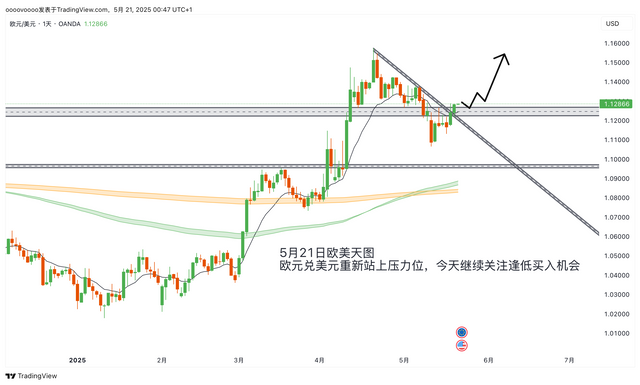
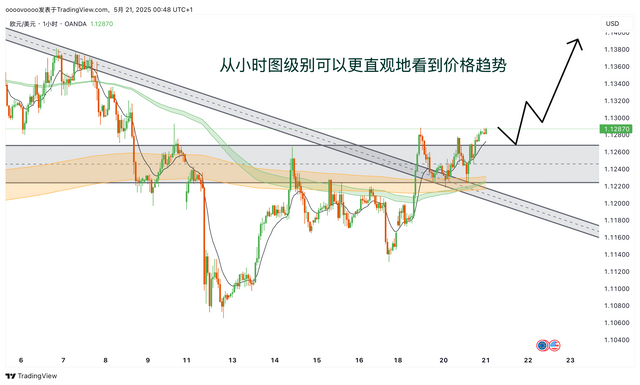
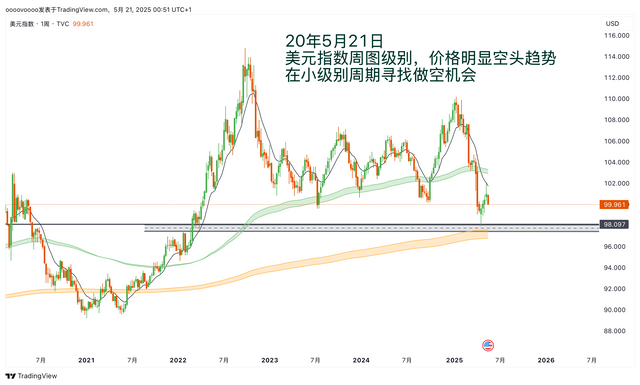
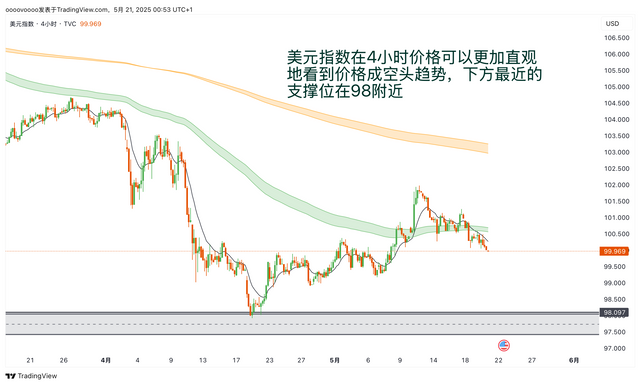
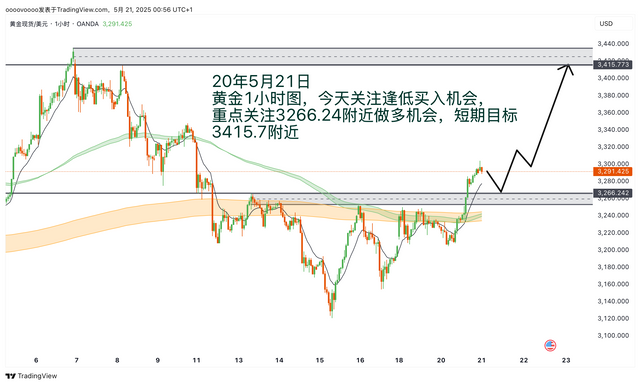
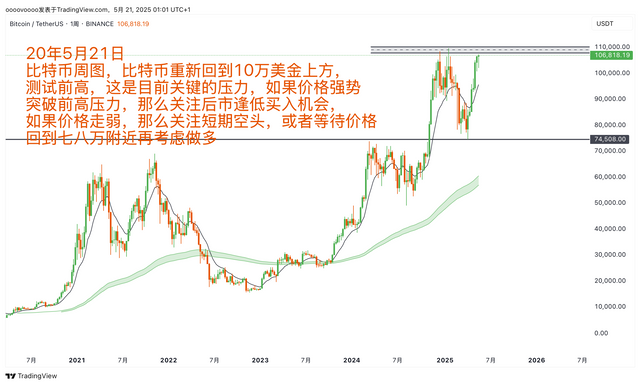
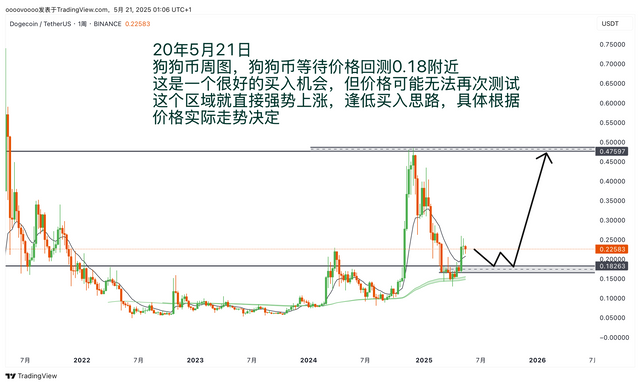
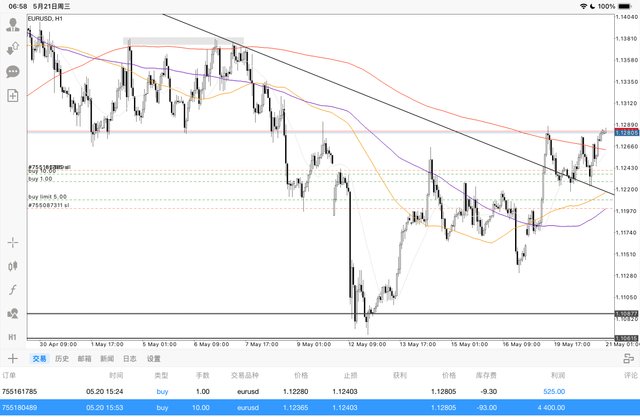
If you don't know how to write a trading plan, you can refer to my trading plan template:
- Determine the Trend
• Multi-dimensional analysis: Judge the trend by combining fundamentals (economic data, central bank policies) and technicals (trend lines, moving averages, MACD and other indicators) to avoid single-dimensional decision-making.
Example: Confirm the trend direction with the moving average system before and after the release of non-farm payroll data.
• Risk warning: Identify current market uncertainties (such as geopolitical events, black swan incidents) to avoid blind chasing of orders.
- Identify Support and Resistance Levels
• Dynamic adjustment: Support and resistance levels are not fixed values. Confirm them dynamically across different timeframes (daily, 4-hour, 1-hour) to avoid being misled by short-term fluctuations.
Example: Daily-level support levels are more reliable and can serve as a basis for long-term positions.
• Validation methods: Verify the effectiveness of support and resistance through historical price testing, volume changes, and candlestick patterns (such as hammer lines, engulfing patterns).
- Wait for Price to Approach Support/Resistance
• Set alerts: Use the price reminder function of trading software to avoid missing opportunities due to fatigue from monitoring the market.
• Avoid forced trading: If the price does not reach the preset level, it is better to miss the opportunity than to chase the order, reducing risks.
- Order Placement and Management
• Position sizing: Keep single-trade position within 2%-5% of total capital to avoid excessive impact on the account from a single loss.
Example: For a $10,000 account, control risk per trade at $20-$50.
• Stop loss and take profit:
◦ Stop loss: Set stop losses based on support/resistance levels and ATR (Average True Range) to avoid subjective assumptions.
◦ Take profit: Take profit in stages (e.g., close 50% of the position at the target level and trail the stop loss for the remaining position with the trend).
• Hedging and scaling in: Novices are advised to focus on single-directional trading first, and attempt hedging or pyramid scaling strategies only after gaining proficiency.
- Closing Positions
• Execute on trigger conditions: Strictly follow the preset stop loss and take profit rules to avoid "holding losing positions" or "exiting too early."
• Dynamic tracking: Lock in profits for winning positions with trailing stops and close positions decisively when reversal signals appear.
- Trading Summary
• Data review: Record entry/exit prices, profit/loss amounts, and trading times for each trade, and calculate statistics such as win rate and risk-reward ratio.
• Causal analysis:
◦ Profits: Were they due to proper plan execution or luck?
◦ Losses: Were they due to strategy failure or discipline issues (e.g., no stop loss)?
• Optimization and iteration: Adjust strategy parameters (e.g., stop loss range, entry signals) based on summaries to form a closed-loop improvement process.
Additional Tips
• Simulated training: Validate strategies with a demo account and complete at least 100 simulated trades before investing real money.
• Emotion management: Establish trading rules (e.g., maximum 3 trades per day) to avoid emotional trading.
• Continuous learning: Stay updated on industry trends (e.g., Federal Reserve interest rate decisions) and study classic trading strategies (e.g., the Turtle Trading System).
Through a systematic trading plan and strict execution, you will have a better chance of achieving stable profits in the forex market over the long term! Feel free to let me know if you need to dive deeper into any section.