Today We will talk a little about the moon and the sun, this topic is very interesting every time I read more about the earth it gives me much more curiosity to continue researching and reading about it.
The sun and the moon
The Earth moves around the sun, and completes one orbit (circuit) each year. At the same time it rotates on its axis, like a top. Together, earth movements control the way their surface is exposed to heat and sunlight.
They direct the rhythm of day and night, the duration of the year and the seasons. The movements are so regular that we adjust the clocks and live according to them. At the same time, the earth has a body that orbits it, the moon, which completes a circuit every month. The force of its gravity is enough to create the tides of the oceans.

Day and night
Every 24 hours, the earth makes a turn on an imaginary line called axis that passes through the poles. It makes the day in the regions facing the sun and night to those who see the other side. The earth turns in the direction of the east, which means that the Sun always appears on the eastern horizon.
The axis of the earth is not at a right angle in its orbit around the sun; it is inclined 23.5 degrees with respect to the vertical.
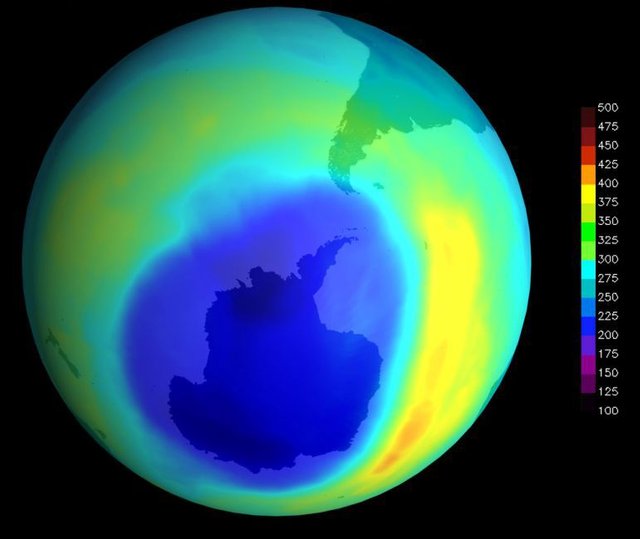
Hole in the layer of o...
Ozone, the form of oxygen in the earth's atmosphere, protects us by absorbing harmful radiation. In the 1970s, it was reported that industrial substances called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) delibited ozone. In 1985 a hole was detected in the ozone layer over Antarctica. The use of CFCs has been prohibited.
The ground stations
The axis of the earth is directed to the sun and creates different levels of sunlight, which we know as seasons. When sunlight falls directly on the exposed hemisphere (north or south), the day is longer, and summer conditions are created.
When that pole moves away, the sunlight is weaker and the days get shorter, creating winter conditions. At any time of the year, each hemisphere experiences opposite seasons.
Solar radiation
The earth absorbs heat and sunlight. We also get other forms of solar energy. These have high-energy shortwave radiation, such as gamma rays, x-rays and ultraviolet (UV) light.
This radiation is harmful. UV can cause skin cancer and damage the eyes. The layers of the Earth's atmosphere protect us from danger. The upper layer of the terrestrial atmosphere reflects gamma rays and x rays, and returns them to space. Under this, the ozone layer absorbs almost all UV light.

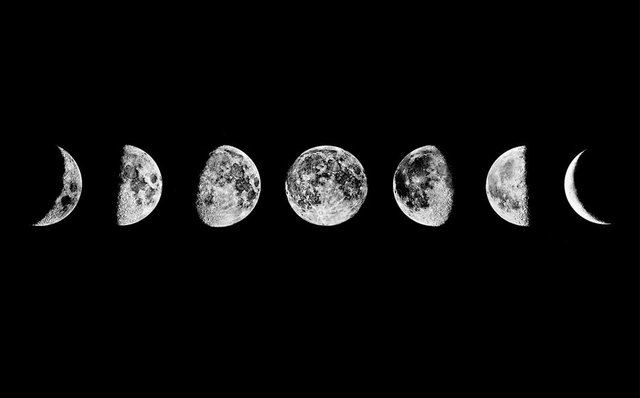
Moon phases
The moon makes a complete return to the earth of 27.3 days. Like the earth, half of the moon always has light. But as it is always changing its position relative to the sun and the earth, every night we see a different proportion of light on the lunar surface.
During the month, the moon progresses from a growing weakening to the full moon and then decreases again to the position of "new moon", when the part illuminated by the sun looks to the side opposite us and nothing of it is visible.
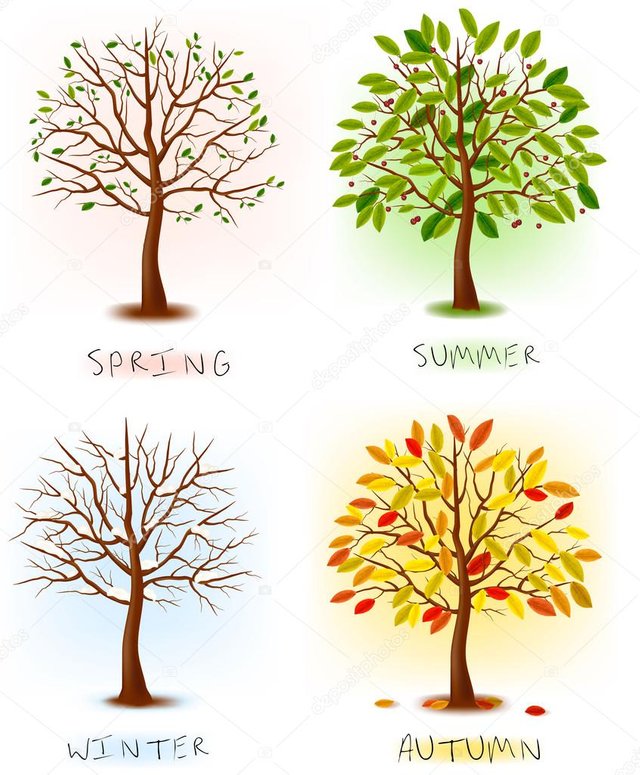
The four stations.
Spring.
The temperate lands between the tropics (the regions on either side of the equator) and the poles have four different seasons. In the northern hemisphere, March 21 or 22 is the vernal (spring) equinox, when the sun shines on the equator. The days lengthen and become lukewarm, which stimulates the growth of plants.
Summer
This is the warmest station. In the northern hemisphere summer occurs between June and September, and in the southern hemisphere, between December and February. On June 21 or 22, the north pole has its maximum inclination towards the sun. In the northern hemisphere, this is the longest day of the year.
Autumn
In autumn, the days become colder and longer. The opposite of the autumnal equinox, which falls in the northern hemisphere on September 22 or 23. The decrease in light slows down the growth of plants, and many trees lose their leaves preparing for winter.
Winter.
Winter is the coldest season. On December 21 or 22 (known in the northern hemisphere as winter solstice), the north pole reaches its maximum distance from the sun. Cold and dark hibernate some animals. Others migrate to the southern hemisphere, which experiences the warmth of the summer solstice.