
Enzyme activities are biological reactions necessary for the growth and repair of damaged tissue. These reactions usually take place in the body of all living organisms and it is called Metabolism. If this reaction stops in the living organisms, it means that the organisms are dead. So enzymes are biological catalysts required in living organisms to reduce the cell consumption of energy. Enzymes help to speed up reactions in the cell, as the protein molecules combine amino acids to form a chain of polypeptides. Today will be looking at the factors that affect the activities of this biological catalyst in living organisms.
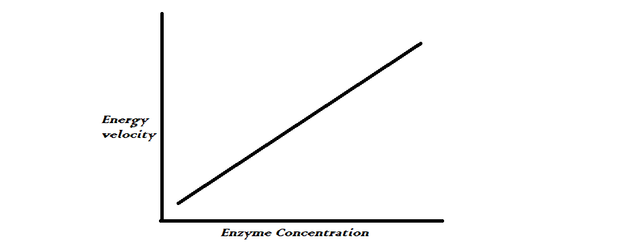
From the graph, you can see that as the concentration of the enzyme increases, the velocity(speed) of the reaction is proportionately moving in the same space. This can be used to follow up on the activities of serum enzymes to diagnose diseases.
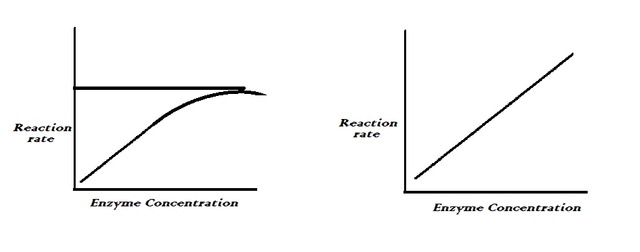
The rate of enzymatic reaction depends on the number of enzymes. so with a given amount, the reaction will increase as the substrate increases until it limits, and the reaction will stop. For the reaction to continue, or make a significant change in the reaction, you need to add a proportionate amount of enzyme to the substrate. The enzyme molecules bond to the substrate and reactions stop. When the enzyme molecules are saturated, excess substrates cannot bond to already bonded enzyme molecules.
As mentioned above, enzymes are proteins in nature and are extremely sensitive to thermal changes which trigger their reactions. Enzymes have a range of temperature(between 37 to 40C°) at which it is more active(Optimal temperature). At optimal temperature, enzymes are more active and gradually decrease as the temperature moves out of the optimal point. When the temperature gets too high or too low, the enzyme activities stop completely due to a change in its natural composition and state.
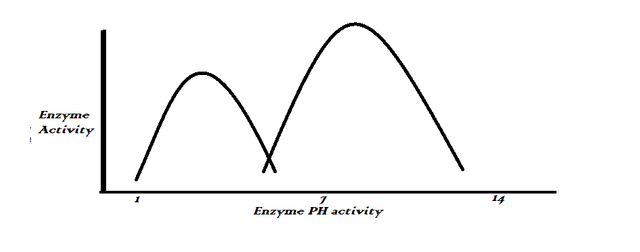
pH (potential of hydrogen) is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution to determine the acidic state, pH helps to determine if a liquid state is acidic, basic, or neutral. When a liquid is acidic when the pH value is below 7, bases or alkaline when pH value is above 7, and neutral when pH value is 7. Given that enzymes are protein substances with amino groups, they are bound to be affected by a change in pH value. Enzymes have a certain pH value and they work at maximum efficiency, which is called the optimal pH. If the pH value goes above or below the optimal pH value, the enzyme activities decrease to the point where it finally stops working.
Some enzymes need certain inorganic metallic cations and anions for optimum activity. Some metallic cation are Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Ca2+, Co2+ etc and anions (chloride ion (CI–))
Enzymes' rate of reaction can greatly be affected by the above-mentioned factors. my work might not be fully detailed, so I will call on you to do more digging to get more knowledge on the effects on living organisms.

Thanks for reading.

Nice points there concerning enzyme activity. I want to add that when the temperature is too low, the enzyme is in active due to the water crystals at the active site of the enzyme and when the temperature is too high the enzyme denatures because of the destruction of the amino acids present at the active site.
Same principle holds for pH
Some of these activators are called cofactors. Some examples include NAD+and NADH+H+, FAD+, AND FADH+H+used as cofactors in glycolysis and the electron transport chain.
Beautiful post there I invite you to go through my post, which is on Staining Methods as Diagnostic Tools
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thanks for the compliment and for your time giving more info on the cofactors.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You are welcome miss. You write good posts
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you for contributing to #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @Reminiscence01 using @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Steem greetings @miss-t,
Steem Cameroon appreciates your dedication and encourages you to do more.
Reviewed by: @fombae
Discord: fombae#5826
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit