Anaphylaxis is a generalized immune reaction of the body, which constitutes one of the most serious and life-threatening complications. Occurs in a certain variety of clinical situations and is almost inevitable in medical practice. Most often, it is the result of immunological reactions to foods, medications and insect bites, but can induce it an agent capable of producing a systemic, spontaneous degranulation of mast cells or basophils.
Although the clear distinction is difficult, Anaphylaxis is different from allergy by the extension of the immune reaction that usually includes one or more organ systems for example: respiratory, vascular, cardiac, etc. When in the manifestations of anaphylaxis is sudden and immediate risk the life of the patient, shock (shock) the term is used anaphylactic.
Anaphylaxis consists of a generalized immune reaction of the body, which constitutes one of the most serious and life-threatening complications. Occurs in a certain variety of clinical situations and is almost inevitable in medical practice. Most often, it is the result of immunological reactions to foods, medications and insect bites, but can induce it an agent capable of producing a systemic, spontaneous degranulation of mast cells or basophils.
Although the clear distinction is difficult, Anaphylaxis is different from allergy by the extension of the immune reaction that usually includes one or more organ systems for example: respiratory, vascular, cardiac, etc. When in the manifestations of anaphylaxis is sudden and immediate risk the life of the patient, shock (shock) the term is used anaphylactic.
Anaphylaxis consists of a generalized immune reaction of the body, which constitutes one of the most serious and life-threatening complications. Occurs in a certain variety of situations.
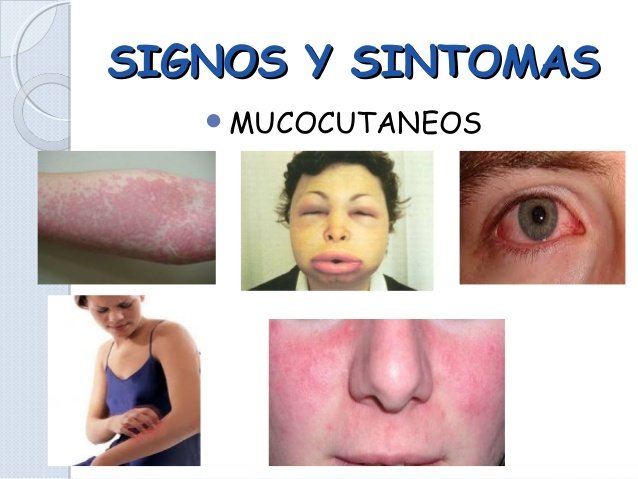
signs and symptoms mocus-cutaneous
Risk factors
It is more common to develop Anaphylaxis in adults with regard to children, the exception being the food anaphylaxis. Women have shown a greater susceptibility to the anaphylactic reaction by latex and for relaxing muscle. The reaction is more frequent and violent if the Antigen have contacts on parenteral administration, followed by contact with mucous membranes and skin. Subjects treated with beta blockers do not have higher incidence of anaphylactic, but when the Anaphylaxis picture is more serious.
Etiology
some allergens are responsible for most cases of anaphylactic shock:
• anesthetics and neuromuscular blockers. These drugs are widely used in surgical procedures, and usually are used simultaneously, so most of the times is difficult to determine the cause. The alfadiona and thiopental are causing major between general anesthetics and as local anesthetic lidocaine.
• The poisons in insects (Hymenoptera). Wasps and bees have equal anaphylactic potential, but the capacity of the wasps to sting repeatedly makes them more dangerous.
• Food. It highlights the role of fruits, nuts, shellfish, milk, and vegetables. The more a food is consumed more easily it can become allergenic.
• Anti-inflammatory aspirin-type drugs.
• Products used for radiographic contrast (procedures such as angiography, colangiografias, urografias, etc.), especially those containing iodine derivatives, as well as the commonly used intravenously.
• Antibiotic drugs are a very common cause of anaphylaxis. Antibiotics belonging to the Group of beta-lactams are drugs that produce an anaphylactic box more frequently. They have been identified as frequent agents to penicillin derivatives, cephalosporins, sulfonamides and tetracyclines.
• Streptokinase, a clot buster used in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction.
• Idiopathic, occurs when a drug is given without knowing the Deputy anaphylactic effect due to ignorance of the patient and/or physician
• Latex: occurs much more frequently in the population subjected to greater exposure such as medical personnel, patients with spina bifida, patients undergoing hemodialysis or multiintervenidos.
There are other drugs that are also capable of inducing anaphylaxis, but with lower frequency.
latex material

Bee Sting

food-allergic
After exposure symptoms, signs, and symptoms appear in a matter of seconds or minutes, but rarely can take some hours. Usually they are limited to the skin, cardiovascular system, the respiratory, the digestive and nervous, and can dominate any of them or occur simultaneously.
General symptoms: diffuse or generalized discomfort, anxiety, feeling of impending doom.
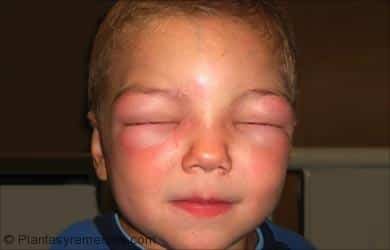
• Skin: pale, diaphoretic (sweating), pruritus (itching), hives and regional or generalized edema (facial, around eyes or mouth).
• Cardiovascular: tachycardia (heart rate over 90/minute), hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg), and ventricular arrhythmias, expressed with weak pulse, irregular or weak heart sounds, cold extremities, and syncope (fainting).
• respiratory: edema of glottis/Epiglottis or serious bronchoconstriction, manifesting dyspnoea (difficult breathing, feeling of shortness of breath), dysphonia (voice altering), stridor (noisy, a whistle-like breathing), wheezing (similar noises, auscultados with stethoscope), and cyanosis (blue oscura-morada color on lips, nails or other sites).
• Digestive system: mainly diarrhea and vomiting.
• Nervous: anxiety, disorientation, dizziness, paresthesias (abnormal sensations such as cold or numbness in the extremities or face), convulsions and loss of consciousness.
In the stroke electrocardiographic are frequent signs: excitability, conduction and disorders primarily Repolarization. Sometimes images of myocardial ischemic injury are recorded. In women, an intense pain from the uterus is a possible symptom of anaphylactic shock. Two features give the anaphylactic shock a particular interes:br • the extreme gravity.
• Extraordinary reversibility, which under proper treatment rapidly evolving to the restoration of the sick.
Treatment
Two notions pathophysiologic must be taken into account in establishing an effective treatment:
• The release by the mast cells, of chemical mediators in response to the income to the agency of a foreign substance (allergen) and the sequence of events humoral and cellular which bring into play the immunoglobulin E, fractions of the complement activated by the alternate pathway or the action of histamine.
• Modifications Exist hemodynamics in the initial stage with fall of the vascular resistances systemic, essentially arteriolares, with maintenance of the filling pressures of the right cavities (PVC) and left (PCP), thanks to the increase in the stroke volume and cardiac output.
Without proper treatment, vasodilation is generalized with severe decrease of venous return, filling pressures of the ventricles, stroke volume and cardiac output.
The hemodynamic impairment of the anaphylactic shock relates to a hypovolemic shock, which can evolve toward ventricular fibrillation and asystole.
Non-pharmacological treatment
Establish and protect the airway, provide oxygen, if indicated.
Intravenous access should be quickly established and fluids should be administered intravenously (for example, saline). The patient should be placed in dorsal decubitus, or Trendelenburg position if hemodynamically unstable.
Curative treatment
epinephrine or intramuscular adrenaline is the drug of first choice. Its properties correct the anomalies of the shock.
• Alfaadrenergicos effects to correct extreme vasodilation, arteriolar and venular; restored systemic blood pressure and decreases capillary permeability.
• Β1 effects reinforce the cardiac activity and improve the debit.
• Β2 effects ensure immediate bronchodilation and can, to some extent, stop mastocitica degranulation by activating intracellular enzymatic process that favours the synthesis of cyclic AMP.
Serious shock requires the use of adrenaline hydrochloride intravenously at a dose of 0.25 to 1 mg, diluted in 10 ml of normal saline, applied very slowly. The drug is usually well tolerated. The risk of a cardiac arrhythmia is minimal, compared with the risk associated with not to manage it. In the less serious forms the intramuscular is preferred at the same dose, possibly repeated 15 minutes if the improvement is not very noticeable.
In the coronary patient, the risk of ventricular arrhythmia can do you prefer an amine Alpha action predominantly, as dopamine or phenylephrine. By cannula oxygen is useful to mitigate the concomitant tissue hypoxia shock. Antihistamines have no actual use, by its low effectiveness of action. Corticosteroids are very useful to prevent late reactions. Hydrocortisone, 200 mg IV every 6 hours is recommended.
Prolonged shock need intensive care service. The transcapillary leaks justifies the recourse of liquid expanders under close of central venous pressure and pulmonary capillary pressure monitoring, since the margin of safety between the hypovolemia and pulmonary overload is fairly tight. Ventilation artificial and, in the case of renal failure, hemodialysis is often necessary.