Steemit is a great example: a social media platform powered by blockchain and supported by another web3.0 creation IPFS; Peer to peer protocols and networks that store & share data using a distributed file system. Together with namecoin, filecoin, golem & storj, these competing technologies are among the growing parts of the web 3.0 equation, collectively helping to create and develop new landscapes, one that no longer rely on large, centralized organizations using technologies that are very disruptive to the traditional way of doing business on the internet.
Some call it technology democratization because networks are often powered by community users, increasingly using regular PC and mobile applications to power the network, others simply say it's just a more efficient way of approaching old problems. imho blockchain and its cohorts are the killer apps the internet has been waiting for and perhaps not many will escape its revolutionary twist, although for many users it would be as invisible as IP addresses, DNS and network sockets.

JACS - Just Another Communication Stack


With an ICO launching in November 2020 JACS is another structural part of the change in the online landscape and one that is impeccably timed to suit the ongoing depletion of internet addresses. In the age of 5G and the Internet of Things internet addresses (commonly known currently as IP or internet protocol addresses) the demand for unique addresses sees no slowing down and the founders of JACS have spent a long time working out how to solve this thorny technical issue. The rollout of 5G introduces low latency which allows for the true beginnings of a fully automated machine economy. JACS meets this challenge head on with astronomical address abundance and the low latency provided by blockchain. This fact cannot be ignored or underestimated.
What is Blockchain?


JACS founders have worked in the ICT industry for many years developing multi-million dollar, global blue-chip data communications projects and JACS has been developed to respond to known and anticipated challenges in the sector. This is an interesting proposition. Due to the current allocation of internet addresses, it is a highly centralized sector with high renewal costs and a number of security concerns.
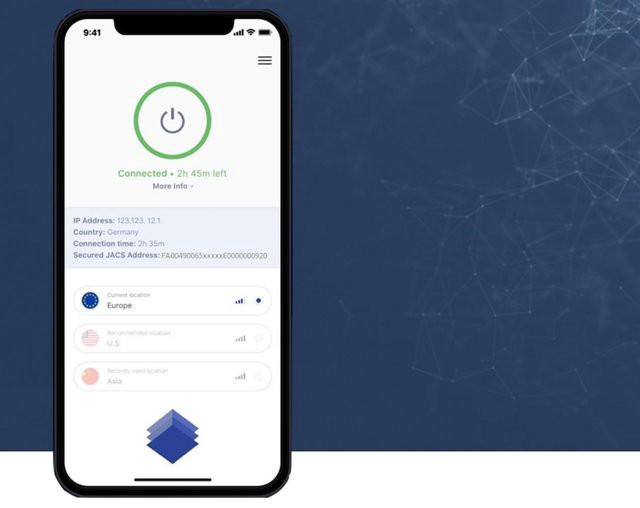
Various ways to expand internet address allocation have been tried before but the JACS project offers a revolutionary approach. The abundant JACS address blocks come with no renewal costs and provide strong security through high-level encryption. A dual stack node structure can also be used in the event of a DDoS attack, giving JACS a competitive advantage with enterprise clients who require super secure, high volume, low latency communication structures. JACS launches a mobile app with free VPN access (limited time) and an unlimited premium version, available soon for MacOS and Android.
Our vision


JACS empowers the advancement of Web 3.0 by providing a decentralized stack of information correspondence that allows existing scattered applications and administrations to work and evolve to achieve tangible factors to come. Allows a network between every grain of sand on the planet and even the past.
JACS Solutions


- JACS or Just Another Communications Stack intends to change the way information networks work today.
- This is the effect of combining two advances: blockchain and CLNS, with a 160-bit ISO NSAP address.
- JACS provides another completely unexpected stack of correspondence than a TCP / IP stack.
- Improved IPv4 address consumption, unified location assignment and security of Internet pointing frameworks.
- JACS address boxes are designated and managed via the blockchain.
- JACS addresses exist worldwide one of a kind for concentrated applications such as: IoT, 5G, and things that pass the creative mind.
PROBLEM


Address exhaustion is a depletion of the pool of unallocated IPv4 addresses. As there are less than 4.3 billion addresses available, depletion has been anticipated since the late 1980s, when the Internet began to experience dramatic growth. This depletion is one reason for the development and implementation of other alternative solutions, such as IPv6. The main market forces accelerating the depletion of IPv4 addresses include a rapidly growing number of Internet users, always-on devices, mobile devices, and more recently the Internet of Things (IoT). The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) created the Routing and Addressing Group (ROAD) in November 1991 in response to scalability problems caused by the classful network allocation system in place at that time. Anticipated drawbacks have been a driving factor in creating and adopting several new technologies, including NAT, CIDR in 1993, and IPv6 in 1998. IPv6, IPv4’s successor technology designed to address this problem, supports approximately 3.4 × 1038 network addresses. . Although the 2008 depletion forecast was nearing its final stage, most Internet service providers and software vendors were only beginning to implement IPv6 at that time. The top-tier reduction occurred on 31 January 2011. Four out of five RIRs have used up allocations of all blocks they did not save for the IPv6 transition; this happened on 15 April 2011 for APNIC, Asia-Pacific, on 14 September 2012 for RIPE NCC, Europe, Middle East and Central Asia, on 10 June 2014 for LACNIC, Latin America and the Caribbean, and on 24 September 2015 for ARIN North America . Individual ISPs still have an unassigned pool of IP addresses, and can recycle addresses their customers no longer need. Each consumes a pool of available addresses at different times.
The current centralized system for managing the global pool of IP addresses is centralized in five transnational organizations, the Regional Internet Registries (RIRs). Each of these RIRs manages a pool of addresses for a large number of countries. Because RIRs are private organizations, they are subject to the legal framework of the country in which they are located. This configuration generates jurisdiction overflow from the legal framework of the country in which the RIR is based on all the countries in which the RIR is located (countries served by the RIR are de facto subject to the legal system of the country where the RIR is located). In addition to the centralized nature of address allocation,
Token Info


Max Token Supply : 536,870,912 (²²⁹: 2 to the Power of 29)
Token Symbol : JACS
Standard Token : ERC-20
Decimals : 18
Token Function : Utility token over JACS Platform
Token Platform : Ethereum dApp then native JACS blockchain Q1, 2022
Creation Date : Q4, 2020
Rewards :18.75% Reserve
18.75% Crowdfund
62.5% Distribution
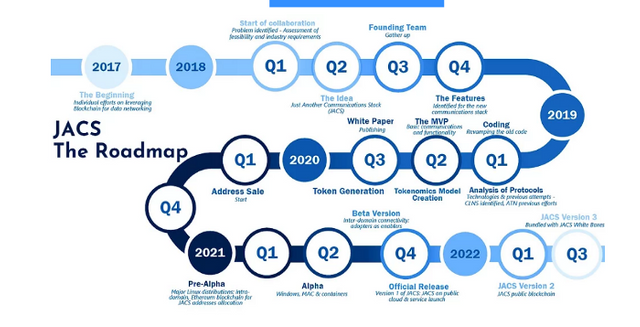
Roadmap


CONCLUSION


In line with technological developments such as IoT and the arrival of the 5G network, there will be many devices in the world connected to the internet network. The TCP / IP technology we use today has many limitations and problems — JACK’s “Just Another Communications Stack” is a platform that uses blockchain and Connection-Less Network Services (CLNS) with a 160-bit ISO NSAP address. JACK aims to change the way data networks work and solve various problems in internet protocols such as IPv4 address depletion, high maintenance costs and recurring updates, etc.
For important information on this project you can see it below:
Website: https://www.jacs.tech/
Whitepaper: https://www.jacs.tech/white-paper
Telegram: https://t.me/jacstech
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/Moustafaamin77
Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCICHtYggmdDTRJsPdOBs-GQ
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/viaBlockLTD
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/JACSTECH/
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/viablock
Ann Thread: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=5279310.0
Author: Bidadari_surga
Bitcointalk Profile: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile;u=1011291
Eth Wallet: 0xBd706dD25c38c5502DbB2B254bFA6bbD54b8F8d3