Watch liftoff live on NASA Television -
https://www.nasa.gov/nasalive
Launch Coverage starts 25.1 at 5 p.m. EST
(2 p.m. PST, 7 p.m. Kourou local time and
The boundary where Earth’s atmosphere gives way to outer space is a complex place: Atmospheric waves driven by weather on Earth compete with electric and magnetic fields that push charged particles, all while our signals and satellites whiz by.

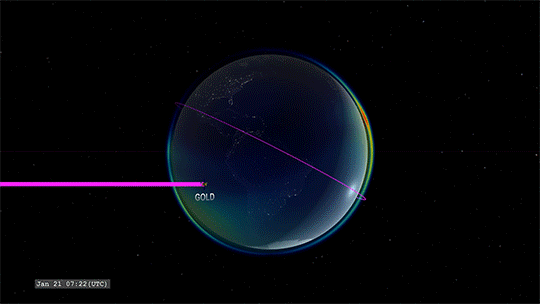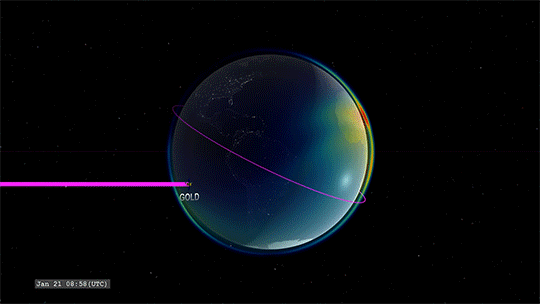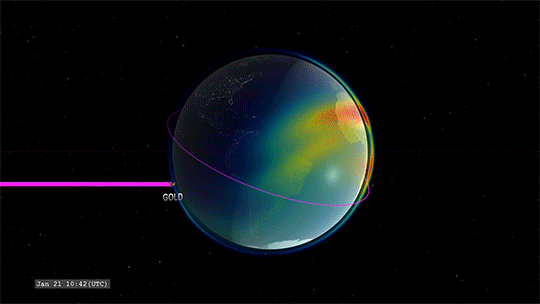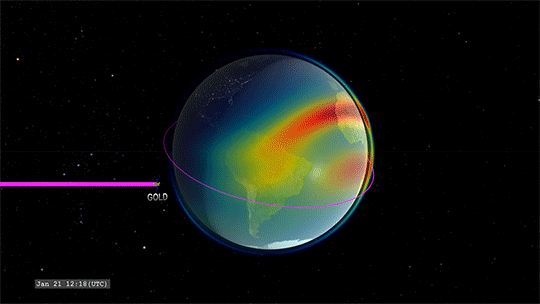
On Jan. 25, we’re launching the GOLD instrument (short for Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk) to get an exciting new birds-eye view of this region, Earth’s interface to space.
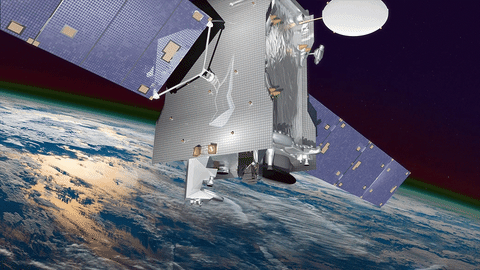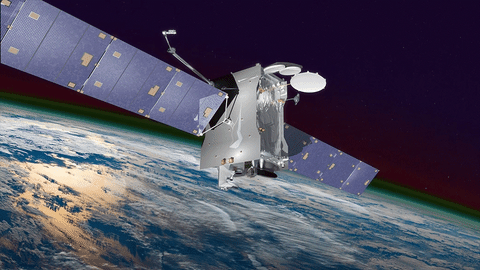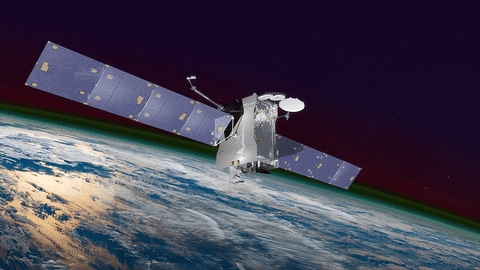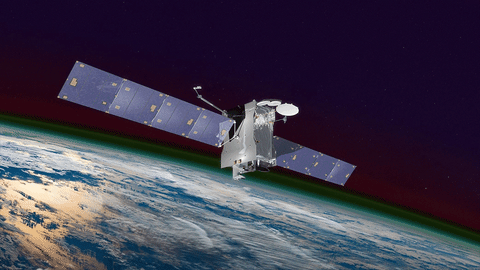
High above the ozone layer, the Sun’s intense radiation cooks some of the particles in the upper atmosphere into an electrically charged soup, where negatively charged electrons and positively charged ions flow freely. This is the ionosphere. The ionosphere is co-mingled with the highest reaches of our planet’s neutral upper atmosphere, called the thermosphere.
Spanning from just a few dozen to several hundred miles above Earth’s surface, the ionosphere is increasingly part of the human domain. Not only do our satellites, including the International Space Station, fly through this region, but so do the signals that are part of our communications and navigation systems, including GPS. Changes in this region can interfere with satellites and signals alike.

Conditions in the upper atmosphere are difficult to predict, though. Intense weather, like hurricanes, can cause atmospheric waves to propagate all the way up to this region, creating winds that change its very makeup.
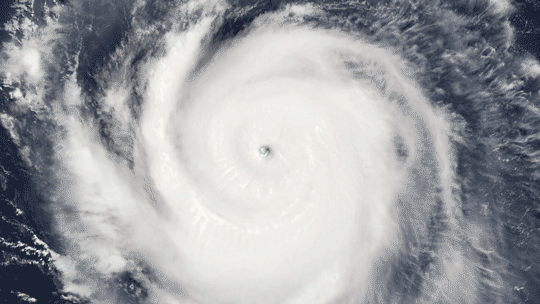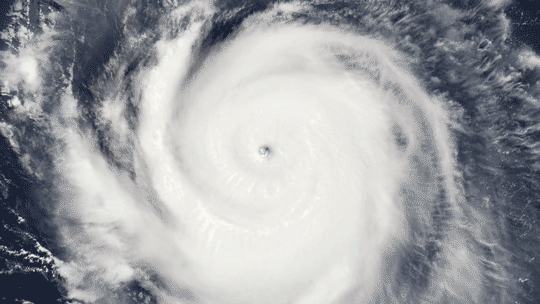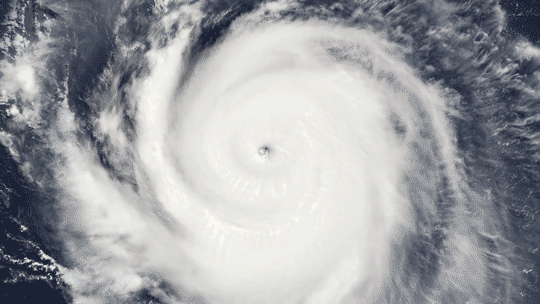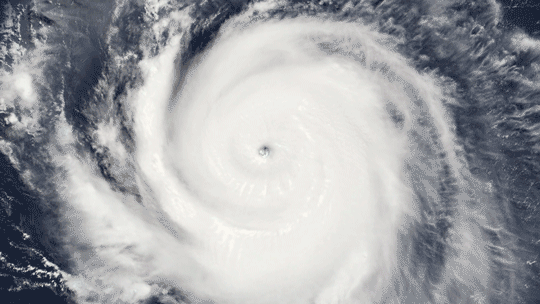
Because it’s made up of electrically charged particles, the upper atmosphere also responds to space weather. Space weather – which is usually driven by activity on the Sun – often results in electric and magnetic fields that push and pull on the ionosphere’s charged particles, changing the region’s makeup. On top of that, space weather can also mean incoming showers of high-energy particles that can affect satellites or endanger astronauts, and, in extreme cases, even cause power outages on Earth.
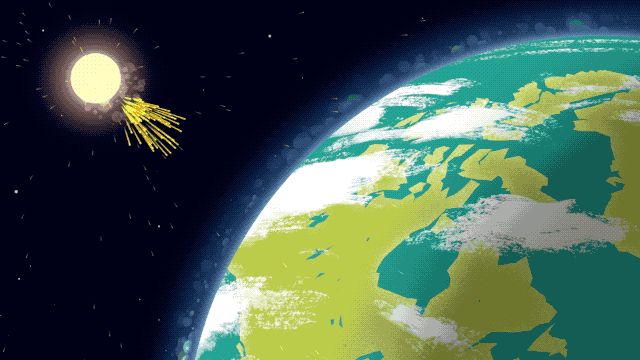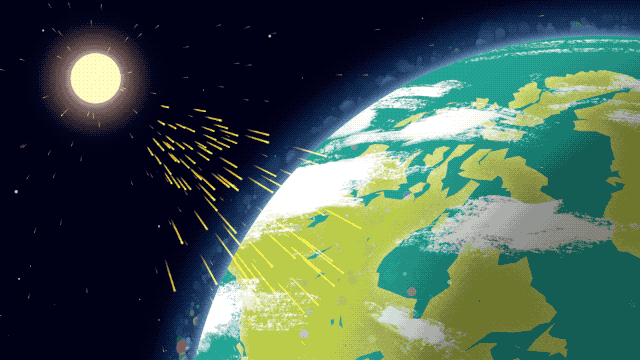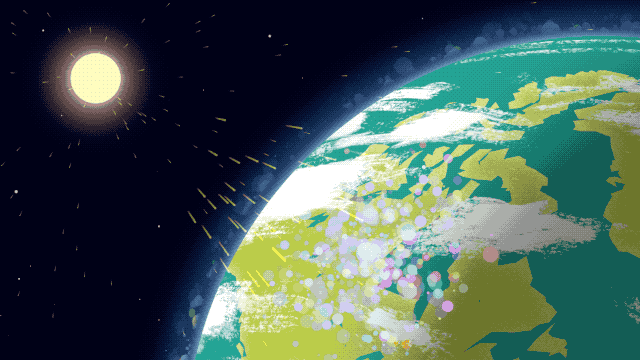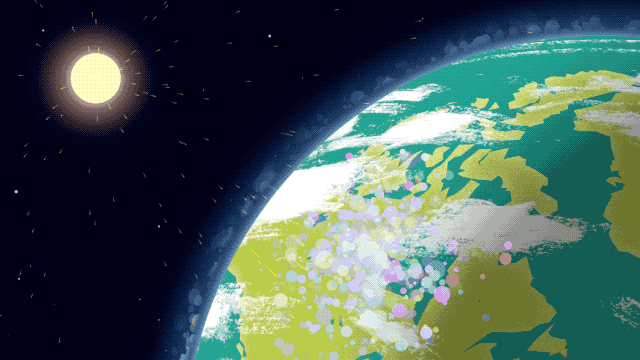
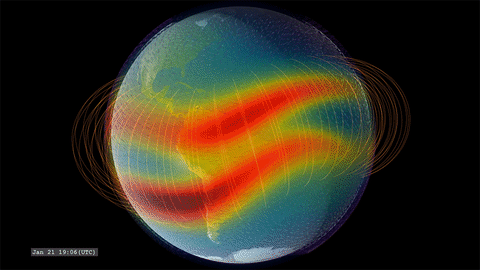
That’s where GOLD comes in. GOLD takes advantage of its host satellite’s geostationary orbit over the Western Hemisphere to maintain a constant view of the upper atmosphere, day and night. By scanning across, GOLD builds up a complete picture of Earth’s disk every half hour.
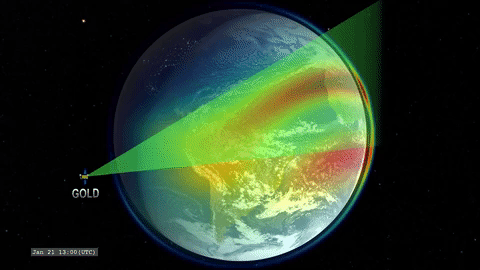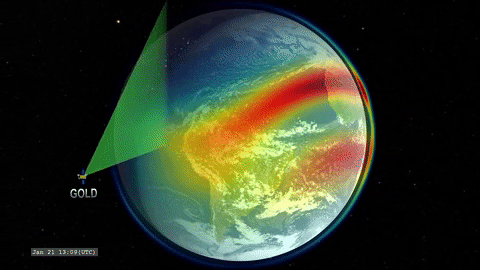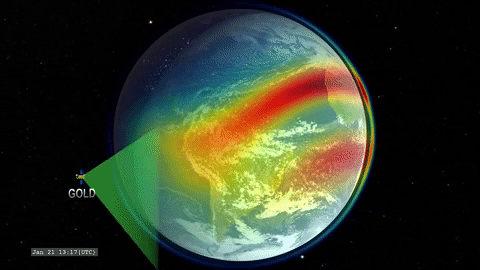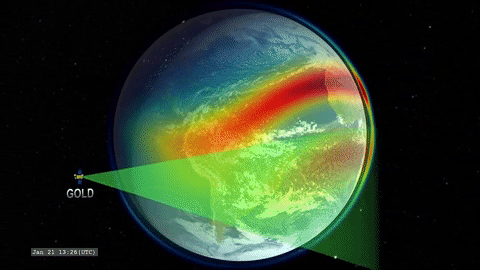
GOLD is an imaging spectrograph, a type of instrument that breaks light down into its component wavelengths. Studying light in this way lets scientists track the movement and temperatures of different chemical species and build up a picture of how the upper atmosphere changes over time. Capturing these measurements several times a day means that, for the first time, scientists will be able to record the short-term changes in the region – our first look at its day-to-day ‘weather.’
GOLD is our first-ever mission to fly as a hosted payload on a commercial satellite. A hosted payload flies aboard an otherwise unrelated satellite, hitching a ride to space. GOLD studies the upper atmosphere, while its host satellite supports commercial communications.
Later this year, we’re launching another mission to study the ionosphere: ICON, short for Ionospheric Connection Explorer. Like GOLD, ICON studies Earth’s interface to space, but with a few important distinctions. ICON employs a suite of different instruments to study the ionosphere both remotely and in situ. The direct in situ measurements are possible because ICON flies in low-Earth orbit, giving us a detailed view to complement GOLD’s global perspective of the regions that both missions study.
Damn i made a mistake. its not starting now but 25.1 5pm est.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit