
The first principle of blockchain is a decentralized way of accounting, and "block" and "chain" are not necessary.
What are first principles
First principle thinking refers to returning to the most basic conditions of things, dividing them into various elements for deconstruction and analysis, so as to find the best way to achieve the goal. The principle originated with the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle and was popularized by Elon Musk. This principle also has something in common with "Tao" in Eastern philosophy.
In a 2014 commencement speech at the University of Southern California Business School, Elon Musk described his first-principles approach to decision-making:
"Perhaps you have heard me say that it is first principles to think in terms of physics. Don't reason by analogy. You break things down to the most basic elements you can imagine, and then you reason from there, which is a good way to determine if something makes sense. This kind of thinking is not easy, and you may not be able to think this way about everything because it takes energy. But if you want to innovate knowledge, this is the best way to think about it. This framework was proposed and developed by physicists who figured out counter-intuitive things like quantum mechanics. So it's a very effective, very powerful approach. By all means, do as much as possible."
Musk takes vacuum capsule high-speed rail as an example, if you use comparative thinking or empirical thinking to design new train products, most people's idea is to improve the existing functions, so that the power is stronger and the fluid dynamics are better. But if you use first principles to analyze product demand, you have to go back to the essential purpose of the transport vehicle: to transport more goods from point A to point B, which is the purpose of the original manufacturing of transport vehicles such as trains, not necessarily with traction to achieve upgrades. Under the support of first principles, Musk proposed to use the model of magnetic levitation plus low vacuum to create vacuum capsule high-speed rail.
First principles in blockchain
So what is the first principle of blockchain?
In his speech at the closing ceremony of the 2024 Web3 Carnival in Hong Kong, Dr. Xiao Feng said: The first principle of blockchain is a new accounting method.
"The blockchain that came out in 2009, as a distributed ledger (DLT), it records digital value and network value, and it is no longer on a private ledger, but on an open and transparent global public ledger, where everyone is in the same ledger and all stakeholders are in the same ledger. This is the first principles of blockchain, the transparent, open "global public ledger," and all Web3 innovations are based on first principles."
The author agrees with Dr. Xiao Feng's point of view, and further elaborates the nature of blockchain based on this point of view.
"Blockchain" three words apart is block + chain, since the first principle of blockchain is a way of accounting, then block and chain is really necessary?
Before answering this question, let's first look at Bitcoin as a distributed ledger, why you need blocks and chains.
In Bitcoin, a block is a digital record containing a set of transaction information, which can be understood as a page in the ledger, and a hash function can be used to calculate a hash value, which is characterized by a slight change in the content of the block, the hash value becomes different. Each block contains the hash value of the previous block, which can be understood as the first row of the N+1 block is written to the hash calculated by the N block, thus forming an immutable chain structure.
In Bitcoin, the mechanism for synchronizing the ledger is the PoW consensus mechanism. When a transaction occurs in the Bitcoin network, these transactions are put into a memory pool (mempool). The miner then selects a set of transactions from the memory pool to try to form a new block. To do this, miners need to find a specific value in the random number, and combine this specific value with the block data to generate a hash value that meets the network difficulty goal, this process is called "mining", who calculates the hash value that meets the conditions first, who gets the billing right, that is, mining success. The difficulty target is a dynamic value that is adjusted every 2,016 blocks (roughly every two weeks) to keep the average Bitcoin block time at around 10 minutes.
Block and chain is the infrastructure of Bitcoin, PoW is the consensus mechanism of Bitcoin, and the combination of the two realizes the decentralized accounting function of Bitcoin. But from the nature of the blockchain, as long as decentralized bookkeeping can be achieved, the bookkeeping can be non-block (such as single-transaction consensus), and the ledger can also be non-chain structure (such as DAG). Therefore, block and chain are not necessary, but the three words blockchain have become deeply rooted in people's hearts, and have become a proxy for the decentralized ledger represented by Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana.
After all, Bitcoin was already a product in 2009. With the continuous development of blockchain research, although most blockchains still follow the traditional block + chain structure, there are also some first-principle-designed blockchains, which start from the most fundamental decentralized accounting problem and have unique data structures and consensus. This article takes Sui and Arweave AO as examples.
Sui: The Way of water

Sui is Layer1, redesigned and built from first principles, with the main team coming from Facebook's (later renamed Meta) defunct Diem and Novi projects. The name Sui derives from the Japanese word for water, and the influence of water can also be seen in its brand image.
Sui uses Sui Move to write its smart contracts, adopting an object-based data model where all transactions take objects as inputs and produce new or modified objects as outputs, allowing independent objects to process transactions in parallel.
In Sui Move, each smart contract is a module, consisting of functions and structural definitions. Structures are instantiated in functions and can be passed to other modules through function calls. Structure instances stored at run time are taken as objects. There are three different types of objects in Sui, namely owner object, shared object and unchangeable object.
Sui does not have blocks, transactions are verified individually, and whether a transaction goes through Sui's sorting and consensus mechanisms depends on whether the objects in the transaction are shared or unshared.
If a transaction does not involve a shared object, called a simple transaction, Sui uses a lightweight algorithm called Byzantine Consistent Broadcast, which references the design ideas of FastPay. The client broadcasts the transaction to all verifiers of Sui, collects the equity-weighted votes of the verifiers, generates a certificate, broadcasts the certificate back to the verifier, and the verifier that receives the certificate can directly execute the transaction.
For transactions involving shared objects, called complex transactions, Sui uses the Narwhal & Bullshark consensus mechanism. Narwhal is a mempool module that is responsible for ensuring the availability of transactions. Narwhal operates based on rounds, each round is divided into two steps, namely transaction distribution (synchronization of transactions to other nodes) and transaction verification (collection of votes of other nodes on transactions), after several rounds, transactions form a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bullshark is a consensus module that is responsible for sorting the transactions of DAGs in Narwhal.
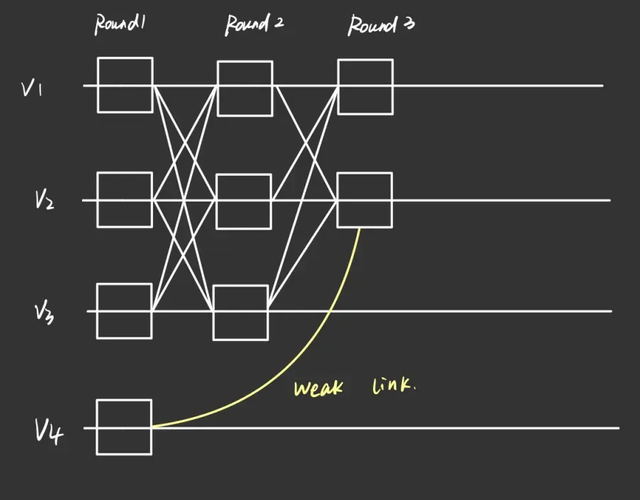
Sui leverages DAG for transaction propagation and consensus, reducing transaction latency and network overhead during communication. At the same time, in order to maintain the integrity and order of historical information, Sui sorts transactions into checkpoints in a separate process, which are linked to each other in a linear manner, providing a structure similar to traditional blockchains for storing and accessing historical data.
In fact, the data structure of Sui is completely different from that of traditional blockchains, in that the transactions that Sui groups into checkpoints have been finalized, while traditional blockchains group transactions that have not been finalized into blocks.
Arweave AO: The Way of Emptiness
Water is impermanent, but it is tangible. Sui also retained the consensus mechanism in the traditional blockchain, and eventually organized the transaction data into the block + chain structure of the traditional blockchain. AO completely subverts the traditional blockchain paradigm, no block, no chain, no consensus, compared to water, AO is symbolically closer to the sky (Sora in Japanese).
AO is a distributed, decentralized, actor-oriented computing system based on Arweave. The first principle is not to build a decentralized ledger, but to build a decentralized computing system. Similar to the relationship between an application and an operating system.
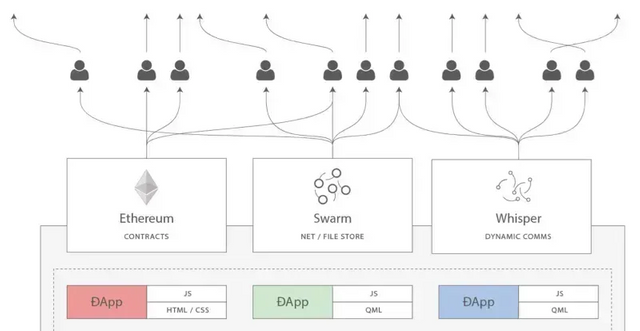
Computing system can be divided into storage, computing and communication three problems, in Web2 have a very mature solution, the difficult is decentralization. One idea is to build a decentralized storage network, a decentralized computing network, and a decentralized communication network, which is actually the idea of the decentralized technology architecture of computing, storage and communication proposed by Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum in 2014. Ethereum (smart contract) is responsible for the decentralized computing part, Swarm is responsible for the decentralized storage part, and Whisper is responsible for the decentralized communication part
.

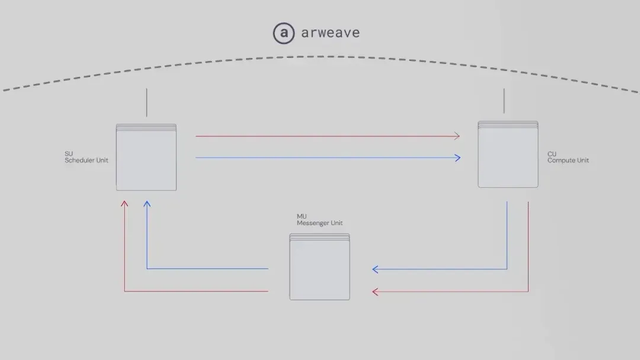
Messenger Unit: Responsible for message communication, passing messages to the computing unit and coordinating to calculate the output;
Scheduler Unit: Responsible for scheduling and sorting messages, and uploading messages to Arweave;
Compute Unit: Responsible for processing calculations and uploading the results to Arweave.
A Process on an AO consists of a set of cells, each of which can be used as a horizontally scalable subnet to execute a large number of transactions simultaneously, enabling high performance computing, but each cell is not a decentralized network. In fact, in the entire AO architecture, the only real decentralization is Arweave, which serves as the underlying storage network.
Processes on AO have verifiable properties by uploading their holographic data to Arweave - because anyone can restore the process on AO using holographic data. This is actually a storage consensus paradigm (SCP), which states that as long as the storage is immutable, the transactions above are traceable, and the same result will be obtained no matter where the application is computed.
AO has no consensus mechanism, but with SCP, the computing layer is separated from the storage layer, making the storage layer permanently decentralized, while the computing layer maintains the pattern of the traditional computing layer. As a result, there are no type limitations to compute scalability on AO, not only can blockchain ledger services with EVM, WASM, or Move virtual machines at their core be implemented, but even any existing Web2 service can be rebuilt as a decentralized version on AO.
Sum up
The first principle is to think about the essence of things from the point of view of physics, and then start from the essence, and design layer by layer. Although Sui and Arweave AO are both blockchains designed based on first principles, due to their different nature, they have designed completely different architectures.
The essence of Sui is a decentralized ledger service, the target of which is a high-performance Layer1 like Solana, so Sui designed an object-oriented data model around a "faster ledger service", a dual consensus mechanism, and parallel execution of transactions based on state access to improve scalability while reducing latency and expense. Enables developers to quickly and inexpensively develop applications based on Sui Move smart contracts.
The essence of Arweave AO is a decentralized computing system, or decentralized cloud service, which is the infrastructure that runs ledger services, so AO proposes SCP around a "verifiable distributed computing system" that computes off-chain, puts storage on chain, and enables the interconnection and collaboration of massively parallel computers. The user experience is almost identical to traditional cloud services, but behind it is a decentralized computing system.