Mutualism
Mutualism is a biological interaction between individuals of different species, where both benefit and improve their biological aptitude. Similar actions that occur between members of the same species are called cooperation.
Mutualisms can be:
Temporary or optional (not essential): both species benefit from each other, but can survive separately.
Permanent or obligated (dependent): in this case one of the parties (or both) is strictly dependent on the other. In this type of interaction, the organism or organisms cannot survive without the presence of their symbiotic companion.
The ant and the aphid
A clear example of mutualism is the relationship that some types of ants have forged with aphids. The latter secrete a dense liquid rich in carbohydrates called molasses. Ants feed on this liquid so they literally graze aphid colonies protecting them from possible predators and allowing aphids to procreate in a safer environment.

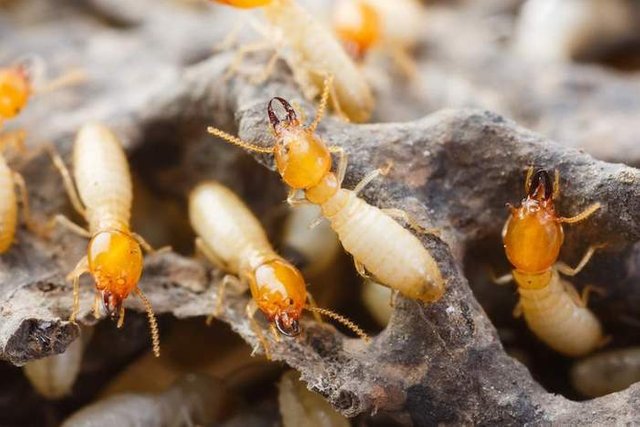
Termites, Protozoa, and Bacteria
Termites feed on wood and other organic substances but their bodies are not prepared to digest them. They need the indispensable help of another species: protozoa. These unicellular organisms inhabit the stomachs of termites and are responsible for digesting wood cellulose, feeding on it in turn. The protozoa, in turn, have bacteria that transform the remains they leave into nitrogen that the termites absorb. In addition, new termites collect protozoa and bacteria by ingesting waste from other termites. This is a three-part relationship where no part could survive without the others.

Lazy, Algae and Moths
Sloths are extremely slow animals. The time when they are most vulnerable is when they go ashore once a week to defecate. Why they do this has an explanation: On their bodies inhabits a type of moth that takes advantage of the trip to earth to lay their eggs in the excrement of the sloths. Once they hatch, the new moths fly to the treetops and move to the fur of these animals. There, they produce a type of fertilizer that boosts nitrogen levels, causing algae and fungi to grow on their fur. The skin of the sloth contains cracks that favor the accumulation of water and helps to grow the algae of which they need to complete their diet low in energy.

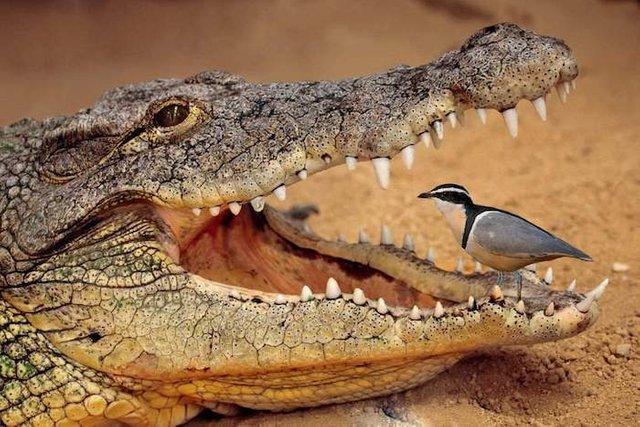
The crocodile and the pluvial (Egyptian plover)
Another clear example of mutualism is the relationship between these two species. Crocodiles have 80 teeth in their jaws that change continuously and replace 2 or 3 times a year. The remains of food between them can cause infections and problems to these animals, which have the strongest bite in the animal kingdom, as well as fast; so they allow the plovers to walk through their mouths feeding on the remains of food between their teeth, and thus both get what they need.

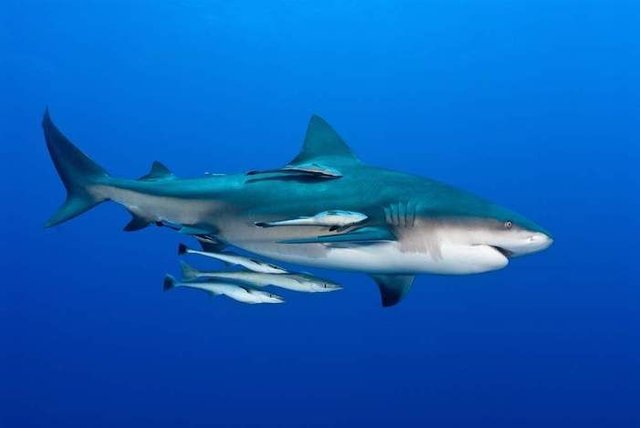
Shark and Remora
A clear case of commensalism is that of the shark and the hawk. This has developed, in the place where the first dorsal fin is placed, a powerful suction cup with which it adheres to the body of the sharks, providing food remains and protection. The advantages of the shark in this relationship are almost indifferent (elimination of certain parasites in its body) in relation to the benefit obtained by the remora.

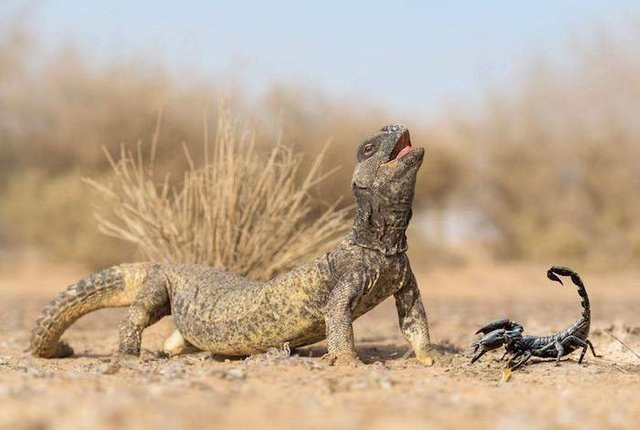
Thorny-tailed lizard and coarse-tailed scorpion
These desert lizards are very jealous of their burrows. They are cool places in the shade often attacked by foxes or other predators. Thick-tailed scorpions like to be in the shade and offer protection from these predators in exchange for being able to live in the same burrow. It is another clear case of mutualism that has led both species to gain a vital advantage for their survival.

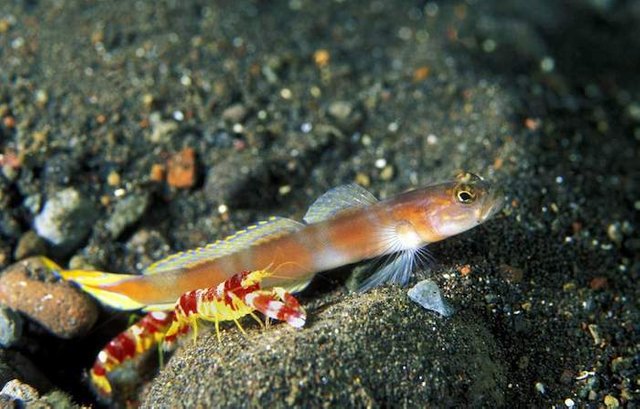
The gorgeous fish and the blind shrimp
The gorgeous fish is an animal with excellent vision. The shrimp, as its name indicates, can barely see. She builds burrows that she always keeps clean and ready and shares with the fish to be both safe. In return, the goby fish always stays with her, alerting her with vibrations when there is the danger that they might hide.

The narrow-mouthed frog and Tarantula
Tarantulas usually hunt small toads, but in the case of the narrow-mouthed frog, there is an exception. These small amphibians keep tarantula eggs free of pests and insects in exchange for protection and shelter. Lucille often hunt narrow-mouthed frog, but with a large tarantula on the side, they will think twice before attacking.

Thank you for reading 😊

If you liked reading this article, feel free to FOLLOW ME, UPVOTE and RESTEEM! It's always appreciated =D. Thank you all for your support and see you soon for the news flamingirl's adventures!


Hi, @flamingirl!
You just got a 0.2% upvote from SteemPlus!
To get higher upvotes, earn more SteemPlus Points (SPP). On your Steemit wallet, check your SPP balance and click on "How to earn SPP?" to find out all the ways to earn.
If you're not using SteemPlus yet, please check our last posts in here to see the many ways in which SteemPlus can improve your Steem experience on Steemit and Busy.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @flamingirl! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
i love nature.. and you explain it beautifully in your post...
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Thank you so much for your nice comment my Steemian friend! =)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit