Understanding the humanistic theories of intelligence and its correspondents in the current times
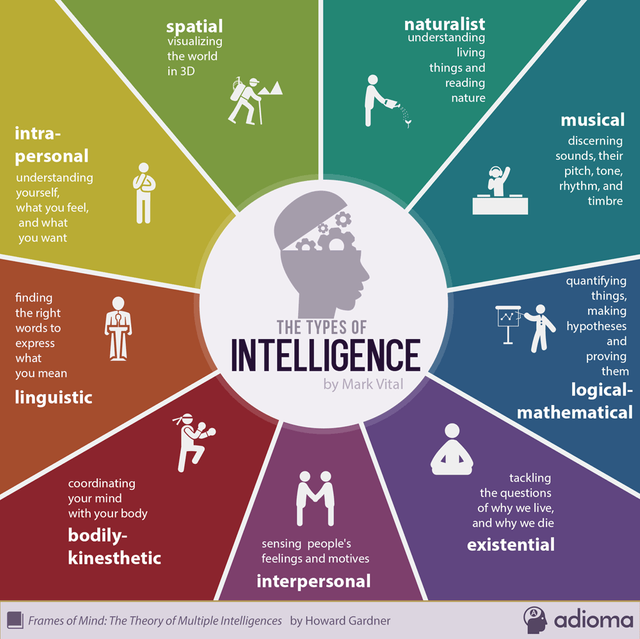
Image Source
Individuals' daily connections are much more prone to be influenced by their implicit theories than by any explicit theories. In job interviews, affirmation interviews, and even day by day discussions, individuals are constantly judging each other's intelligence, construct not in light of any formal and explicit theories however all alone implicit theories of intelligence.
Implicit theories are of interest in their own particular right. Some portion of the investigation of psychology is seeking an understanding how individuals think, and given the significance of intelligence to society, learning how individuals consider intelligence is a commendable undertaking. Implicit theories regularly fill in as the reason for generating explicit theories.
The formal explicit theories of numerous psychologists had their origins in these person's implicit theories. How have psychologists considered intelligence? None of these perspectives are enough communicated by Boring's operationistic perspective of intelligence as what intelligence tests test.
For instance, a symposium on specialists' meanings of intelligence asked leading analysts how they conceptualized intelligence. The scientists underscored the significance of the capacity to learn and the capacity to adjust to the earth. These abilities appear to be imperative. Is it true that they are the abilities that assume a noteworthy part in explicit theories of intelligence?

Image Source
3 Humanistic theories of intelligence
- Generalizability
- Mental abilities
- Fluid and Crystallized abilities
Presumably the most powerful theory in the historical backdrop of intelligence look into is the two-factor theory, which was first proposed by Spearman however has been conveyed forward by numerous cutting edge theorists as g theory. Jensen, himself a g theorist, compresses quite a bit of this work. Spearman saw that tests implied to quantify intelligence display a positive complex.
They tend to correspond positively with each other. He concocted a strategy called factor analysis that was designed to dissect these intercorrelations with a specific end goal to distinguish the indicated wellsprings of individual contrasts underlying the watched examples of test scores.
His factor analysis revealed two types of factors;
- General factors
- Specific factors
Spearman proposed two separate theories to clarify the unavoidable nearness of g. One theory credited the general factor to mental energy, an idea that he accepted originated with Aristotle. The other theory was a more cognitive theory. Spearman suggested that three information-processing components were common to the greater part of the tests.

Image Source
Qualitative components of cognition
- Apprehension of experience
- Eduction of relations
- Eduction correlates
Jensen has characterized g as a distillate of the common wellspring of individual contrasts in every single mental test. He has suggested that underlying g are singular contrasts in the speed or proficiency of the neural processes that influence the sorts of conduct estimated by tests of mental capacity.
He has manufactured his argument in terms of converging operations that appear to show unequivocally the nearness of some biologically based common wellspring of variety in performance on mental tests. The theory of general intelligence has been the longest lasting and maybe the most broadly acknowledged in the greater part of the psychological literature. The proof is noteworthy, unquestionably more so than that garnered for any competing theory.
A few theorists suggest that a general factor is gotten in tests of intelligence in light of the fact that the tests are restricted to a class of genuinely scholastic and to some degree fake errands. They argue that the general factor vanishes or possibly is greatly debilitated when a more extensive range of undertakings is utilized. As opposed to the claim of Jensen, a general factor completes have a tendency to show up as a mathematical regularity when factorial arrangements are left unrotated.
Such a factor has a tendency to be delivered on the grounds that the strategies for both common components analysis in far reaching use today amplify the amount of fluctuation that they put in each progressive factor. The sheer number of concentrates supporting a general factor does not really engender support of the theory in extent to the number of studies. The large lion's share of these examinations tends to utilize a to some degree limited range of assignments, circumstances in which intelligence is tried, and even members.

Image Source
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_intelligence_(intelligence_gathering)
http://www.sparknotes.com/psychology/psych101/intelligence/section1.rhtml
http://otec.uoregon.edu/intelligence.htm
This is very interesting! We should all do our best to gain knowledge from all the different types.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Very informative article thank you for your such a great article.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Unbelievable. We have a lot to learn more :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This is what our mind does. Thank you for thus nice article. Very much informative.. :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Just found my best read for the day before preparing for the content that I am planning to share here. More, more!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit