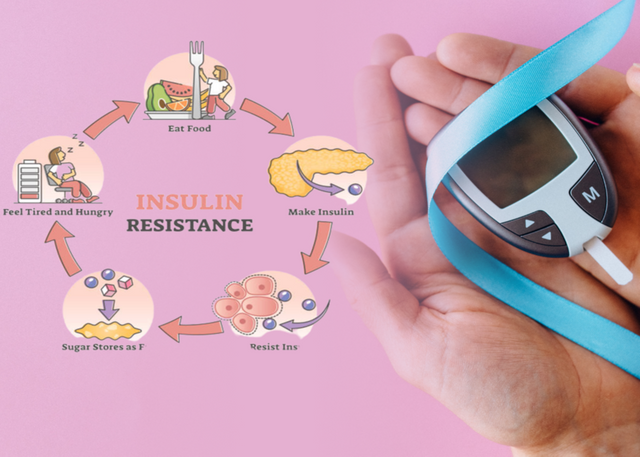
Insulin resistance is a condition that affects the body's ability to properly utilize insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When the cells in the body become resistant to the effects of insulin, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin, leading to high levels of insulin in the bloodstream. Over time, this can result in various health complications, including type 2 diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Recognizing the symptoms of insulin resistance is crucial for early detection and intervention. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
Weight gain and difficulty losing weight: One of the primary symptoms of insulin resistance is unexplained weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area. Despite efforts to maintain a healthy diet and exercise regularly, individuals with insulin resistance may find it challenging to shed pounds.
Increased hunger and cravings: People with insulin resistance often experience intense and frequent hunger pangs. This is because the cells are not effectively absorbing glucose from the bloodstream, leading to a feeling of constant hunger. Cravings for sugary and high-carbohydrate foods are also common.
Fatigue and low energy levels: Insulin resistance can affect energy levels due to the body's inability to properly metabolize glucose for energy. Fatigue and a general feeling of tiredness, even after adequate rest, are often reported by individuals with this condition.
High blood sugar levels: While not everyone with insulin resistance will develop diabetes, elevated blood sugar levels are often an early sign of the condition. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can help identify potential insulin resistance.
Skin issues: Insulin resistance can manifest on the skin in various ways. Dark patches of skin, known as acanthosis nigricans, may appear on the neck, armpits, or other areas of the body. Skin tags, which are small, soft growths, are also more prevalent in individuals with insulin resistance.
Irregular menstrual cycles: Women with insulin resistance may experience hormonal imbalances, leading to irregular menstrual cycles or even the absence of menstruation altogether (amenorrhea). This is particularly common in individuals with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which is often associated with insulin resistance.
High blood pressure: Insulin resistance is closely linked to hypertension (high blood pressure). When cells are resistant to insulin, the blood vessels may become constricted, resulting in increased blood pressure levels.
Sleep disturbances: Insulin resistance has been associated with sleep disorders such as sleep apnea. Disrupted sleep patterns can further contribute to fatigue and exacerbate insulin resistance.
It is important to note that while these symptoms may indicate insulin resistance, they can also be present in other health conditions. If you suspect you may have insulin resistance, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. Early detection and management of insulin resistance can help prevent or delay the onset of more serious health conditions like type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, weight loss (if applicable), and medication under medical supervision are often recommended to manage insulin resistance effectively.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of insulin resistance is essential for timely intervention and prevention of complications. If you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider to undergo appropriate testing and develop a comprehensive treatment plan. By addressing insulin resistance early on, you can take control of your health and reduce the risk of developing more severe conditions down the line.
|
|
Source