
Many will always look at the water cycle as a simple circular cycle of water in the form of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. Well, that is the actual model, but the reality is more complicated than we think. So it is all about the impact of water on the ecosystem that has made it look complicated and put it on a global scale. For example, forecast weather, climate, water resources, ecosystem health, etc.
What is Water Cycle
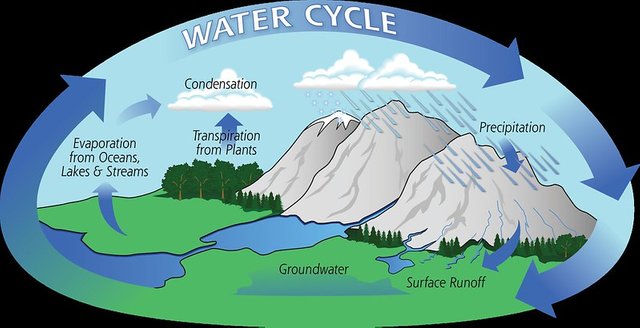
The water cycle is a hydrological cycle used to describe the circulation of water within the atmosphere and the earth. During this process, the water state changes as the different stages hold the exact amount of water particles.
Stages of Water Cycle
Evaporation: When the sun hits the water molecules on the surface of water bodies, the molecules become excited and rise to the atmosphere and accumulate as water vapor in the cloud. There is also another situation that occurs in the leaves of plants called evapotranspiration, which is a huge contributor to water vapor in the atmosphere.
Sublimation: Sublimation is the process where snow or ice changes directly to water vapor without changing to water. It usually occurs at mountain peaks where we have dry winds or low humidity. Here the snow is sublimated into the water using less energy as the air pressure is quite low.
Condensation: Here, is the process of conversion of water vapor into tiny droplets of water and ice. Due to low temperature at high altitudes, the water vapor cools down and forms the clouds with the water droplets and ice.
Precipitation: Commonly called rainfall, is the process where water vapor condenses into droplets. When a good number of droplets form and merge, it falls out of the cloud to the earth's surface. In some cases due to extremely low air pressure, the water droplets will freeze and fall out of the cloud as snow or hail.
Infiltration: Infiltration is the stage where water on the earth's surface is absorbed into the ground. The amount of water will also depend on the topography of the area, rocks will absorb less water as compared to the sandy area.
Runoff: Rainwater comes from rainfall, which is not absorbed into the soil and follows gravity flowing down the side of mountains and hills down into the valleys. This process is called runoff and eventually forms rivers and small water bodies down the slope.
The water cycle on Earth
Following the stage I mentioned above, you can easily understand the cycle of water on earth. Water has three states, that is Solid, Liquid and gas. These three states interchange within the air, cloud, water bodies, plants, mountain peaks, etc.
Water cycles, as I mentioned, are a continuous movement of water in different states within the earth and the atmosphere. Water is evaporated due to heat energy from the sun, into vapor. The vapor rises into the cloud, which then condenses due to low temperature and falls back to the earth as rain or snow.
Implications of Water Cycle
- A rise in temperature in the greenhouse
- It is an integral part of biological cycles
- Directly involved in all life processes on earth
- It helps to clear the air
Water cycles are part of our daily lives and have provided huge opportunities for us, scientists, to explore nature.

Thanks for reading.

Thank you for contributing to #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @fabio2614 using @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit