
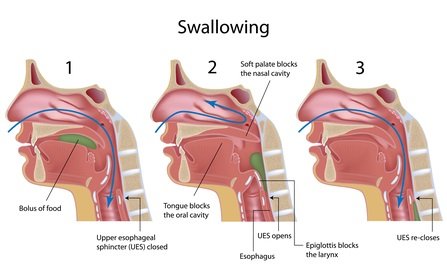
Oropharyngeal dysphagia (difficulty in transferring food from the mouth into the esophagus, often associated with symptoms of regurgitation and aspiration pulmonary nasopharyngeal) must be distinguished from esophageal dysphagia which is characterized by heaviness of the passage of food through the esophagus down. A careful history usually directs correct diagnosis.
Dysphagia typically require search process obstructive esophageal motility disorders or (achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm). Progression of symptoms is usually found in neoplasms and motility disorders; networks and esophageal rings produce intermittent symptoms. Acute onset of dysphagia, usually in temporal relation to mass, suggesting food impaction.
Odynophagia (painful swallowing) indicate the presence of oesophagitis, infectious oesophagitis especially due to the drugs.
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is usually caused by neuromuscular disorders or oropharynx and esophagus involving structural proximal. Assessment begins by videofluoroscopie barium and may include detailed examination of the ear, nose and throat exam and CT laboratory (for polymyositis, myasthenia gravis and other neuromuscular disorders).
Esophageal Dysphagia is investigating insidious onset of rule by upper endoscopy; however subtle rings and networks can not visualize if it is given a barium swallow solid using a bolus. Barium swallow is also an initial test in esophageal dysphagia although biopsies and endoscopy require esophageal dilation. Esophageal manometry esophageal motor disorders can specify when other tests are normal or suggest a motility disorder.
Acute esophageal obstruction is investigating best by endoscopy. Patients with prolonged dysphagia, which produces weight loss is necessary to solve nutritional needs; Patients with dysphagia are recommended to chew food well and eat foods of soft consistency.
Investigations
Upper endoscopy is the investigation of choice for evaluating persistent heartburn, odinofagiei and structural abnormalities detected by barium examination. Apart from direct viewing, endoscopic mucosal biopsy allows modified and dilation of strictures.
Videoesofagoscopia with rapid sequence evaluates oropharyngeal dysphagia best especially if done by an experienced specialist.
Esofagografia with dye versus endoscopy provides limited information on esophageal motility. Many clinicians perform direct endoscopy when suspected mechanical damage. Dysphagia in patients with esophageal motility disorders due to a possible, be performed first Esophagoscopy barium.
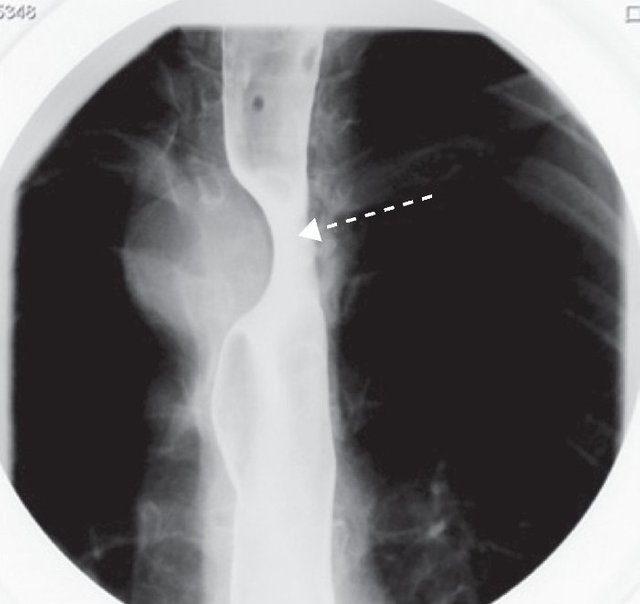
Esophageal manometry esophageal motility investigating best. Introducing a nasopharyngeal catheter sensitive to small variations in pressure allows assessment of the dynamics of the upper and lower esophageal sphincters and peristalticii esophagus. This is the best exam for assessing dysphagia in patients in whom endoscopy or barium examination ruled out mechanical obstruction.
Ambulatory pH monitoring of the esophagus. It can be continuously monitored using a probe nazoesofagiene small which is attached to a portable device for recording the pH. The probe and the recording device worn by the patient for up to 24 hours. Registration can be analyzed to quantify gastroesophageal acid reflux and to correlate patient symptoms with reflux registered.
Treatments
Dysphagia. Patients with dysphagia orogfaringiana may benefit from dietary changes and swallowing maneuvers. Enteral feeding through a gastrostomy tube may be indicated in patients with tracheal aspiration franca to attempt to swallow. Sialorrhoea patients can be treated with anticholinergic medication (scopolamine transdermal).
Inflammatory myopathies and myasthenia may respond to medical therapy, while benign tumors or those in initial stage and treating Zenker diverticula surgery. Structural benign lesions, including networks and rings can be dilated using rigid dilators. Recurrent dysphagia may occur but usually it responds to repeat expansion.
Placing a stent esophageal dysphagia can remove the inoperable malignancy. Endoscopic extraction of a food bolus obstructed can lead to resolution of dysphagia spectacular acute food impaction. You can try glucagon (2-4 mg IV bolus), but often it does not work; It can also manage, sublingual nitroglycerin, but should not be used for tenderizing meat mixtures. It will schedule dilation and oesophageal manometry when needed and prescribe subsequent suppression of acidity.
Odynophagia. This generally respond to the specific treatment of the lesion that caused esophagitis. Simultaneously, suppression of acidity and solutions viscous lidocaine of "rinse and swallowing" allow further improvement of symptoms.
