Understanding Horizontal Milling: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Milling is a fundamental process in the manufacturing industry, used to shape metal or other materials by removing material from a workpiece. While vertical milling machines are common, horizontal milling machines offer distinct advantages in certain applications. This guide will explore the horizontal milling process, its advantages, and how it fits into modern machining.
What is Horizontal Milling?
Horizontal milling is a machining process where the cutting tool rotates on a horizontally-oriented spindle. Unlike vertical mills, which use a vertically rotating spindle, horizontal mills use cutters mounted on a horizontal arbor. This configuration is ideal for cutting slots, grooves, or even gear teeth.
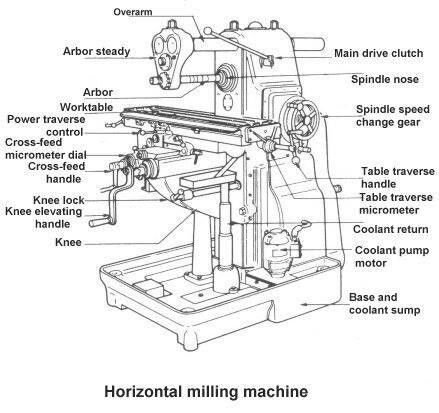
Key Components of a Horizontal Milling Machine
• Spindle: The spindle is positioned horizontally and holds the cutting tool, which rotates to remove material from the workpiece.
• Arbor: A horizontal bar that supports the cutting tool, allowing for more stability when working with larger materials.
• Table: The workpiece is clamped to a table that moves in three directions—X, Y, and Z axes—allowing precise positioning under the cutting tool.
• Cutter: Horizontal mills typically use disk-shaped cutters, ideal for making deeper and heavier cuts.
Horizontal Milling vs. Vertical Milling
Feature Horizontal Milling Vertical Milling
Spindle Orientation Horizontal Vertical
Best For Cutting slots, grooves, and gears Precision cutting, drilling
Material Removal Rate Higher due to cutter stability Moderate
Cutting Tools Disk-shaped cutters End mills, face mills
Horizontal milling machines are preferred when dealing with heavier, larger materials and projects that require high-volume material removal. They are also great for making cuts along the side of a workpiece, unlike vertical mills, which focus more on precision and surface finishing.
Applications of Horizontal Milling
Horizontal milling is widely used in several industries, including:
1. Gear Manufacturing: The ability to cut deep, precise slots makes horizontal milling perfect for gear teeth and other detailed mechanical parts.
2. Heavy Material Machining: The design allows for the removal of more material in a single pass, making it ideal for working on large, heavy workpieces like steel plates.
3. Tool and Die Manufacturing: Horizontal mills are used to cut features into dies and molds, offering precision for large-scale manufacturing.
Advantages of Horizontal Milling
1. High Material Removal Rate: Due to the stable cutter design and power, horizontal mills can remove large amounts of material quickly, reducing the overall production time.
2. Durability: Horizontal milling machines are robust and built to handle heavy-duty machining tasks without compromising precision.
3. Reduced Tool Deflection: The horizontal orientation provides better support for the cutting tool, reducing the likelihood of tool deflection and providing a more accurate cut.
4. Versatility: Horizontal mills can easily handle bulky workpieces and allow for cutting on multiple sides of a material in a single setup.
Disadvantages of Horizontal Milling
1. Larger Footprint: Horizontal milling machines are often bulkier than their vertical counterparts, taking up more space in a workshop.
2. Higher Costs: Due to the complexity and power of horizontal mills, they are typically more expensive to purchase and maintain.
Conclusion
Horizontal milling machines play a crucial role in the machining world, offering unparalleled capabilities when it comes to cutting slots, grooves, and handling large-scale projects. Their ability to remove more material in less time makes them essential for heavy-duty machining, but they may not be the best choice for precision work. Whether you’re manufacturing gears, automotive components, or large metal plates, a horizontal mill could be your best option for efficient production.
Are you considering using a horizontal milling machine in your operations? Let me know in the comments! 💬