Kingdom Plantae is made up of organisms of different sizes from tiny mosses to giant trees, but with the similarity that all are multicellular and eukaryotic. Plant cells have a membrane, nucleus that holds chromosomes in them. All plant cells possess chlorophylls pigment, which is used to convert the sunlight energy into chemical energy by the process of photosynthesis. Plants are generally independent of their nutritional needs and store the excess as macromolecules of starch.
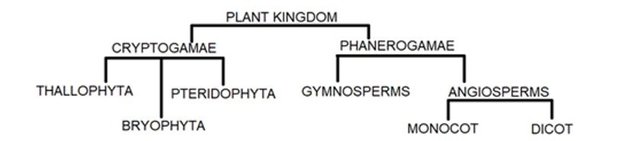
Around us, we can find different types of planets, starting from leaves, stems, and fruits. For this reason, the scientist decided to break them, before we look into them. let's see their general characteristics
- They are multicolor organisms
- They have vacuolate eukaryotic cells
- They contain photosynthetic pigment for nutrition
- They live anchored to a substrate
- Reproduction is asexual or sexual.
- They have a life cycle called the alternation of generation
Thallophyta (Algae)
They are simple algae plants that are autotrophic non-vascular, having unicelled sex organs with no formation of an embryo.
- They can grow on snow or ice (Cryophytes plants)
- They can grow in hot water (Thermophytes plants)
- They can grow on other plants(Epiphytes plants)
- Some blue-green algae can grow inside other plants(Endophytes plants)
- Some alga Cephaleuros can grow a parasite on a tea leave(Parasites plant)
Bryophyta
They are the simplest and most primitive land plant regarded as *amphibians of the plant kingdom. Bryophyta (Gk: Bryon = moss; phyton = plants) are common in a shady and moist environment.
- They can grow in extremely dry and watery situations.
- They reproduce sexually with the antheridium (male sex organ ) and Archegonium(female organ)
Pteridophyta
They are plants with feather-like fronds of ferns, with no flowers or seeds with a sporophytic body. Pteridophytes (Gk. Pteron = feather and phyton = plants) are mostly terrestrial and are growing in shady habitats. They have a single apical cell, having three cutting faces in the shoot apex. Pteridophytes are divided into sub-phyla
Sub-phylum: Psilopsida:
These are fossil plants with relatively less differentiated bodies, for example, absence of roots on these plants.. here these plants have dichotomously branch rhizome
Sub-Phylum: Lycopsida:
These are plants whose body is divided into root, stem, and leaves. The leaves are small with unbranched veins. (microphyllous)
Sub-Phylum: Sphenopsida:
These are plants whose stems are divided into nodes and internodes with microphyllous leaves.
Sub-Phylum: Pteropsida:
These are plants with well-differentiated bodies into roots, stems, and leaves. Here the leaves are megaphyllous and pinnately compound.
Angiosperms
These are flowering plants, angiosperms are the most dominant vascular plants. They are responsible for the coloration of the earth's vegetation. This has been achieved from the colorful, beautiful fragrance of their flowers.
Angiosperms enclose their seeds within a hollow cover. They are subdivided into t Dicotyledon and Monocotyledons
Dicotyledon
- Some have taproots
- They have net-like leaves
- Their flowers are tetramerous or pentamerous (four or five members)
- Seeds are dicotyledon (two cotyledons)
Monocotyledons
- They have adventitious roots
- They have parallel venation leaves
- Their flowers are trimerous (three members)
- Seed is monocotyledons (one cotyledon)
Gymnosperms
These are giant planets that are arboreal, evergreen, woody, etc, and can be grown as wood trees.
- They are fully differentiated into root, stem, and leaves.
- They have well-developed taproots
- The stem is erect, woody, solid, and branches which hold the leaves
- Their leaves can be microphyllous or megaphyllous.
Conclusion
As I mentioned, kingdom Plantae is classified into Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Angiosperms, and Gymnosperms.




