
The science-fiction writers ‘visions go through the scientists’ laboratories and become, from time to time, reality. Although R. Daneel Olivaw, Isaac Asimov’s most famous positronic robot, is still not waiting for the metro with humans, humanoid robots are already becoming more and more frequent in research laboratories.
But there are technologies invented by writers half a century ago that are now upgraded and used. The first private space flight or computer glasses are just a few of the futuristic technologies that came true this year.
Few were the science-fiction creations that inspired so many scientists like Star Trek. The ideas of the creator of the Enterprise universe, Gene Roddenberry, raised questions and raised hopes in the souls of those who had the courage to open their eyes to the future.

No more than half a century since the first Star Trek movie, many of its so-called SF devices saw the light of day. Mankind is now preparing to meet the physics of the impossible: teleportation, androids, phasers, or travels over time. Only a few of these ideas will remain forever in science fiction because the researchers have made great strides in actually transferring the universe imagined by Roddenberry.
Even more confident in the future is American researcher Michio Kaku, a specialist in theoretical physics and string theory. In his book “The Physics of the Impossible: A Scientific Exploration into the World of Phasers, Force Fields, Teleportation, and Time Travel,”. The physicist divides the “impossibilities” into three classes.
The first of these includes intergalactic spacecraft, teleportation, shields, phasers, and robots, that is, the devices that, in his opinion, can be made at the latest in the next century.
The second-class combines the ideas that are at the limit of our knowledge of physics, and which would require thousands, perhaps even millions of years, to materialize. Michio Kaku enumerates here: travels with super-light speeds, time backs, and parallel universes.
The last of these categories brings together the ideas that should radically change our conceptions of physics and the universe to be applied. Kaku includes mobile Perpetuum devices and those that could tell us the future.
Cyborg is among us
The term “cyborg” belongs to Manfred E. Clynes, who wrote about partially biologically robot organisms, in an article published in “Astronautics” in 1960. Since then, bionic members have become a common presence in science fiction.
The Star Trek Borg and the Darth Vader are just two of the best-known examples. Technology has become a reality this year, for the first time: a paralyzed woman was able to control a robotic member and feed herself by transmitting all commands directly from the source via pulses from the brain.

It is now possible to achieve a brain-to-computer interface that is efficient enough to allow for consistent actions of the robotic components. Although the bionic limbs still do not look like fictional, the connection technology through external electrodes implanted in the skull is no longer a film scenario, it is a reality.
Professor Michio Kaku claims that two major obstacles that researchers have to go through to create smart robots: “pattern recognition and … good sense.” “Robots can see better than we do, but I do not understand what they see,” writes the professor in his book, Physics of the Impossible.
“When he steps into a room, a robot sees a lot of lines and curves, no chairs, tables or lamps. Our brain recognizes the objects without realizing trillions of trillions of operations, an activity we are not aware of, “said Michio Kaku.

The second milestone, common sense, seems even more difficult to overcome in the physicist’s opinion: “People know water is wet, mothers are older than daughters, time does not flow upside down … But there is no No mathematical expression to arrive at these conclusions, and so far we have failed to incorporate these common sense laws into a computer because there are too many. ”
The solution for building a “Data” can be imitating the way children learn. Massachusetts Institute of Technology specialists in the United States have succeeded in creating the first robots that have traced the obstacle course on the insect model.
Today, some of their “followers” have arrived on Mars, where they have sent us photos. However, when the reproduction of the learning mechanisms of the evolved species was attempted, the cars failed.
Whatever the robots would eventually develop, it could have before us what can be considered a disadvantage (in a different view from that of volcanoes): lack of emotions. For Android Data, love is unfortunately only a software …
Quantum teleportation and communication
Although the teleporting of objects is not yet possible just like in Star Trek, the first step was done this year, with the transport of photons from one place to another made in intangibleness. Quantum transportation has been working in specialized laboratories for a long time, but the distance traveled was only a few meters, writes mashable.com. The dash record set in 2012 is 143 kilometers.
In addition to teleportation, scientists have built the quantum internet as well. Though only at the beginning, photon teleportation would allow for infallible communication to computer attacks of any kind.
What exactly comes to mind when thinking about teleportation? Most likely, Enterprise Star Trek Enterprise and “Engage!”.
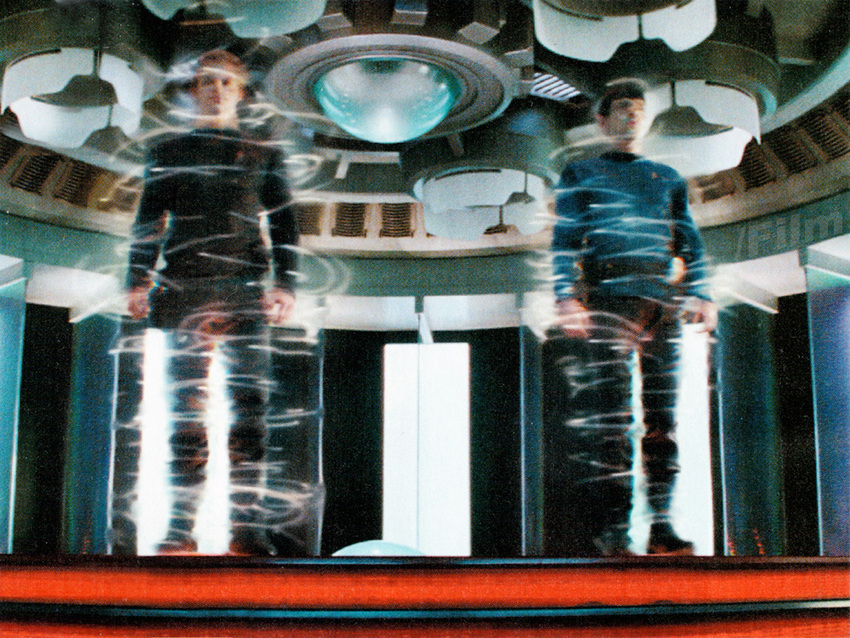

Quantum teleportation is based on the quantum inseparability property of a set of quantum objects (photons) that are created at the same time and in the same place in space and thus share the same existence.
This property continues even if the quantum objects are separated by a certain distance – meaning that any measurement on one influences the state of the others, regardless of the distance between them.
The connection between quantum objects can be used to transfer quantum information – by downloading the information associated with a photon through the inseparable bond it has with another photon, the second taking its identity. So, quantum teleportation is not a process by which transports matter but information.
A team of Chinese scientists took the process a little further, announcing that they managed to beam the information of a particle from Earth to a satellite on an orbit.
At the beginning of July 2017, a team of 32 researchers announced that they managed to beam a particle from Ngari to the Micius satellite in space for a distance of 1400 kilometers. The previous record was about 100 kilometers.
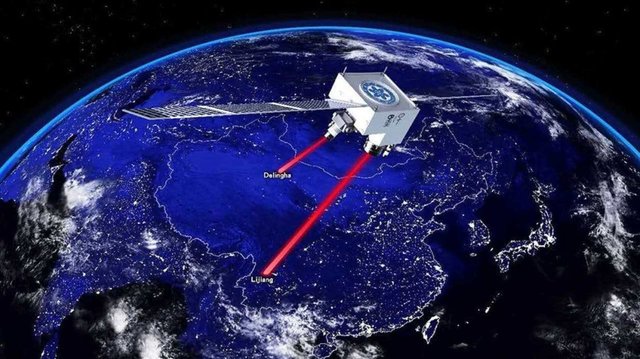
Indeed, there have not been teleported matter or particles as we have seen in Star Trek, but what the Chinese have done is impressive. Quantum teleportation refers to the instantaneous transfer of a quantum state, or a quantum information bit, from one particle to another, along with a certain distance.
In order for this teleportation to be possible, two or more particles must be bonded. In quantum physics, this means that the two are the same particle, even if they exist in different places. If one has a certain polarization, the other will provide the same measurement, even if they are separated by huge distances.
Even sending them into space is difficult. The transmitter must be sufficiently precise to overcome atmospheric distortions and launch the particle to the satellite. In addition, the satellite receiver must be sensitive enough to detect the particle when it arrives, write inverse.com.
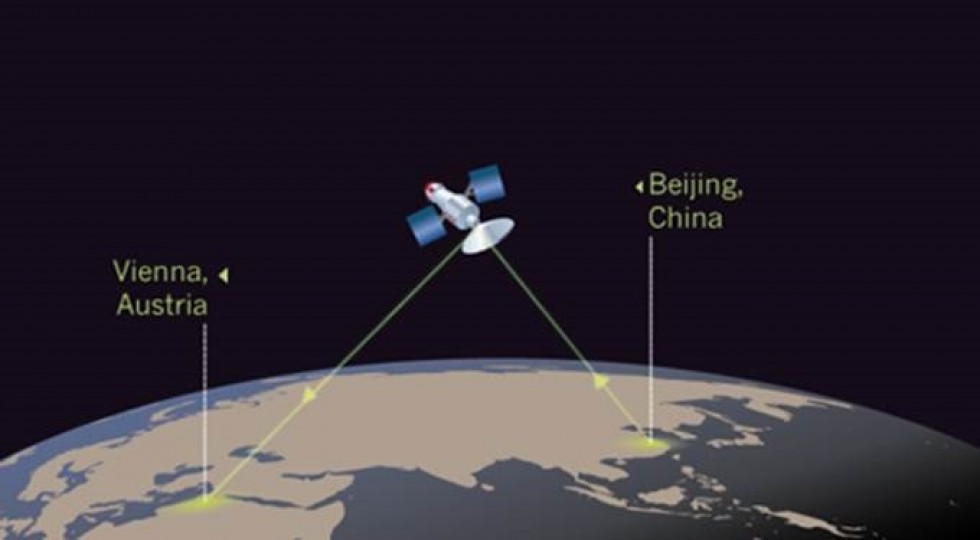
The Chinese have succeeded this six times. Each time, two particles were connected to Earth and one was sent into space. Thus, the Chinese have made a huge step in quantum communications research.
When it comes to moving from one place to another, things get complicated, and mistakes have no place. “In order to teleport someone, you have to know exactly where every atom is in the person’s body,” says Professor Michio Kaku in his book.
The physicist argues, however, that the progress made in the field is leading us to hope that in a not too distant future we will be able to go a long distance in a few seconds. But as there is fear of flying by plane, there will probably be fear of teleportation, because the process involves destroying the human body and rebuilding it far away.
Star Trek medicine is becoming true
A team of researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology has transformed Star Trek medicine into a reality. Several scientists have invented an “injector” of drugs that do not use needles.
Medicines are administered to patients with a high-pressure jet, and the medical gadget can be programmed to deliver various doses between the layers of the epidermis.
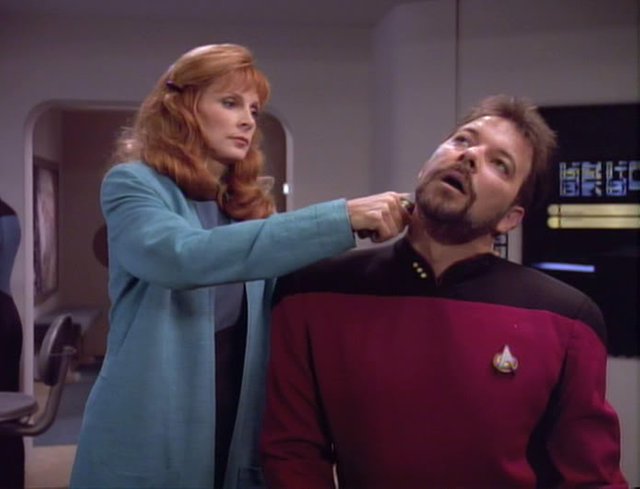

The “fear” factor among patients is significantly reduced, writes Daily Mail.
It seems that the invention enjoys a real success, is extremely useful. Would you use such a device instead of the classic injection?
Medical technology that could regenerate your body instantly
The ability to heal wounds quickly is one of the most attractive technologies imagined by the fantastic science world. The famous Star Trek doctors, able to cure wounds and burns instantly, regenerating the patient’s tissue with a laser “medical weapon” is one of the most famous examples in this respect.
Such technologies may seem simple fantasies, but specialists claim we are close to developing such medical devices. Mark Bass’s research team managed to successfully use an ultrasound emitter to speed up tissue restoration.
The “fear” factor among patients is significantly reduced, writes Daily Mail.
It seems that the invention enjoys a real success, is extremely useful. Would you use such a device instead of the classic injection?
Medical technology that could regenerate your body instantly
The ability to heal wounds quickly is one of the most attractive technologies imagined by the fantastic science world. The famous Star Trek doctors, able to cure wounds and burns instantly, regenerating the patient’s tissue with a laser “medical weapon” is one of the most famous examples in this respect.
Such technologies may seem simple fantasies, but specialists claim we are close to developing such medical devices. Mark Bass’s research team managed to successfully use an ultrasound emitter to speed up tissue restoration.!
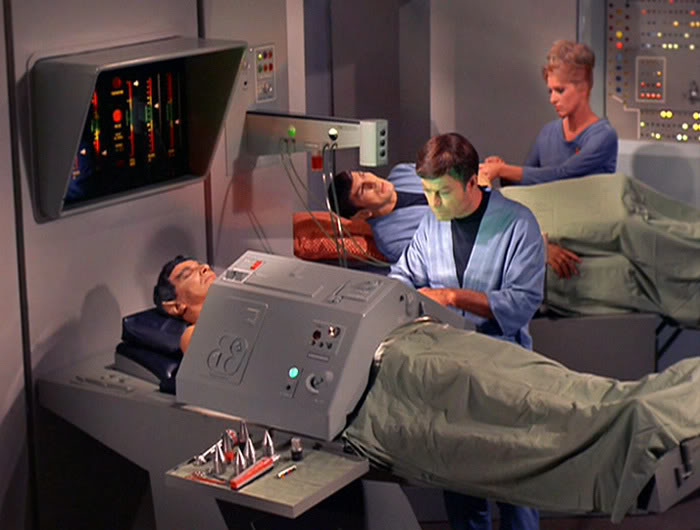
It does not yet have the results from Star Trek, but it could reduce the convalescence by about 30%. The patient enjoys greater comfort and the wounds are susceptible to infections for a much shorter period of time.
This technology could be truly saving, especially for those who heal more slowly. After the age of 30, the human body’s ability to heal decreases, and after 60 years this is a very big problem. Other risk factors that help reduce the body’s ability to heal are diabetes, obesity, and smoking. Therefore, a large part of the population suffers from these healing problems, write IFL Science.
As this effect occurs, the lesions can turn into chronic diseases that are no longer healing, because damaged skin cells become latent. These include sleeping injuries or various forms of an ulcer.
In addition to being painful, in extreme cases, these lesions lead to amputation of the limbs. “We have found that ultrasound treatments can reactivate latent cells and thus restart the healing process,” says Bass.
“Star Trek Traction Ranges” could be used in medicine for high-precision operations
A team of Scottish scientists created a “tractor beam” similar to Star Trek, which uses light to attract objects. Scientists hope their invention is useful in medicine, allowing targeting and attracting individual cells.
Study of Researchers at St. Andrews, which was published in the journal Nature Photonics, shows that the “tractor beam” can only attract microscopic particles. In SF movies and serials like Star Trek, this beam is used to move massive objects.
Scottish researchers are not the first to try to turn the idea of American screenwriters into reality. In 2011, a team of scientists from China and Hong Kong showed how such a “tractor beam” could be made using laser beams of a specific shape. Also, NASA’s space agency funded a study that studies how this method could be used to manipulate the samples collected in space.
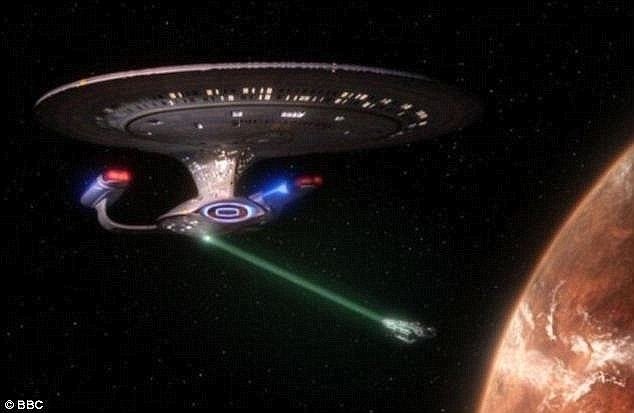

Scientific theories on tractors have been designed since 1960, but the success of Scottish scientists is the first concrete success in which a ray is used to attract microscopic objects to the light source.
In the past, scientists have used a technique called “optical whirlwind” to move individual particles by means of lilies, but the new method works in liquids and vacuum.
“Traction Radius” first appeared in a fiction work in 1928, in the story “The Skylark of Space,” written by American author EE Smith. Smith was referring to an “attracting ray”.
Since then, this technology has been featured in numerous SF films, allowing spacecraft to be moved by light rays. Dr. Cizmar pointed out that the technique developed by his team will not allow this.
“Unfortunately, this is an energy transfer. On a microscopic scale this is OK, but on a macro scale would cause huge problems. It would generate a huge heater of the maneuverable object, for example, a spacecraft. So this is excluded, “Dr. Cizmar explained.
Diagnosis and treatment like Star Trek
The Star Trek scene has in the center a miraculous device for our minds – in his name, Tricorder. When one of the characters had a health problem, the camera made the analyses on the spot, immediately indicated the diagnosis and the guide and the treatment to follow. Wow!
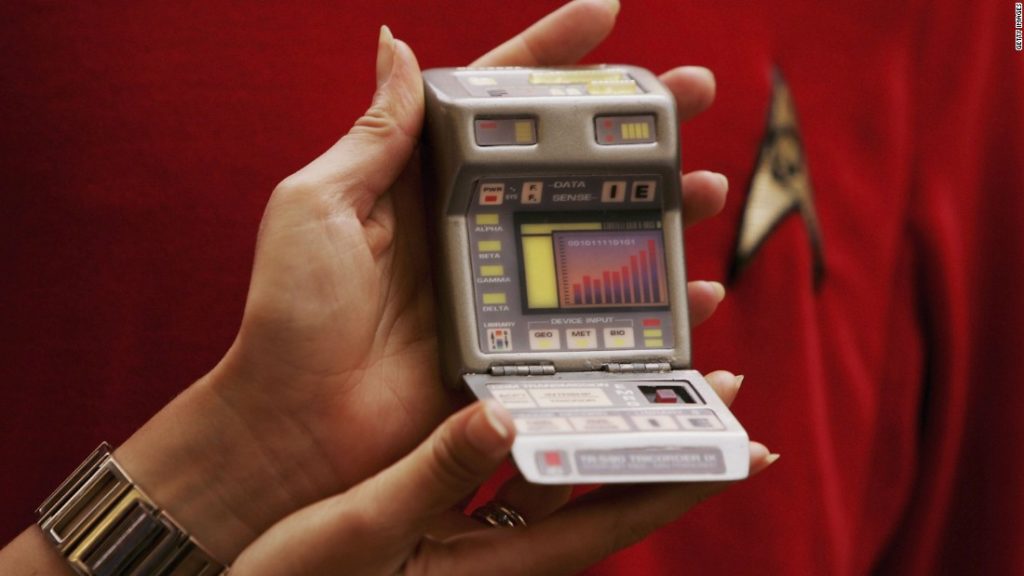

But, as is often the case, life beats the movie. And the next image is part of today’s reality.
Star Trek Tricorder is called, in our everyday life, “Scout”, a device imagined by Scanadu for measuring, analyzing and tracking vital signs in time.
STAR TREK FACTS
Researchers Nigel John and Jonathan Roberts are now working to build a “virtual cocoon” that could be the precursor of Star Trek holographic camera.
Scientist Michio Kaku, 62, believes he will only see one of his “impossibilities”: invisibility.
Where can the passion for Star Trek go? Englishman Tony Alleyne turned his apartment into the bridge on the Enterprise. But at some point, he decided to auction him on eBay. The final price was $ 838,563:
Patrick Stewart (Picard) has been asked by manufacturers to wear a wig at their meeting with Paramount executives, for fear of being denied, Chelsea. The studio bosses agreed to give him the lead role, provided he gave up his “strange wig”. Patrick Stewart also had reservations about Star Trek. In the first six weeks of filming, he refused to remove his clothes from the suitcase, to be ready, anytime, to leave.
Georgi La Forge (LeVan Burton) and Q (John de Lancie) are characters baptized in honor of two fans. George La Forge did not lack any Star Trek convention, though he was struggling with a serious illness: muscular dystrophy. The character named for him has a disability, is blind, but he has a special device that helps him see even better than his colleagues on the ship. Englishman Jane Quarton is the one who started the character Q, an alien entity with an incredible intelligence coefficient, 2005, and powers comparable to those of the gods.
The sliding doors of the Enterprise Shuttle were extremely noisy in the first Star Trek movies. That is why the actors were asked to interrupt the dialogues as they moved
Wolff’s Klingon’s mother tongue was created by James Doohan (Scotty), but American linguist Marc Okrand built his grammar and improved his vocabulary (the English-Klingon-English dictionary now has 191 pages!). For fans of the Roddenberry universe, it is a pride in learning Klingon, and some even managed to translate famous works such as Hamlet (“taH pagh taHbe” “or” to be or not to be “) or Gilgamesh. Even Google has come into play and has created a special version for Worf’s mother language. Unfortunately for Spock, the volcano is not so successful.
Star Trek creator, Gene Roddenberry is now where he ever wanted! His ashes were sent in space together with his wife. His full name is Eugene Wesley Roddenberry. The character of Wesley Crusher not only imbues his name, but also his youthful goals. Another character close to the creator, but who only appears as a voice is a Computer, played by Majel Barrett, Roddenberry’s wife.
Now, the destiny of the galaxy lies in the hands of two young people born in different worlds: James Tiberius Kirk (Chris Pine), a boy looking for strong sensations, and Spock (Zachary Quinto), an ambitious volcano who learns to discover his half human. The latest Star Trek: The Future Begins series, which premiered on May 8, 2009, places the two in the camp, but in the opponents. On their first mission on board the Enterprise, they have no chance to meet a Romulan ship from the future to destroy the planet Vulcan and the other planets of the Federation. Captain Christopher Pike (Bruce Greenwood), medical officer Leonard “Bones” McCoy (Karl Urban), Montgomery chief engineer “Scotty” Scott (Simon Pegg) and communications officer Uhura (Zoe Saldana). The story is exciting, the special effects are superlative, but the real fans of Star Trek have complained that the film has little to do with the universe created by Roddenberry. Star Trek: The Future Begins (Star Trek XI) Trailer
References:
@originalworks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
The @OriginalWorks BETA V2 bot has checked this post!
Some similarity seems to be present here:
http://galacticconnection.com/star-trek-the-future-is-now-technologies-become-reality/
This is an early BETA version. Reply if you feel this is an error.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
The @OriginalWorks BETA V2 bot has checked this post!
Some similarity seems to be present here:
http://galacticconnection.com/star-trek-the-future-is-now-technologies-become-reality/
This is an early BETA version. Reply if you feel this is an error.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit