
Fats (a.k.a. Lipids)
Lipids contain a broad category of fats and oils and other substances that generally do not easily interact with water. Just like carbohydrates there are some lipids that are better than others. Before we look at that lets get a little better understanding of what lipids are. [Brace for some boring stuff]
Some of the more important lipids in human biology are:
Fatty acids: A basic lipid structure that forms a building block for more complex lipids. Chemically they are made of hydrocarbon chains that have carboxylic acid groups on their ends.
A fatty acid hydrocarbon chain looks like this:
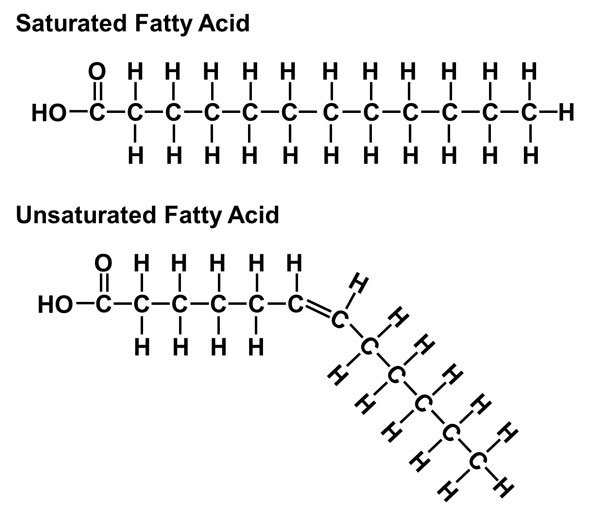
Where C is the carbon element and H is the hydrogen element.
A carboxylic acid group looks like this:
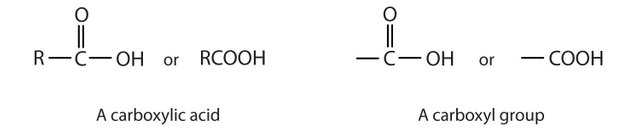
The C is obviously carbon, the O is oxygen, the OH is a combination of oxygen and hydrogen, the R represents the rest of whatever is attached to the carboxylic acid.
Put the hydrocarbon chain onto the carboxylic acid group and you have a fatty acid. Easy right? Here is a simple representation of one type of fatty acid, the jagged line represents the hydrocarbon chain:

Notice that the line that is straight is called trans-Oleic acid and the line that is crooked is called a cis-Oleic acid. This is known as cis/trans isomerism and indicates how the hydrocarbon chain can be linked up differently in the same type of fatty acid. You see it happening at the point where a little line is drawn in the middle of the jagged line (hydrocarbon chain). This indicates that a double bond between carbon atoms exist at this point and that it can have more than one configuration. This double bond is "stuck" in this position and thus creates a difference in the same type of fatty acid.
In the case of Oleic acid it is usually found in the cis configuration in abundance in olive oil. You can see in the illustration that there is a double bond in the hydrocarbon chain of Oleic acid. This means the fatty acid is unsaturated. Which simply means that the hydrocarbon chain is missing a hydrogen atom. Unsaturated fatty acids tend to be liquid at room temperature (72).
Glycerolipids
There are mono, di and tri glycerolipids. The most well known being triglycerides since most animal fat is made of this stuff.
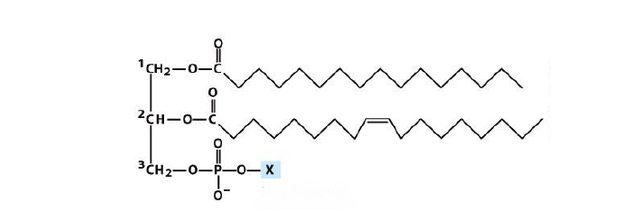
You can see from the picture of the chemical shorthand formula for a triglyceride why it is called a triglyceride. It has three fatty acid chains attached to some glycerol molecules. You can see by the little double lines on the fatty acid chain that this triglyceride is not completely saturated. Vegetable oil has a lot of unsaturated triglycerides and animal fat has more saturated triglycerides as you can see when you buy vegetable oil or a beef steak at the store. When you eat this stuff pancreatic lipase and bile breaks the bonds between the three chains and makes diglycerides and monoglycerides and free fatty acids so you can absorb this fat into the cells of your digestive system. The next step is for the enterocytes lining your intestines to rebuild these fatty acids into chylomicrons. The enterocytes then give up the chylomicrons to the lymph system and are transported to large blood vessels close to your heart where they enter the blood stream. Your bodies cells then use this fat for energy, construction/destruction and transportation.
Phospholipids
Well known to be a huge part of the membrane or outer wall of your cells and the cells of the food you eat. Phospholipids are interesting because one end is hydrophilic (water soluble) and one end is hydrophobic (non-water soluble). This allows your cells to be particular what it lets pass through into the cytoplasm or internal workings of the cell.
Here is a good illustration of what phospholipids look like in cell membranes.
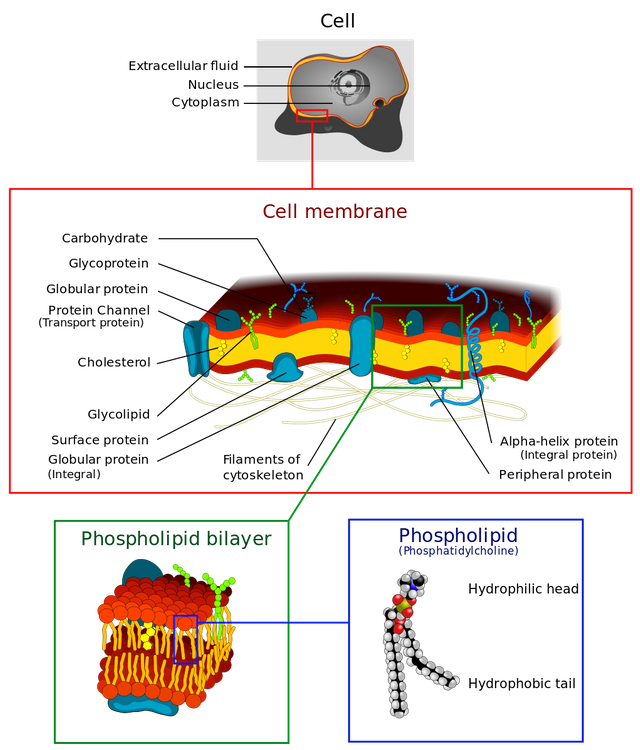
(derivative work: Dhatfield)
Sphingolipids
A pretty chemically complex lipid that is believed to protect cell surfaces, help regulate cell nutrient uptake and several other cell activities. Problems with sphingolipid metabolism in humans are related to several genetic diseases.
Here is a simple shorthand chemical formula of a sphingolipid.
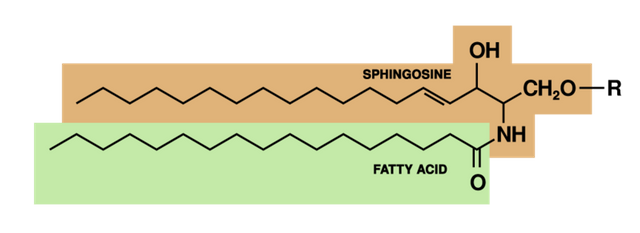
Sterol Lipids
The most famous sterol lipid is cholesterol which, among other things, is a precursor for steroid hormones, vitamin D and bile acids. Cholesterol can be found in the membrane of your cells where it helps transport substances, and communicate information to other parts of the cell. New information indicates that cholesterol can even act as an antioxidant. Cholesterol is produced by many cells throughout the body through a pretty complex process. A lot of cholesterol is produced in the liver. People with high levels of cholesterol may be producing them because of high levels of oxidative stress causing inflammation. Blaming heart and vascular disease and other problems on high levels of cholesterol might be like blaming the symptoms of a disease for the cause. In other words the scab doesn't cause the wound. The scab is a result of the wound.
More will be said about vascular and heart disease in regards to cholesterol later. Meanwhile here is what a chemical representation of cholesterol looks like.
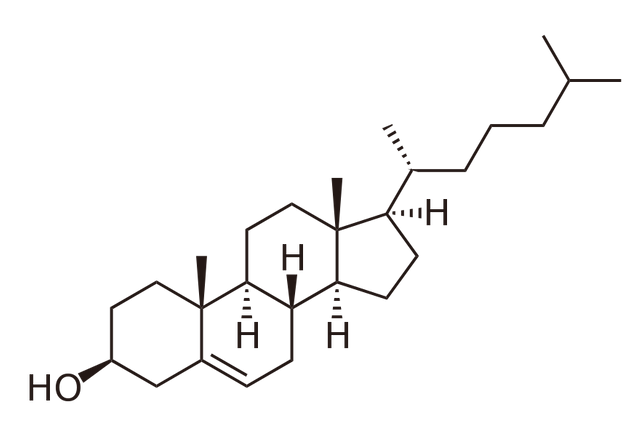
After eating high cholesterol foods your blood will measure high for cholesterol (J Lipid Res. 1994 Nov;35(11):1993-2007. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7868978) , but since your body compensates for this the levels of cholesterol go down after about eight hours. (Br J Nutr. 2011 Jul;106(1):6-14. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511000237. Epub 2011 Mar 9. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21385506)
If you had a bacon and eggs breakfast and then got a cholesterol test you would probably measure on the high side for cholesterol. On the other hand, if you fasted that morning and got a cholesterol test you might be measured as having low cholesterol. This illustrates one of the main problems with reductionist health science, it has trouble including all the factors that may affect measurements.
You hear a lot about LDL ("bad cholesterol") and HDL ("good cholesterol") now days in their relation to heart disease. Unfortunately, science has once again associated a symptom with a cause (garbage makes flies) and the more we learn about LDL and HDL the more confused we get. Some research now indicates that HDL "cholesterol" is associated with heart disease (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Feb 12;51(6):634-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.09.060. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18261682)
People take statin drugs in order to lower their cholesterol levels presumably to reduce risk of heart disease. The effectiveness of statins to reduce heart disease will be looked at in the drugs section of this article series. Of note is the research saying that eggplant juice can significantly reduce cholesterol levels. ("In hypercholesterolemic rabbits egg plant juice significantly reduced weight, plasma cholesterol levels, aortic cholesterol content and the MDA concentrations in native-oxidized LDL and in the arterial wall and increased the endothelium-dependent relaxations." - Arq Bras Cardiol. 1998 Feb;70(2):87-91. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9659714)
Saturated/Unsaturated fats
Saturated fatty acids are simply fatty acids that have less hydrocarbon chain double bonds. They tend to be hard at room temperature or have a higher melting point like coconut oil.
Trans fats
Lets talk about trans-fatty acids. You here a lot in the media about how trans fatty acids are bad for you, but why is that? The major problem that is created with trans-fatty acids is that they are produced during artificial hydrogenation of unsaturated cis-isomer fats like vegetable oils. This is how margarine (fake butter) is created. Vegetable oils that are normally liquid at room temperature are hydrogenated which adds hydrogen to the hydrocarbon chain and makes the oil artificially saturated. This creates an artificial trans-fat that the human body doesn't easily recognize. Even though natural trans-fat can be found in small quantities in foods like beef and dairy it is not the same as artificial trans-fats. These natural trans-fats have actually been shown to be beneficial (J Nutr. 2010 Jan;140(1):18-24. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.105163. Epub 2009 Nov 18. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19923390) While artificial trans-fats are detrimental to health. ("This study shows that TFAs from industrially produced and from natural sources have different effects on CVD risk factors in women." - Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Mar;87(3):558-66. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18326592)
So, what is the difference in artificially produced trans fats and naturally produced trans fats? The difference is in where the double bond is located on the hydrocarbon chain. Most trans fats are still partially unsaturated so there are some double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain. Naturally saturated trans fats are much more likely to have a double bond at position eleven on the hydrocarbon chain whereas artificially saturated trans fats have double bonds that are more spread out over the hydrocarbon chain making the molecule "look" different to the bodies cells than natural trans fats. This may be why the human body gets benefit from natural trans fats and sees detriment from artificial trans fat. (http://www.dairynutrition.ca/nutrients-in-milk-products/fat/natural-trans-fats)
What types of fats are there?
Monounsaturated fats - found in things like olive oil, avocodos, nuts and seeds.
Polyunsaturated fats - includes the famous omega 6 and omega 3 fatty acids, nuts and seeds.
Saturated fats - Coconut oil, animal fats, butter, etc.
Trans fats - a.k.a. partially hydrogenated oils (probably should avoid).
"There is abundant research showing the benefit of fats, saturated fats from animal sources in particular. Good Calories, Bad Calories by Gary Taubes, Know Your Fats by Dr. Mary G. Enig, 'The Whole Health Source' blog done by Stephan Guyenet, a number of articles by Dr. Joseph Mercola on www.mercola.com, along with thousands of other books, blogs and articles, present the well-reasoned, scientifically-grounded arguments for abundant fat consumption." - http://www.sott.net/article/230686-Everything-About-Fat
"Polyunsaturated Fats - These are usually from nut and seed oils. You can tell whether an oil is mostly made up of polyunsaturated fats if it stays liquid even when it's put in the fridge. They are often referred to as 'essential fats' or 'essential fatty acids' (EFAs) because they are needed for the proper functioning of our bodies, but they cannot be created from other fats. You also hear them referred to as omega-3s or omega-6s. However, polyunsaturated fats should never be used for cooking or otherwise heated. These fats are quite delicate and can easily go rancid, turning them into harmful oils which promote disease. As such, they need to be protected from heat, light and even air. Polyunsaturated oils should be sold in a dark bottle, only be 'cold pressed' (i.e. no heat is used in the extraction process) and should never be used as a cooking oil. Unfortunately, the oils from the grocery store sold in clear plastic bottles for the express purpose of cooking are all polyunsaturated oils!
Polyunsaturated Fats include - safflower oil, grapeseed oil, sesame oil, sunflower oil, hemp seed oil, flaxseed oil, borage oil, fish oils
Best used for - cold applications only: salads, smoothies, supplements (as with flaxseed or fish oil)
Look for - dark bottles, sold in the refrigerated section, cold pressed, organic" http://www.sott.net/article/230686-Everything-About-Fat
"Monounsaturated Fats - These fats are found in some vegetables, nuts and fruits and make up a good part of the fats found in meats. They are a little bit heartier than polyunsaturated oils and can be used for some light-heat applications like light sautéing or baking. The most common vegetable-sourced monounsaturated fat is olive oil. You can tell whether an oil is mostly monounsaturated fats because it becomes gelatinous and sludgy when put in the fridge but stays liquid at room temperature.
Monounsaturated Fats include - olive oil, avocado oil, walnut oil, hazelnut oil
Best used for - cold applications like salads, dips or pestos; light sautéing or some baking
Look for - dark glass bottles, cold pressed, organic" - http://www.sott.net/article/230686-Everything-About-Fat
"Saturated Fat - Don't believe the hype - saturated fat is good for you! Despite almost a century of dietary recommendations against intake of saturated fat, the public is finally starting to catch up with what some researchers and holistic health professionals have known all along: that saturated fat consumption actually promotes health. Saturated fats are found in meats, some dairy products, and eggs, as well as some tropical vegetables. They are ideal for cooking as they can withstand much higher temperatures than other oils. You know a fat is saturated if it is solid or semi-solid at room temperature.
Saturated Fats include - duck fat, goose fat, beef tallow, butter, ghee, lard (pork fat), coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and red palm oil. Note: duck fat and lard actually have a higher content of monounsaturated fats than saturated fats but are grouped in with saturated fats since they make up a third or more of their total fat, and because everyone thinks that animal fats are entirely saturated; an unfortunate misconception.
Best used for - all high-heat applications including searing, frying, deep or shallow-frying, baking, etc.
"Fats to avoid at all costs - all polyunsaturated oils sold for cooking, anything sold in clear plastic bottles, margarines or other tub spreads, any hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils, trans fats, interesterified fats, vegetable shortening, 'vegetable oil', cottonseed oil, all genetically modified oils like canola oil, corn oil and soy oil." - http://www.sott.net/article/230686-Everything-About-Fat
More quotes from articles:
" A damaged double bond means the fat is rancid. Rancid fats are actually quite dangerous to eat, causing free radical formation that can cause damage to cells. "
" Most polyunsaturated oils are processed extensively to maximize extraction. The seeds are heated, then distilled, refined, bleached and deodorized. This process damages the antioxidants and damages the oils themselves. A preservative chemical, such as the carcinogenic BHA or BHT, is generally added to replace the lost antioxidants and to prevent further spoilage. But make no mistake, these oils are rancid from the get-go. The only reason you can't tell is because they have been deodorized and ultra-refined. They are not fit for human consumption! " "Omega-6 fats convert to inflammatory prostaglandins in the body and, while some inflammation is necessary, too many inflammatory fats can lead to chronic inflammation. Conversely, w3 fats are converted to
anti-inflammatory prostaglandins in the body and are thus highly essential."
" EPA and DHA keep blood platelets from becoming sticky, which results in blood becoming more prone to clotting. They have also been found to lower the necessity for repair proteins in the blood, a build-up of which leads to atherosclerosis (that's right, fat is good for the heart!). EPA and DHA also lower levels of blood triglycerides, LDL and VLDL cholesterol, decreasing hypertension and the risk of strokes and heart attacks. In animal studies, w3 fish oils have also been found to inhibit the growth of tumors. " - http://www.sott.net/article/230686-Everything-About-Fat
Research:
Omega 3 fat
"For these children, both reading ability and behaviour reported by parents have shown a significant improvement in those children who received active treatment compared with those on placebo over the 16-week treatment period." - The DHA (docasahexaenoic acid) Oxford Learning and Behaviour (DOLAB) confirmatory study Research Cluster: CEBI Start Date: 01.09.2012 End Date: 31.08.2015 http://www.spi.ox.ac.uk/research/details/the-dha-docasahexaenoic-acid-oxford-le.html
"The Mediterranean diet, rich in virgin olive oil, improves the major risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as the lipoprotein profile, blood pressure, glucose metabolism and antithrombotic profile. Endothelial function, inflammation and oxidative stress are also positively modulated. Some of these effects are attributed to minor components of virgin olive oil. Therefore, the definition of the Mediterranean diet should include virgin olive oil." - European Journal of Clinical Investigation Volume 35, Issue 7, pages 421–424, July 2005 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2005.01516.x/abstract?deniedAccessCustomisedMessage=&userIsAuthenticated=false
"This anti-HER2 property of OA offers a previously ously unrecognized molecular mechanism by which olive oil may regulate the malignant behavior of cancer cells." Clinical and Translational Oncology
January 2006, Volume 8, Issue 1, pp 15-21 http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12094-006-0090-0
"In a multivariate model, considering all food items simultaneously, the protective effect of exclusive olive oil use and sage remained statistically significant. Our results indicate that some food items typical of the Mediterranean diet are associated with decreased lung cancer risk." Nutrition and Cancer Volume 46, Issue 1, 2003 http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1207/S15327914NC4601_04#.U8bvc6h7Qvo
"...higher consumption of olive oil (rich in monounsaturated fat) was significantly related to a lower risk of breast cancer..." http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ijc.2910580604/abstract?deniedAccessCustomisedMessage=&userIsAuthenticated=false International Journal of Cancer Volume 58, Issue 6, pages 774–780, 15 September 1994
"As a working hypothesis, it is proposed that the high squalene content of olive oil, as compared to other human foods, is a major factor in the cancer risk-reducing effect of olive oil. Experiments in vitro and in animal models suggest a tumor-inhibiting role for squalene." Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev December 1997 6; 1101 http://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/6/12/1101.short
"We have investigated the scavenging actions of some olive oil phenolics, namely hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, with respect to superoxide anion generation, neutrophils respiratory burst, and hypochlorous acid. The low EC50s indicate that both compounds are potent scavengers of superoxide radicals and inhibitors of neutrophils respiratory burst: whenever demonstratedin vivo,these properties may partially explain the observed lower incidence of CHD and cancer associated with the Mediterranean diet." Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications Volume 247, Issue 1, 9 June 1998, Pages 60–64 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006291X98987356
"Olive oil may have a protective effect on the development of CRC [Colorectal Cancer]. The proposed hypothesis is that olive oil may influence secondary bile acid patterns in the colon that, in turn, might influence polyamine metabolism in colonic enterocytes in ways that reduce progression from normal mucosa to adenoma and carcinoma." J Epidemiol Community Health 2000;54:756-760 doi:10.1136/jech.54.10.756 http://jech.bmj.com/content/54/10/756.short
"Fish oil and olive oil are capable of influencing crucial processes responsible for colorectal cancer development. COX-2 and Bcl-2 may be important mediators of some of these effects." Clinical Nutrition Volume 22, Issue 1, February 2003, Pages 71–79 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261561402906278
Animal fats
"The ratios of 18:2 n-6 [omega 6] to18:3 n-3 [omega 3] in plasma-TAGs [triacylglycerols], three and seven hours after the ALA-rich [alpha-linolenic acid] oil meal, were 1.5 and 2.4, respectively. The corresponding values after the olive oil meal were: 13.8 and 16.9; and after the butter meal: 9.0 and 11.6." - Lipids Health Dis. 2011; 10: 106.
Published online Jun 28, 2011. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-106 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3141546/
I looks like butter is slightly better than even olive oil in providing a balanced omega 6 to omega 3 ratio of EFA's.
"A meta-analysis of prospective epidemiologic studies showed that there is no significant evidence for concluding that dietary saturated fat is associated with an increased risk of CHD [coronary heart disease] or CVD [cardiovascular disease] ." - First published January 13, 2010, doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27725 Am J Clin Nutr January 2010 ajcn.27725 http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/early/2010/01/13/ajcn.2009.27725.abstract
"Current evidence does not clearly support cardiovascular guidelines that encourage high consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and low consumption of total saturated fats." - Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(6):398-406. doi:10.7326/M13-1788 http://annals.org/article.aspx?articleid=1846638#tab10Div
"...in Framingham, Mass, the more saturated fat one ate, the more cholesterol one ate, the more calories one ate, the lower the person's serum cholesterol." - Arch Intern Med. 1992;152(7):1371-1372. doi:10.1001/archinte.1992.00400190013003 http://archinte.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=616375
"Current evidence does not clearly support cardiovascular guidelines that encourage high consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids and low consumption of total saturated fats." - Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(6):398-406. doi:10.7326/M13-1788 http://annals.org/article.aspx?articleid=1846638
"The NCEP Step I diets containing primarily LRM or LWM produced similar reductions in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and elevations in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, which were maintained thoughout 36 weeks of treatment." - Arch Intern Med. 1999;159(12):1331-1338. doi:10.1001/archinte.159.12.1331 http://archinte.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=485065
"... the equivalent of one fatty fish meal per week) was associated with a 50% reduction in the risk of primary cardiac arrest..." - JAMA. 1995 Nov 1;274(17):1363-7. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7563561
The Omega Diet talks about how Omega 3 fatty acids are good for brain. http://www.amazon.com/The-Omega-Diet-Lifesaving-Nutritional/dp/0060930233
" During the chemoradiation therapy, cell-mediated immune function was improved significantly in the patients fed enterally with EPA [ eicosapentaenoic acid] ethyl ester (n = 5), when compared with the patients without EPA (n = 14)." - Nutrition. 1998 Jun;14(6):551-3. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9646301
EPA: "It is obtained in the human diet by eating oily fish or fish oil, e.g. cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon, menhaden and sardine, and various types of edible seaweed. It is also found in human breast milk." - wiki
" Eggs from hens fed under free-range conditions had a higher concentration of total (n−3) fatty acids than eggs from hens fed the commercial diet (P<0.05). Eggs from layers on free-range had a higher concentration of α-tocopherol than those of hens maintained in cages and fed the commercial diet (P<0.01)." - Animal Feed Science and Technology Volume 72, Issues 1–2, May 1998, Pages 33–40 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0377840197001806
" Cows grazing pasture and receiving no supplemental feed had 500% more conjugated linoleic acid in milk fat than cows fed typical dairy diets..." - J Dairy Sci. 1999 Oct;82(10):2146-56. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10531600
" Conjugated linoleic acid is unique because it is present in food from animal sources, and its anticancer efficacy is expressed at concentrations close to human consumption levels." - Cancer. 1994 Aug 1;74(3 Suppl):1050-4. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8039138
"... A diet composed of CLA-rich foods, particularly cheese, may protect against breast cancer in postmenopausal women..." - Nutr Cancer. 2000;38(2):151-7.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11525591
" Our findings suggest that diets lower in carbohydrate and higher in protein and fat are not associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease in women." - N Engl J Med. 2006 Nov 9;355(19):1991-2002. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17093250
" Stearic acid, the main saturated fat found in beef, lamb and other meats, is easily converted by the body into oleic acid, the much-hyped monounsaturated oil found in "heart healthy" olive oil. Lauric acid, the main saturated fat found in coconut oil, has antibacterial and antiviral properties that make it highly valuable in the diets of those who eat coconut regularly. Butyric acid, the saturated fat found in butter, is used as fuel for the cells of the colon and was found to increase mitochondrial activity (energy production), energy levels, lower blood triglyceride levels and to increase insulin sensitivity in studies of mice. It also suppresses inflammation in the gut and increases resistance to metabolic and physical stress. I could go on; the benefits of saturated fats go much further than this!" - http://www.sott.net/article/230686-Everything-About-Fat
"A wide variety of evidence suggests that the ketogenic diet could have beneficial disease-modifying effects in epilepsy and also in a broad range of neurological disorders characterized by death of neurons." - Behav Pharmacol. Sep 2006; 17(5-6): 431–439. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2367001/
What about other oils and fats?
"Thirty-two percent of adenomas progressed to carcinoma in rats fed 23.5% calories from corn oil compared with only 3% in those fed the same proportion from olive oil." - http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/%28SICI%291097-0142%2819980201%2982:3%3C448::AID-CNCR4%3E3.0.CO;2-L/full Cancer Volume 82, Issue 3, pages 448–453, 1 February 1998
"...simultaneous feeding of a fat diet and heme-iron produced a significant increase (P < 0.05) in the incidence of colon cancer compared with a diet without hemoglobin...lipid peroxides and heme components generate peroxyl radical species that exert DNA-cleaving activity. A plausible explanation is that lipid peroxyl radicals thus generated, which originated from routine dietary components such as fat and red meat, may contribute, at least in part, to the high incidence of colon cancer." Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev November 1998 7; 1007 http://cebp.aacrjournals.org/content/7/11/1007.short
"Weston A. Price foundation and Fat Experts Sally Fallon and Mary Enig state:
“Like all modern vegetable oils, canola oil goes through the process of refining, bleaching and degumming -all of which involve high temperatures or chemicals of questionable safety. And because canola oil is high in omega-3 fatty acids, which easily become rancid and foul-smelling when subjected to oxygen and high temperatures, it must be deodorized. The standard deodorization process removes a large portion of the omega-3 fatty acids by turning them into trans fatty acids. Although the Canadian government lists the trans content of canola at a minimal 0.2 percent, research at the University of Florida at Gainesville, found trans levels as high as 4.6 percent in commercial liquid oil. The consumer has no clue about the presence of trans fatty acids in canola oil because they are not listed on the label.” http://draxe.com/canola-oil-gm/
Volume 241, Issue 3, 15 December 2009, Pages 303–310 "High-fat diet exacerbates inflammation and cell survival signals in the skin of ultraviolet B-irradiated C57BL/6 mice." - They don't say in the abstract what kind of fat they used. Other research indicates type of fat makes a big difference.
" A meta-analysis of prospective epidemiologic studies showed that there is no significant evidence for concluding that dietary saturated fat is associated with an increased risk of CHD or CVD.' - First published January 13, 2010, doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.27725 Am J Clin Nutr January 2010 ajcn.27725 http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/early/2010/01/13/ajcn.2009.27725.abstract
Is high cholesterol a disease?
" High admission cholesterol may be associated with increased long-term survival after IS [ischemic stroke]." - J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014 Jan;23(1):e47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Oct 6 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24103674
" These associations indicate that high lipoprotein levels do not seem to be definitely harmful in the general population." - Scand J Prim Health Care. 2013 Sep;31(3):172-80. doi: 10.3109/02813432.2013.824157. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23941088
" Only the group with low cholesterol concentration at both examinations had a significant association with mortality ... These data cast doubt on the scientific justification for lowering cholesterol to very low concentrations (<4.65 mmol/L) in elderly people. " - Lancet. 2001 Aug 4;358(9279):351-5.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11502313
" the failure of cholesterol lowering to affect overall survival justifies a more cautious appraisal of the probable benefits of reducing cholesterol concentrations in the general population. " - BMJ. 1990 Aug 11;301(6747):309-14.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2144195
Almost half the people hospitalized with coronary artery disease had low cholesterol levels.
" In a large cohort of patients hospitalized with CAD, almost half have admission LDL levels <100 mg/dL. More than half the patients have admission HDL levels <40 mg/dL " - Am Heart J. 2009 Jan;157(1):111-117.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2008.08.010. Epub 2008 Oct 22.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19081406
" In this cohort, substituting dietary linoleic acid in place of saturated fats increased the rates of death from all causes, coronary heart disease, and cardiovascular disease. An updated meta-analysis of linoleic acid intervention trials showed no evidence of cardiovascular benefit. These findings could have important implications for worldwide dietary advice to substitute omega 6 linoleic acid, or polyunsaturated fats in general, for saturated fats." - BMJ. 2013 Feb 4;346:e8707. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e8707.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23386268
" A recent journal article put omega-3-rich fish oils head-to-head with omega-6-rich coconut oil. Guess what they found? A diet rich in omega-3 fish oil alone led to a significant decrease in the body's ability to fight free-radical damage, presumably due to a noticeable drop in blood levels of vitamins E and A. " - http://www.doctoroz.com/blog/audrey-kunin-md/going-nuts-about-coconut-oil
Eggs are okay?
" ...a number of recent clinical trials that looked at the effects of long-term egg consumption (as a vehicle for dietary cholesterol) reported no negative impact on various indices of cardiovascular health and disease." - Adv Nutr. 2012 Sep 1;3(5):711-7. doi: 10.3945/an.111.001321. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22983850
Thanks for up-voting, following and re-steeming.
After reading your article, I am going to try to switch to only buying oil sold in glass containers!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yeah, I would say...dark glass, cold pressed organic extra virgin olive oil, organic coconut oil, etc.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit