INTRODUCTION
Scoliosis become at the start a greek phrase which means curved or bent. Scoliosis (said sko-lee-o-sis) is a three-dimensional deformity that takes place while the backbone turns into abnormally circled and curved sideways. It can affect any part of the spine, but the most common regions are the chest area (thoracic scoliosis) and the lower section of the back (lumbar scoliosis).
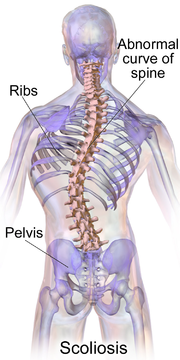
source:https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a7/Blausen_0785_Scoliosis
While scoliosis can be caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, Most regularly this deformity has no known recognized cause. in which case it's called idiopathic scoliosis. Even as the cause is unknown, idiopathic scoliosis does are inclined to run in households and families.
There are three capital types of idiopathic scoliosis which are classified according to the age of onset.
INFANTILE – A curvature that develops afore a adolescent is two years old. Nine out of ten of these curves will spontaneously resolve. Infantile idiopathic scoliosis is a attenuate condition. The cause is unknown, but possible factors consist of beginning role and slumbering function after birth. it is greater common in boys. it has a tendency to improve with simple measures together with stretching and changing sound asleep function. early analysis and remedy is essential as the smaller curves are actually curable in most cases.
Scoliosis affection in adolescents
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is essentially the most original form of scoliosis, and influences children who're at the least 10 years old. Idiopathic implies that there is not any recognized motive. Signs can incorporate:
- the pinnacle is slightly off middle
- the ribcage will not be symmetrical - the ribs could also be at distinctive heights
- one hip is extra distinguished than the other
- garments do not cling adequately
- one shoulder, or shoulder blade, is greater than the other
- the character could lean to one facet
- uneven leg lengths
- a bulge on one side of the chest
*Inbabies, the baby might consistently lie curved to one side - in more severe cases, the heart and lungs may not work properly, and the patient may experience shortness of breath and chest pain

http://embed.widencdn.net/img/veritas/ruqg5ptxwn/1200x630px/adolescent-thoracic-scoliosis
Scoliosis treatment
The majority of children with scoliosis have mild curves and don't need treatment. In such cases, the doctor will recommend regular follow-ups every 4-6 months to monitor the curve of the spine periodically with X-rays.
The following factors will be considered by the doctor when deciding on treatment options:
- Sex - females are more likely than males to have scoliosis that gradually gets worse.
- Severity of the curve - the larger the curve, the greater the risk of it worsening over time. S-shaped curves, also called "double curves," tend to get worse over time. C-shaped curves are less likely to worsen.
- Curve position - if a curve is located in the center part of the spine, it is more likely to get worse compared with curves in the lower or upper section.
- Bone maturity - the risk of the curve worsening is much lower if the patient's bones have stopped growing. Braces are more effective while bones are still growing.
A video to know more about scolosis
Other treatment of scoliosis
Casting
In young children, plaster jackets are applied around the trunk under a general anaesthetic to straighten the curve. The child is in hospital for a day. The cast stays on for between 1 and 4 months before being changed. Casting is useful in treating small, fast-growing children where a brace would be quickly outgrown, or when curves are too big to be braced (generally over 50 degrees). Casting is usually reserved for children under 6 years of age.Bracing
Braces similar to those used in adolescents are commonly used when there is a progressive curve between about 20 and 50 degrees. A brace will last 1 to 2 years depending on the growth of the child. It needs to be worn for 16 to 20 hours per day, until either the curve disappears (which can happen, particularly in children under 3 or 4 years) or until the end of growth.
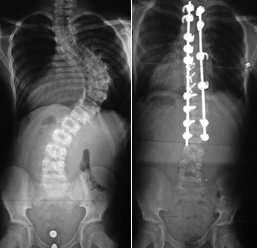
source:https://www.rchsd.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/scoliosisGrowing Rods
These are used when the other methods have failed. They are not first line treatment, given the high complication rate. The principle of the surgery is to put anchor points on the upper and lower ends of the curve (screws or hooks), without exposing the rest of the spine. Then rods are inserted under the skin or muscle to be attached to the anchor points. The rods then act as a type of internal splint that allow continued growth.Surgery
If the curve continues to progress despite bracing, surgery could be considered. The most common surgical option for scoliosis today is a posterior spinal fusion, which can offer better corrections with fewer fusion levels (preserving more back mobility) than what was done in years past.
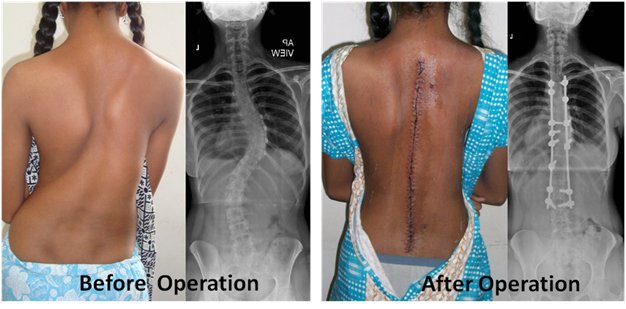
source:http://qualitylife4u.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/scoliosis2
Scoliosis surgery
In severe cases, scoliosis can progress over time. In these cases, the physician may recommend spinal fusion. This surgery reduces the curve of the spine and stops it from getting worse.
Scoliosis surgery involves the following:
- Bone grafts - two or more vertebrae (spine bones) are connected with new bone grafts. Sometimes, metal rods, hooks, screws, or wires are used to hold a part of the spine straight while the bone heals.
2.Intensive care - the operation lasts 4-8 hours. After surgery, the child is transferred to an ICU (intensive care unit) where they will be given intravenous fluid and pain relief. In most cases, the child will leave the ICU within 24 hours, but may have to remain in hospital for a week to 10 days. - Recovery - children can usually go back to school after 4-6 weeks, and can take part in sports roughly 1 year after surgery. In some cases, a back brace is needed to support the spine for about 6 months.
The patient will need to return to the hospital every 6 months to have the rods lengthened - this is usually an outpatient procedure, so the patient does not spend the night. The rods will be surgically removed when the spine has grown.
