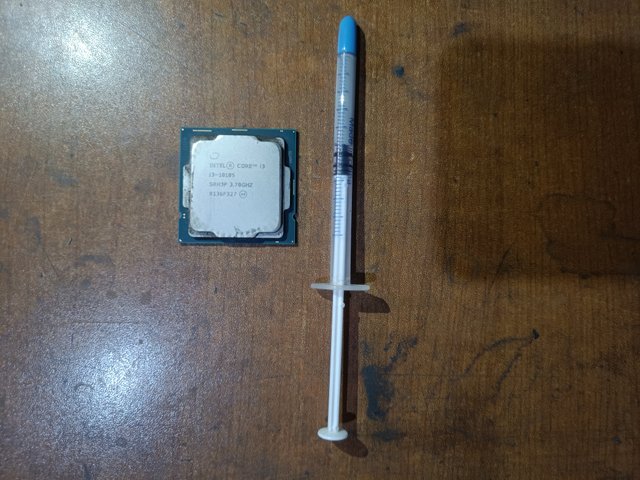

Good quality thermal paste should be applied
B) Proper thermal paste application:
Pressing the thermal paste like dots or crosses on the CPU with the cooler will automatically spread it evenly throughout the CPU.

Apply thermal paste according to the rules
C) Regular thermal paste change:
The CPU should be removed after one year, and the thermal paste should be changed. If we change the thermal paste after one year, the CPU's lifetime will increase.
Temperature settings:
Temperature settings should be checked regularly by going to the BIOS/UEFI configuration. The PC shuts down when the CPU heats due to a dry thermal paste or a cooling system fault.

| SL No. | My Invited Steemit Friends |
|---|---|
| 1 | @memamun |
| 2 | @dove11 |
| 3 | @lirvic |

This is my Twitter share link :
https://twitter.com/mahadih83660186/status/1898421466380853393?t=6PldoAJKpVTU3jLLRvzgWg&s=19
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit