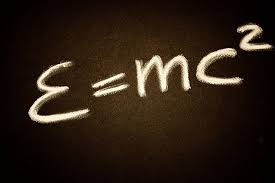
Da anni scienza e Chiesa si sono dibattuti nel cercare una risposta convincente, è la Terra situata al centro del sistema solare? é giusto basarsi sulle teorie eliocentriche, oppure sono più corrette quelle geocentriche? Galileo aveva ragione?
La teoria della relatività è davvero corretta?
For years science and Church have been debating in seeking a convincing answer, is the Earth located at the center of the solar system? is it right to rely on heliocentric theories, or are geocentric ones more correct? Was Galileo right?
Is the theory of relativity really correct?
![download.png] (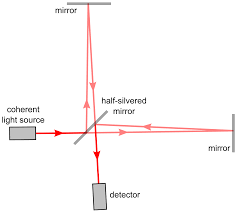 )
)
Il tutto partì con l'esperimento di Michelson e Morley del 1887, i quali volevano verificare se esisteva o meno un vento dell'etere. Decisero così di misurare la velocità della luce, munendosi di un interferometro, ossia uno strumento che permette di suddividere due fasci di luce, in direzioni perpendicolari, facendoli successivamente convergere su uno schermo dove formano una figura di interferenza.
Se fosse stato presente, questo presunto vento di etere, avrebbe fatto si che l'apparecchio riportasse due differenti velocità della luce, nelle varie direzioni, ma non venne rilevato nulla, nemmeno quando all'esperimento partecipò anche Edward Morley.
In questo caso venne utilizzato un interferometro più potente, montato su una lastra di pietra quadrata di 1,5 m di lato e circa 30 cm di spessor; insieme ad un sistema di specchi che rimandava il raggio di luce 8 volte avanti e indietro, per far sì che il percorso fosse più lungo possibile.
La velocità della Terra, rispetto al vento di etere, sarebbe dovuta cambiare per via della rotazione della Terra, e del suo moto orbitale.
Tre sono le possibili cause del fallimento dell'esperimento di Michelson e Morley:
- la Terra è ferma rispetto al vento dell'etere
- il braccio dell'interferometro si accorcia nella direzione del moto dell'etere
- la velocità della luce è uguale in tutte le direzioni
It all started with the experiment of Michelson and Morley of 1887, which wanted to verify if there was a wind of the ether or not. So they decided to measure the speed of light, using an interferometer, that is an instrument that allows to divide two beams of light, in perpendicular directions, making them later converge on a screen where they form an interference figure.
If it had been present, this presumed wind of ether, would have made that the apparatus reported two different speeds of light, in various directions, but nothing was detected, not even when Edward Morley also participates in the experiment.
In this case a more powerful interferometer was used, mounted on a square stone slab of 1.5 m on the side and about 30 cm of thickness; together with a system of mirrors that postponed the ray of light 8 times backwards and forwards, to make the path as long as possible.
The speed of the Earth, compared to the wind of ether, would have to change due to the rotation of the Earth, and its orbital motion.
There are three possible causes of the failure of the Michelson and Morley experiment:
- the Earth is firm with respect to the wind of the ether
- the arm of the interferometer is shortened in the direction of the motion of the ether
- the speed of light is the same in all directions
Einstein prese per vera la terza soluzione, ed elaborò la Teoria della Relatività dove parlava dell' Isotropia dello spazio, affermando che in verità non esiste alcun etere, o comunque non è necessario verificarne l'esistenza, perché la velocità della luce è indipendente dal moto della sorgente e dell'osservatore.
Einstein took the third solution as true, and elaborated the Theory of Relativity where he spoke of the Isotropy of space, stating that in truth there is no ether, or in any case it is not necessary to verify its existence, because the speed of light is independent of motion of the source and the observer.
Nel 1905 venne appunto elaborata la Teoria della relatività ristretta, che mette in relazione i concetti di velocità, luce, ed energia.
In 1905 the Theory of special relativity was elaborated, which links the concepts of speed, light, and energy.
E=mc2
Vediamo nel dettaglio la teoria della relatività:
Let's see in detail the theory of relativity:
∆m=∆E/c2
Se facciamo variare l'energia di un corpo, allora la sua massa dovrà variare di conseguenza di una quantità pari alla variazione di energià diviso c2.
If we vary the energy of a body, then its mass will have to vary accordingly by an amount equal to the variation of energià divided by c2.
L'inerzia di un corpo dipende dal suo contenuto di energia?
Per comprendere al meglio, definiamo cos'è la massa.
La massa è uguale a P=mg, dove g sta per accelerazione di gravità.
Quindi se prendiamo due persone, ad esempio un lottatore di sumo ed una modella, sulla Terra ovviamente il primo peserà maggiormente della seconda, ma se mandiamo il lottatore di sumo sulla luna dove g diminuisce, peserà meno della modella.
C'è poi una massa collegata ad un concetto di energia, che fa si che sia più complicato spingere una scatola piena rispetto ad una scatola vuota.
Quella piena ha più massa e quindi ha più resistenza al moto, per cui la forza per accelerare o rallentare la scatola piena è maggiore.
La massa inerziale è una caratteristica del corpo.
Does the inertia of a body depend on its energy content?
To better understand, we define what mass is.
The mass is equal to P = mg, where g stands for gravity acceleration.
So if we take two people, for example a sumo wrestler and a model, on the ground obviously the first will weigh more on the second, but if we send the sumo wrestler to the moon where g decreases, it will weigh less than the model.
Then there is a mass connected to an energy concept, which makes it more complicated to push a full box than an empty box.
The full one has more mass and therefore has more resistance to the bike, so the force to accelerate or slow down the full box is greater.
Inertial mass is a characteristic of the body.
Definiamo ora il concetto di Energia.
Cominciamo a parlare di quella più facile, l'energia cinetica, se un corpo possiede una velocità ha un'energia.
Abbiamo visto che le velocità dipendono da dove osserviamo un oggetto, se ci mettiamo nel sistema di riferimento del corpo la sua velocità sarà nulla, per quanto fermo un corpo ha ancora dell'energia, ossia l'energia potenziale se il soggetto è sottoposto alla forza gravitazionale, oppure potrebbe avere energia cinetica, se all'interno il corpo è formato da piccole parti che si muovono tra loro, c'è poi l'energia termica quella che si trasmette ad un corpo quando lo si scalda.
Tornando all'equazione,ci dice che se faccio variare l'energia di un corpo, allora ne faccio variare anche la massa inerte.
Let us now define the concept of Energy.
Let's start talking about the easiest one, the kinetic energy, if a body has a speed it has an energy.
We have seen that velocities depend on where we look at an object, if we place ourselves in the body's reference system its velocity will be zero, no matter how firm a body still has energy, that is, potential energy if the subject is subjected to force gravitational, or could have kinetic energy, if inside the body is formed by small parts that move between them, then there is the thermal energy that is transmitted to a body when it is heated.
Returning to the equation, tells us that if I change the energy of a body, then I also vary the mass inert.
Esempio:
Se scaldo dell'acqua che c'è nel bollitore, gli dò energia termica, ebbene la sua massa dovrebbe aumentare ma quando lo sposto non mi sembra che ci sia maggiore inerzia rispetto a quando l'ho messo sul fuoco, il motivo è perché la variazione è piccolissima.
Example:
If I heat the water in the kettle, I give it thermal energy, well its mass should increase but when I move it does not seem to me that there is more inertia than when I put it on the fire, the reason is because the variation is very small.
Ora proviamo a non guardare la variazione (togliamo il delta) e andiamo all'estremo. Cosa succede se considero tutta la massa e tutta l'energia? La fomula dice che se tolgo tutta la massa da un corpo, è come se gli levassi tutta l'energia.
é strano perché sembrava che la massa fosse proprio una caratteristica del corpo.
In realtà la massa altro non è che l'energia contenuta in un corpo.
Da questa equazione discerne che un corpo non possa superare la velocità della luce, perché esso, arrivato a tale velocità, per essere accelerato avrebbe bisogno di un'energia infinita, e pertanto la velocità della luce è una velocità limite.
Now let's try not to look at the variation (remove the delta) and go to the extreme. What happens if I consider all the mass and all the energy? The fomula says that if I remove all the mass from a body, it is as if I take all the energy out of it.
It is strange because it seemed that mass was just a feature of the body.
In reality the mass is nothing but the energy contained in a body.
From this equation he discerns that a body can not exceed the speed of light, because it, having arrived at such speed, would need infinite energy to be accelerated, and therefore the speed of light is a limit velocity.
Nel 1925 però, Michelson ripetè l'esperimento. assieme al fisico Gale.
Questa volta venne utilizzato un interferometro ad anello, molto più grande, che appoggiato al suolo, avrebbe dovuto mettere in evidenza il movimento di rotazione della Terra, nell'ipotesi che quest'ultima abbia effetti sulla propagazione della luce, in prossimità della superficie terrestre.
L'esperimento ebbe esito positivo, e confermò nei limiti dell'errore, il valore della velocità angolare della Terra misurato con metodi astronomici.
In 1925, however, Michelson repeated the experiment. together with the physicist Gale.
This time it was used a ring interferometer, much larger, which leaning on the ground, should have highlighted the rotation of the Earth, in the hypothesis that the latter has effects on the propagation of light, near the earth's surface.
The experiment was successful, and confirmed within the limits of the error, the value of the angular velocity of the Earth measured with astronomical methods.
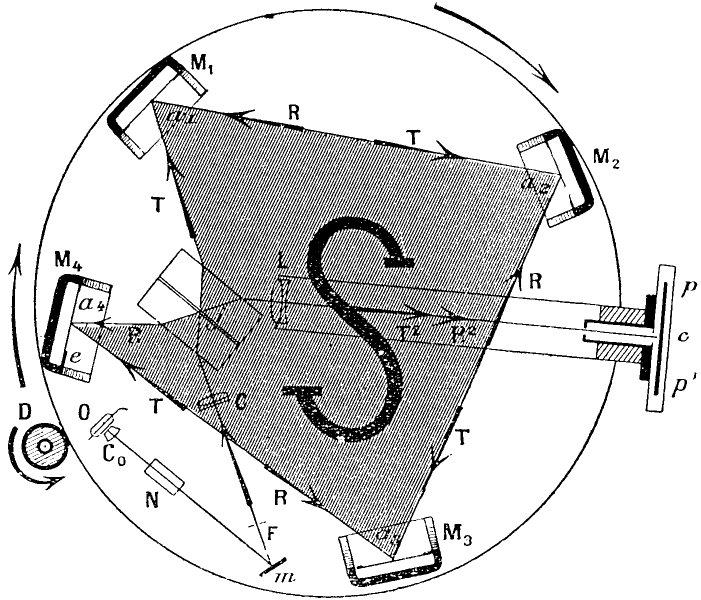
Questo andava a confermare anche l'esperimento condotto da Sagnac nel 1913, che come già accennato nei precedenti esperimenti, consiste in uno sfasamento tra due fasci luminosi coerenti, prodotti da uno stesso raggio di luce, inviati a diffondersi in senso opposto l'uno rispetto all'altro su una piattaforma in rotazione, quando questi ritornano al punto di partenza.
I due segnali arrivano cioè in tempi diversi, e a tale ritardo temporale corrisponde un ritardo di fase.
Di conseguenza montato un interferometro sulla piattaforma, questo registrerà uno spostamento delle frange di interferenza.
This was also to confirm the experiment conducted by Sagnac in 1913, which as already mentioned in the previous experiments, consists of a displacement between two coherent beams of light, produced by the same ray of light, sent to spread in the opposite direction to the other on a rotating platform, when they return to the starting point.
The two signals arrive at different times, and a phase delay corresponds to this time delay.
Accordingly mounted an interferometer on the platform, this will record a shift of the interference fringes.
La formula trovata da Sagnac, che descrive il ritardo temporale è la seguente :
The formula found by Sagnac, which describes the time delay is as follows :
∆ z=4Aomega/c2
dove A rappresenta l'area racchiusa dal percorso tra i due segnali luminosi, omega la velocità angolare della piattaforma,e c la velocità della luce nel vuoto, pari a circa 3x10 elevato all'ottava m/s.
where A represents the area enclosed by the path between the two light signals, omega the angular velocity of the platform, and c the speed of light in the vacuum, equal to about 3x10 raised to the octave m/s.
La formula per il ritardo di fase si trova semplicemente moltiplicando tale espressione per il rapporto tra la velocità della luce e la sua lunghezza d'onda λ.
The phase delay formula is simply multiplying this expression by the ratio of the speed of light to its wavelength λ.
Si ottiene:
You get:
∆z=4Aomega/λc
λ è relativa al particolare tipo di radiazione luminosa utilizzata.
λ it is related to the particular type of light radiation used.
Alcune perplessità:
come mai l'esperimento del 1925e il precedente esperimento di Sagnac hanno rilevato il delta della frangia, riportato dall'interferometro, e invece l'esperimento di Michelson e Marley, non ha rilevato lo stesso delta?
Se la velocità della luce è uguale in tutte le direzioni, lo scarto non doveva essere rilevato in nessun caso.
Caso strano al Cern di Ginevra, il dottor Antonio Ereditato si è dimesso dopo aver constatato la velocità dei neutrini, superiore a quella della luce,ed il team ha dato la responsabilità a problemi con la porta usb del pc.
Some perplexities:
how come the experiment of 1925 and the previous experiment of Sagnac have detected the fringe delta, reported by the interferometer, and instead the experiment of Michelson and Marley, did not detect the same delta?
If the speed of light is the same in all directions, the gap should not be detected under any circumstances.
Odd case at Cern di Ginevra, Dr. Antonio Ereditato has resigned after finding the speed of neutrinos, higher than that of light, and the team has given responsibility for problems with the usb port of the pc.
é questa la verità?
é possibile che esista un sistema alternativo alla teoria eliocentrica, attualmente vigente? Con questo non voglio affermare che la teoria geocentrica sia corretta, perché la Terra non ha di fatto una massa così attrattiva, ma questi esperimenti devono trovare approfondimento.
Rivedendo ed ipotizando un sistema misto sul modello di Tycho Brahe, la Terra girerebbe attorno al Sole, ma quest'ultimo insieme all'astro nero farebbe un'orbita concentrica, attorno al centro del sistema solare ( ove si trova la Terra).
La Terra di fatto rimarrebbe ferma pur muovendosi come fa il cane dentro la ruota delle Fiandre.
Is this the truth?
is it possible that there is an alternative system to the heliocentric theory currently in force? With this I do not want to say that the geocentric theory is correct, because the Earth does not in fact have such an attractive mass, but these experiments must be investigated.
Reviewing and hypothesizing a mixed system on the Tycho Brahe model, the Earth would revolve around the Sun, but the latter together with the black star would make a concentric orbit, around the center of the solar system (where the Earth is).
The Earth in fact would remain still while moving likethe dog in the wheel of Flanders.
Il cane dentro la ruota- cenni storici.
Nelle fattorie delle Fiandre, gli agricoltori per rendere meno dispendiosa la produzione del burro, facevano girare il barile di burrificazione con l'aiuto di una grande ruota nella quale correva un cane; quest'ultimo avanzava senza sosta nella ruota, ma per il suo stesso movimento, la ruota lo riportava verso il basso, ed egli camminava senza avanzare.
The dog inside the wheel - historical background.
In the Flanders farms, farmers made the butter-making barrel run with the help of a large wheel in which a dog ran, to make the production of butter less expensive; the latter advanced relentlessly in the wheel, but by his own movement, the wheel brought him back down, and he walked without advancing.
è possibile dunque aprirsi a nuovi scenari, e rivedere le teorie precedenti?...
is it possible therefore to open up to new scenarios, and to review previous theories?...
Fonti: wikipedia, appunti universitari, Corriere della sera, libro di testo "Galileo aveva torto o ragione" di Crombette
Me lo sentivo che ci andava 1/2 prima della m
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Articolo molto impegnativo ma ben fatto.
Complimenti.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Grazie mille
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit