
When we talk of seamounts, we are looking at underwater ecosystem communities, and science suggests that they have irreversible impacts on the seamounts communities. This is a broad study in biology, but I will give a summary hoping we all look into the details of seamounts' ecology.
What are Seamounts
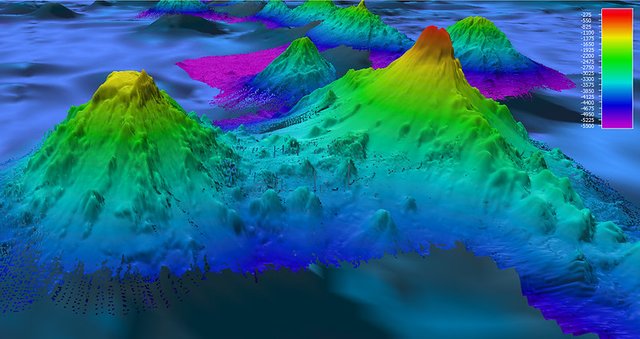
Seamounts refer to as sea mountains with a height below sea level. These mountains are easily found in ocean water with about 100 000 seamounts in ocean bodies and an amount of 50000 seamounts in the Pacific Ocean. Seamounts have a major influence on the physical nature of the ocean water column and are the formation of eddies. The oceanographic effect of seamounts can be associated with the upwelling of nutrient-rich water, which can lead to an increase in water coverage on the surface land.
Why are seamount communities important?
- Seamounts serve as habitats, feeding grounds, and reproduction sites for many deep-sea species of fish, sea turtles, sharks, sea birds, and marine mammals.
- Seamounts are made of geological hard substrates and sediment, which serve as a habitat for animals like the bioherms.
- Corals may form deepwater reefs on seamounts which introduce additional complexity to the environment.
- Seamounts provided more comfortable habitats similar to what we will find on shallow-water tropical coral reefs.
- Seamount's geographic region is highly unique and limited be it a seamounts chain or a single seamounts location
- Most seamounts species are slow in growth(mature) and have extremely long lifespans (over 100 years)
- Seamounts species are vulnerable to overexploitation due to the dense aggregation form during reproductions making them an easy target for trawlers.
What are the current threats?
Seamounts continue getting an impact on a human due to the continued practice of fishing activities. Fishing activity targets species of corals, and fish which greatly improve the seamount's communities. Statistics have shown that trawl fisheries have a greatly destructive impact on benthic communities living on seamounts. Most of the time the bottom trawled destroys the coral's framework leaving bare rock and an impoverished fauna behind. In such a situation, it will take thousands of years for the coral's framework to build back into a natural reef. This action by humans turns to slow growth in the seamount as recolonization will have to start over again due to the impact of fishing. Under any circumstance, limiting the range of seamounts species will lead to the extinction of the species.
As I said, this area is slowly studied in modern biology since its impact doesn't generally affect a wider ocean ecosystem. Not to mention that seamounts have a major influence on the natural structure of the water column and can deflect ocean currents. I hope this my post pushes you to read more to know more about seamounts

Thanks for reading.
Thank you for contributing to #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @maazmoid123 using @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Steem greetings @miss-t,
Your post has been curated with the Steem Cameroon Curation Account.
Steem Cameroon appreciates your dedication and encourages you to do more.
Continue updating your CSI and bringing more contents
Reviewed by: @majerius
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit