Human evolution is the process by which our species, Homo sapiens, has developed and changed over time. It is a complex and ongoing process that spans millions of years. Here are some key points about human evolution:
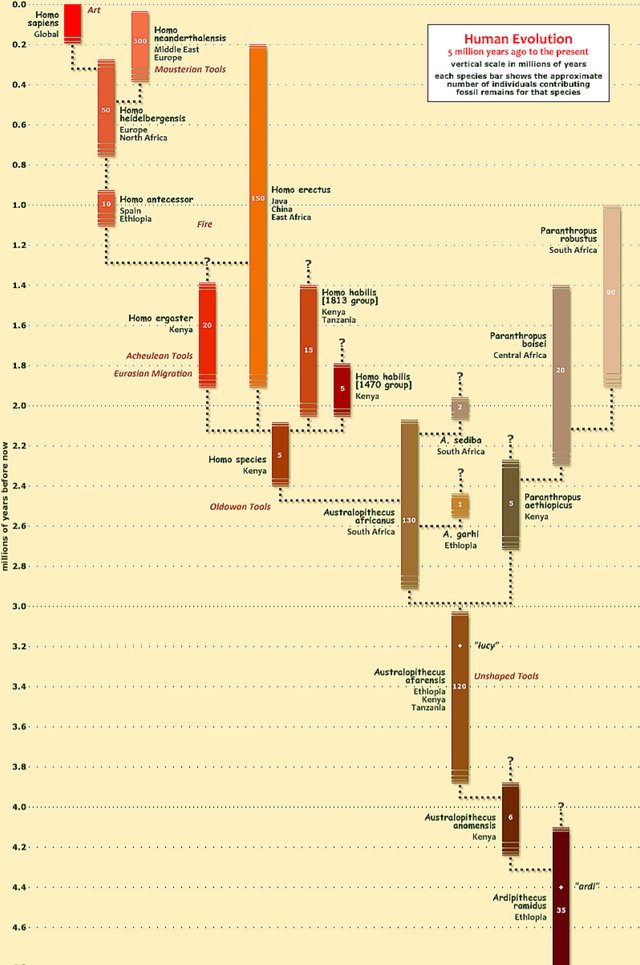
Origins: The earliest human ancestors appeared in Africa around 6-7 million years ago. These early hominins, such as Sahelanthropus and Australopithecus, were bipedal (walked on two legs) and shared some characteristics with both humans and apes.
Genus Homo: The genus Homo, which includes modern humans, emerged around 2-3 million years ago. Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo neanderthalensis are some notable members of this genus. Homo erectus was the first hominin to migrate out of Africa and spread to other parts of the world.
Homo sapiens: Our species, Homo sapiens, evolved in Africa approximately 300,000-200,000 years ago. Homo sapiens possessed unique characteristics such as a larger brain capacity, advanced cognitive abilities, and complex social behaviors. This allowed us to develop language, tools, and culture.
Out of Africa migration: Around 70,000-50,000 years ago, Homo sapiens began to migrate out of Africa and spread to other continents, eventually replacing other hominin species like the Neanderthals and Denisovans. This migration is known as the "Out of Africa" theory and is supported by genetic and fossil evidence.
Cultural evolution: Unlike other species, humans have the ability to transmit knowledge and culture from one generation to the next. This cultural evolution, including the development of language, art, technology, and social organization, has played a significant role in shaping human societies and our ability to adapt to various environments.
Modern human variations: While all humans share a common ancestry, we also exhibit genetic and phenotypic variations due to local adaptations and evolutionary processes. These variations include differences in skin color, body shape, and susceptibility to certain diseases. However, these variations are relatively minor compared to the genetic similarities that unite us as a species.
It's important to note that human evolution is an ongoing process, and we continue to evolve today. However, modern lifestyle and advancements in technology have had a significant impact on the rate and nature of human evolution in recent centuries.