Lithium - the lightest metal:
Lithium is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3 in the periodic table. It is the lightest metal and belongs to the alkali metal group. Lithium is silvery-white, soft and reacts strongly with water. It is known for its high reactivity and is often used in industrial applications in the form of lithium compounds such as lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide.
Geologically, lithium is relatively rare in the earth's crust and occurs mainly in the form of minerals such as spodumene, lepidolite and petalite. The largest lithium deposits are located in South America, particularly in Chile, Argentina and Bolivia, as well as in Australia and China. These countries have rich lithium reserves and play a decisive role in global lithium production.
Lithium is mainly extracted using mining and extraction methods. In conventional mining methods, lithium minerals are extracted and then processed into concentrate, from which lithium compounds are extracted. In some regions, lithium is also extracted from salt lakes by extracting lithium chloride. The processing of lithium involves various steps such as crushing, flotation, roasting and chemical processing to produce pure lithium compounds that are used in various industries.

Lithium batteries in electric cars:
Lithium-ion batteries are a type of rechargeable battery that use lithium as the electrolyte. They consist of a positive cathode material, a negative anode material and an electrolyte that enables lithium ion transport. The lithium-ion battery market has developed rapidly in recent decades and is now the preferred power source for electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops and other electronic devices.
The development of lithium-ion batteries dates back to the 1970s, when researchers began looking for an efficient way to use lithium as an electrolyte in batteries. Since then, continuous progress has been made in materials science, electrochemistry and battery technology, resulting in improved performance, higher energy densities and longer lifetimes for lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries offer a number of advantages for electric vehicles, including high energy densities, fast charging times, low weight and long life. They also allow for greater flexibility in vehicle design and help to reduce CO2 emissions in the transportation sector. Nevertheless, lithium-ion batteries also face challenges such as limited raw material resources, safety concerns and high manufacturing costs.

The role of lithium in electric vehicles:
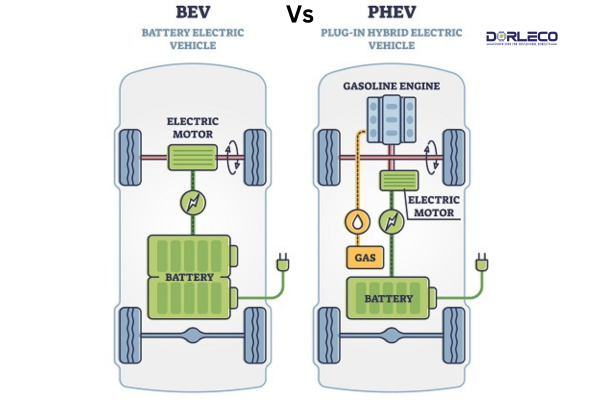
Lithium in battery electric vehicles (BEVs):
In battery electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are used as the primary energy source to power the electric motor. These batteries store the electrical energy that is generated either from the power grid or from renewable sources such as solar energy. Lithium enables BEVs to achieve long ranges and deliver reliable performance over long periods of time.
Lithium in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs):
Plug-in hybrid vehicles combine an internal combustion engine with a lithium-ion battery and an electric motor to utilize both electric and internal combustion engine energy. The lithium-ion battery allows PHEVs to cover short distances purely electrically while offering the flexibility to switch to the combustion engine when a longer range is required.
The impact of lithium on electric vehicle performance and range:
Lithium plays a crucial role in the performance and range of electric vehicles. The energy density of lithium-ion batteries determines the storage capacity and therefore the range of an electric vehicle. Advances in lithium technology, such as the use of silicon anodes and solid electrolytes, can further improve the performance and efficiency of batteries and extend the range of electric vehicles.
The impact of lithium on the automotive industry:
Lithium supply has a direct impact on the automotive industry, particularly on the cost and availability of electric vehicles. Fluctuations in lithium demand and supply can affect battery prices and impact the profitability of electric vehicles. Car manufacturers are therefore looking to enter into long-term supply contracts and develop alternative sources of lithium to hedge against risks in the raw materials market.
The sourcing of lithium is also critical for car manufacturers to ensure a continuous supply of batteries for electric vehicles. Automotive manufacturers need to work closely with suppliers to ensure a reliable and sustainable supply chain for lithium. This often involves investing in mining companies and promoting recycling initiatives to close the lithium loop.
The increasing demand for lithium has led to increased investment and innovation along the lithium supply chain. Automotive manufacturers, mining companies, battery manufacturers and governments are investing in new mining and processing technologies to increase efficiency, reduce environmental impact and secure lithium supplies for the future.

Environmental impact and sustainability in the lithium industry:
Lithium mining can have an ecological impact on the environment, especially if it takes place in sensitive ecosystems. Traditional mining methods can lead to landscape degradation, soil and water pollution and degradation of habitats and ecosystems. It is important to develop and implement sustainable mining methods to minimize these impacts. To reduce the environmental impact of lithium mining, sustainable practices are increasingly being used in the extraction and processing of lithium. These include techniques such as dry mining, waterless processing methods and the reuse of wastewater. In addition, measures are being implemented to rehabilitate mining sites and protect biodiversity in order to maintain ecological integrity.
The use of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles contributes to the reduction of CO2 emissions in the transportation sector by reducing the use of fossil fuels and supporting renewable energy. Electric vehicles have lower CO2 emissions compared to conventional combustion engines and therefore contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.

Future prospects and challenges:
The future demand for lithium in the automotive industry is expected to increase significantly as the transition to electric vehicles progresses worldwide. However, new technologies and innovations in lithium processing could lead to greater efficiency and sustainability in the lithium supply chain and secure the supply of this important raw material.
One of the biggest challenges for lithium supply is the limited availability of lithium resources and the increasing demand for this raw material. In order to overcome this bottleneck, investments in exploration, the development of new deposits and the promotion of recycling technologies are required. In addition, alternative sources of lithium such as geothermal energy and seawater must be investigated in order to meet demand in the long term.
Ongoing research and development in lithium technology could lead to significant breakthroughs that improve the performance, durability and safety of lithium-ion batteries. New materials, designs and manufacturing techniques could reduce costs and accelerate the market penetration of electric vehicles, leading to a further reduction in CO2 emissions and more sustainable mobility.

Lithium- curse and blessing:
The use of lithium in the automotive industry is crucial for the transformation towards more sustainable mobility. By integrating lithium-ion batteries into electric vehicles, CO2 emissions in the transportation sector can be reduced and dependence on fossil fuels can be decreased. However, it is important to consider the environmental and social impacts of lithium mining and promote sustainable practices to ensure that lithium supply is guaranteed for future generations.