.png)
Source
Hi everyone,
Today's lesson is to help us to understand and manage the various forms of fractures.
FRACTURE
Fracture is a crack or broken bone. Bones protect the internal organs as well as providing the body with nutrients such as calcium. This simply means when fracture casualty is not managed well, all the vital organs within the body would be in danger and by extension death of the victim.
CAUSES OF FRACTURE
Bone being the hardest tissue in the body can not withstand stress or be forced beyond its strength. Therefore if force is applied to the bone, it can cause a fracture. This force can either be direct or indirect.
Direct Force
When the fracture occurs at the spot where the action is applied. e.g. A car running over someone's leg and the bones in the leg getting broken.
Indirect Force
When the fracture occurred away from the spot where the action was applied or a distance away from the site of injury.
TYPES OF FRACTURE
There are two main types of fractures
- Simple fracture
- Compound Fracture
Simple Fracture
This occurs when the bone breaks and stays within the flesh or body.
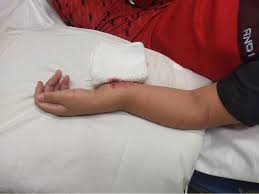
Source
Compound/ Open
This occurs when the bone breaks and the ends pierce through the skin. In this case, a wound created may permit infection if care is not taken.
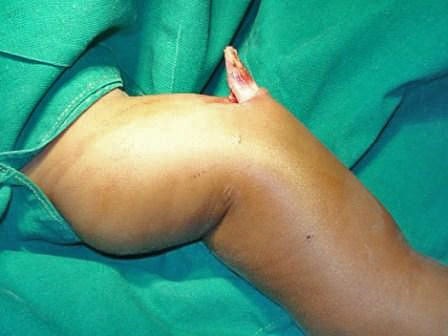
Source
NB; I have in previous posts taught you how to manage wounds to prevent infection.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF FRACTURE
- Pain and tenderness at the site
- Swelling, burger of muscles or effusion of blood
- Deformity of the affected part
- Crepitus ( cracking sound of the bone )
- Unnatural movements
- Loss of power in the limb
- Discoloration
- Broken bone
MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE
The main aim in managing fracture is to keep the fractured bone in position or immobilize it for a period of time to heal by itself.
NB; You must ensure that both the upper and the lower joints of the fractured part are immobilized and inlineSplint the affected part by using a rigid material ( Wood, folded paper, or cards ) to keep the bone in correct alignment and to prevent further damage to the muscles
Paddling the splints prevents damage or pressing down on any blood vessel or nerve
Bandages are required to keep the splints in position.
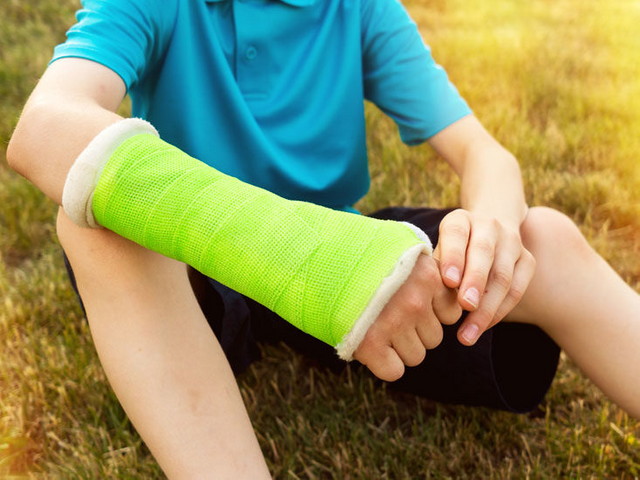

SourceMedicinal (drug)
Give appropriate calcium supplements to the patient. The most common forms are calcium carbonate and calcium citrate. Encourage the intake of fresh calcium-based fruits and fish.Antibiotics are required to control any infections that may arise.
Thank you for following through with today's session. I hope you have learned a lot.
The next lesson will be on Knowledge and management of DISLOCATIONS
THANK YOU.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks for the education
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
thank you our steem physio
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I guess the nickname has come to stay then 😂😂.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit