
Intelink
Intelink is a group of secure intranets used by the United States Intelligence Community. The first Intelink network was established in 1994 to take advantage of Internet technologies (though not connected to the public Internet) and services to promote intelligence dissemination and business workflow. Since then it has become an essential capability for the US intelligence community and its partners to share information, collaborate across agencies, and conduct business. Intelink refers to the web environment on protected top secret, secret, and unclassified networks. One of the key features of Intelink is Intellipedia, an online system for collaborative data sharing based on MediaWiki. Intelink uses WordPress as the basis of its blogging service.

Classified Computer Network
A classified (computer) network is one that stores information that is sensitive and should not be made
available to the general public. The purpose of this document is to point out some common elements from the
guidelines published to regulate computer security and suggest administrative action and technical solutions
to build a network that may be connected to the Internet, and still obtain/retain a classification up to and
including NATO RESTRICTED.

Tailored Access Operations
The Office of Tailored Access Operations (TAO) is a cyber-warfare intelligence-gathering unit of the National Security Agency (NSA). It has been active since at least circa 1998. TAO identifies, monitors, infiltrates, and gathers intelligence on computer systems being used by entities foreign to the United States. TAO is reportedly "now the largest and arguably the most important component of the NSA's huge Signals Intelligence Directorate (SID) (SIGINT), consisting of more than 1,000 military and civilian computer hackers, intelligence analysts, targeting specialists, computer hardware and software designers, and electrical engineers". A document leaked by former NSA contractor Edward Snowden describing the unit's work says[not in citation given] TAO has software templates allowing it to break into commonly used hardware, including "routers, switches, and firewalls from multiple product vendor lines". According to The Washington Post, TAO engineers prefer to tap networks rather than isolated computers, because there are typically many devices on a single network. The unit is now called Computer Network Operations.

Computer Network Operations
(CNO) is a broad term that has both military and civilian application. Conventional wisdom is that information is power, and more and more of the information necessary to make decisions is digitized and conveyed over an ever-expanding network of computers and other electronic devices. Computer network operations are deliberate actions taken to leverage and optimize these networks to improve human endeavor and enterprise or, in warfare, to gain information superiority and deny the enemy this enabling capability.
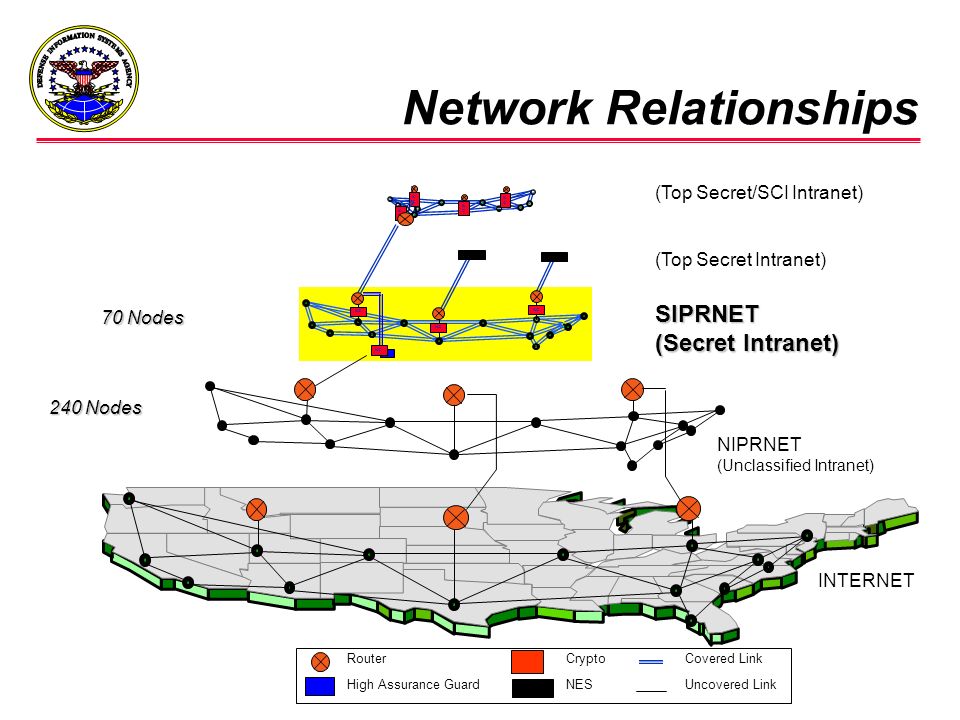
SIPRNet
The Secret Internet Protocol Router Network (SIPRNet) is "a system of interconnected computer networks used by the U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Department of State to transmit classified information (up to and including information classified SECRET) by packet switching over the 'completely secure' environment". It also provides services such as hypertext document access and electronic mail. As such, SIPRNet is the DoD's classified version of the civilian Internet. SIPRNet is the SECRET component of the Defense Information Systems Network.[1] Other components handle communications with other security needs, such as the NIPRNet, which is used for nonsecure communications, and the Joint Worldwide Intelligence Communications System (JWICS) which is used for Top Secret communications.It was one of the networks accessed by Chelsea Manning, convicted of leaking the video used in WikiLeaks' "Collateral Murder" release as well as the source of the US diplomatic cables published by WikiLeaks in November 2010.
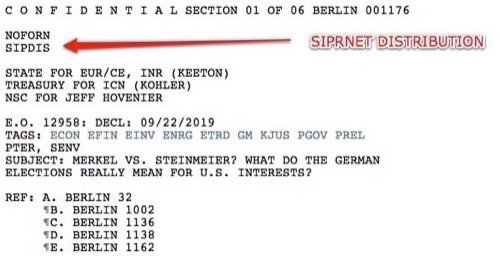
Sipdis
Sipdis" which appears on the string of address codes heading each cable published by WikiLeaks in November 2010.
NIPRNet
The Non-classified Internet Protocol (IP) Router Network (NIPRNet) is a private IP network used to exchange unclassified information, including information subject to controls on distribution, among the private network's users. The NIPRNet also provides its users access to the Internet.NIPRNet is composed of Internet Protocol routers owned by the United States Department of Defense (DOD). It was created in the 1980s and managed by the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) to supersede the earlier MILNET.
Over the last decades, NIPRNet has grown faster than the U.S. Department of Defense can monitor. DoD spent $10 million in 2010 to map out the current state of the NIPRNet, in an effort to analyze its expansion, and identify unauthorized users, who are suspected to have quietly joined the network. The NIPRNet survey, which uses IPSonar software developed by Lumeta Corporation, also looked for weakness in security caused by network configuration. The Department of Defense has made a major effort over the last few years,[when?] to improve network security.[5] The Pentagon announced it was requesting $2.3 billion in the 2012 budget to bolster network security within the Defense Department and to strengthen ties with its counterparts at the Department of Homeland Security. SIPRNet and NIPRNet are referred to colloquially as sipper-net and nipper-net (or simply sipper and nipper), respectively.
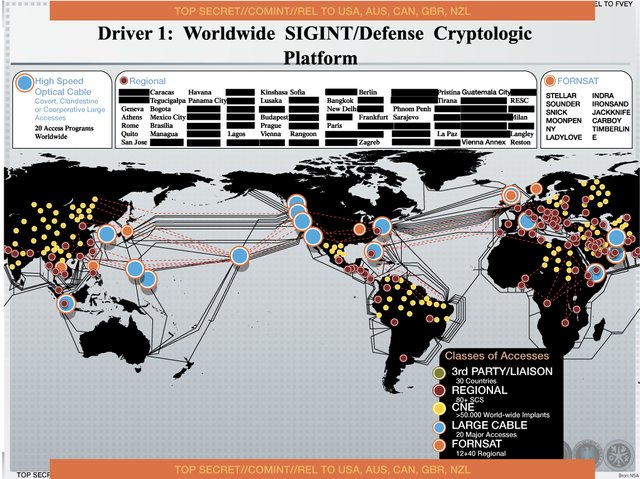
SIGINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is intelligence-gathering by interception of signals, whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly used in communication (electronic intelligence—abbreviated to ELINT). SIGINT provides a vital window for our nation into foreign adversaries' capabilities, actions, and intentions.

OPSEC
Operations security (OPSEC) is a process that identifies critical information to determine if friendly actions can be observed by enemy intelligence, determines if information obtained by adversaries could be interpreted to be useful to them, and then executes selected measures that eliminate or reduce adversary exploitation of friendly critical information. The term "operations security" was coined by the United States military during the Vietnam War.
FBCB2 (Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below)
Force XXI Battle Command Brigade and Below (FBCB2) is a Linux-based communication platform designed for commanders to track friendly and hostile forces on the battlefield. It increases a vehicle commander's situational awareness of the battlefield by gathering information near real-time based on vehicle locations being updated on the battlefield. This information is viewed graphically, and exchanged via both free and fixed text message formats (instead of verbal collection of reports).The location data for friendly forces is collected through the Enhanced Position Location Reporting System (EPLRS) line of sight tactical radio network and Blue Force Tracking (BFT) satellite network.
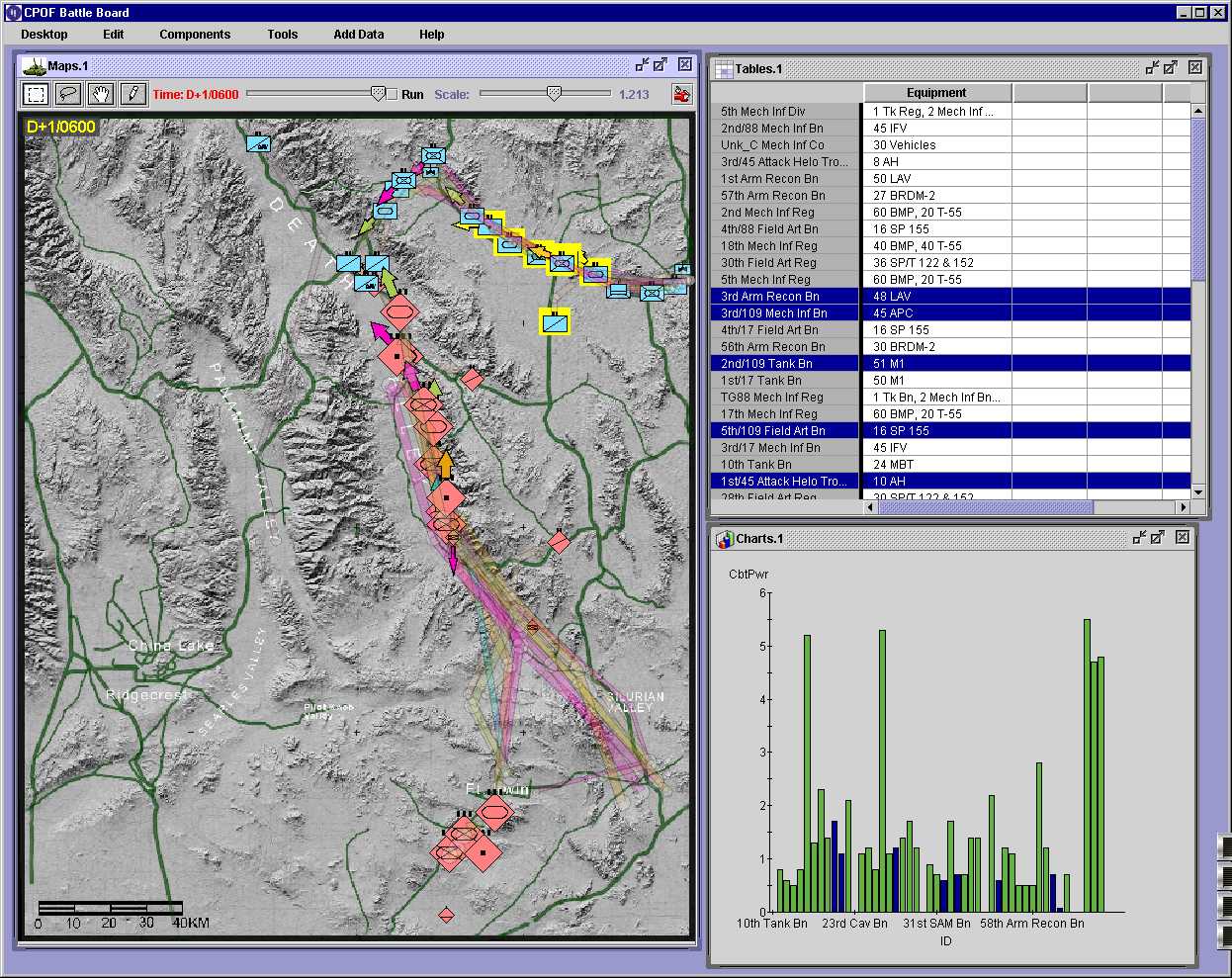
CPOF (Command Post of the Future)
The United States Army's Command Post of the Future (CPOF) is a C2 software system that allows commanders to maintain topsight over the battlefield; collaborate with superiors, peers and subordinates over live data; and communicate their intent. Originally a DARPA technology demonstration, in 2006 CPOF became an Army Program of Record. It is managed by the Product Manager Tactical Mission Command at Aberdeen Proving Ground, Maryland, and integrated with the Army's Maneuver Control System and other products. The prime contractor on the CPOF program is General Dynamics C4 Systems, which purchased the original developer of the software (MAYA Viz Ltd) in 2005.

TF ODIN (Task Force Observe, Detect, Identify, andNeutralize)
Task Force ODIN, whose name is an acronym for observe, detect, identify, and neutralize, is a United States Army aviation battalion created in August 2006 to conduct reconnaissance, surveillance and target acquisition (RSTA) operations to combat insurgent operators of improvised explosive devices in Iraq. The unit was formed at Fort Hood, Texas, and first deployed in October 2006. An Army article says the unit is meant to meet "the critical requirement to 'win back the roads' using Army Aviation assets to maintain a persistent stare over demonstrated at-risk areas for IEDs." The United States Army stood up TF ODIN as a Quick Reaction Capabilities project whose efficacy proved so effective it shaped the Secretary of Defense Directive to establish the Air Force Project Liberty and other ISR related missions. ODIN is the Army's only unit that flies the MQ-1B Warrior-Alpha unmanned aerial vehicle. Built by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, the extended-range multi-purpose hybrid UAV has an advanced sensor package incorporating electro-optical sensors, including FLIR, and synthetic aperture radar together with a laser rangefinder and a laser designator, the latter for "painting" targets for strikes with Hellfire missiles and laser-guided bombs. By September 2007, the Warrior-Alpha had flown more than 6,000 hours and had contributed to the killing of 3,000 insurgents in Iraq. The task force trains operators for active, reserve, and Army National Guard. These analysts work with every type of unit including the military's top secret units.
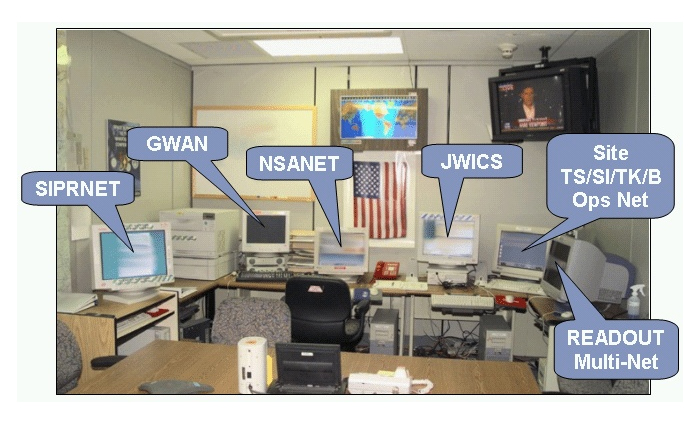

RIPR
The RIPRNet (Releasable Internet Protocol Router Network) is a TCP/IP based computer network for joint ROK-US access, analogous to the SIPRNet. Whereas SIPRNet is the de facto SECRET-level TCP/IP network for general use, RIPR is for information classified as Releasable to the Republic of Korea and US Secret. In other words, RIPR is a secure coalition network for joint ROK-US usage. Like SIPR and NIPR, it is commonly pronounced "ripper".

CRONOS
Crisis Response Operations in NATO Operating Systems (CRONOS) is a system of interconnected computer networks used by NATO to transmit classified information. It provides NATO Secret level operations, with access to NATO intelligence applications and databases. As of 1999, a wide area network of NT computers used in NATO in Europe. CRONOS provides e-mail, the Microsoft Office Suite, etc. It provides informal messaging (e-mail) and information sharing within the NATO community. There is no connectivity between CRONOS and any US network or with the coalition wide area network.
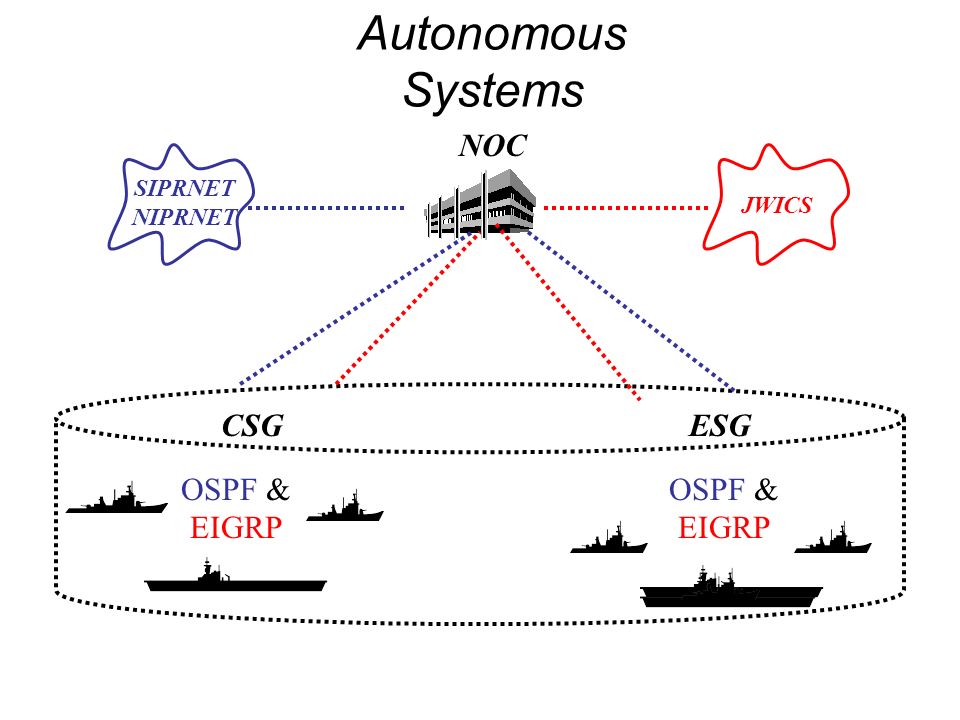
JWICS
The Joint Worldwide Intelligence Communications System (JWICS), pronounced JAYwicks), is a Top Secret/SCI network run by the United States' Defense Intelligence Agency and used across the Department of Defense, Department of State, Department of Homeland Security and Department of Justice to transmit especially sensitive classified information.
In other words, JWICS is DoD's Top Secret intranet together with its Secret counterpart, SIPRNet. JWICS superseded the earlier DSNET2 and DSNET3, the Top Secret and SCI levels of the Defense Data Network based on ARPANET technology.

Turbo10
Use Turbo 10 to search the Deep Net. Deep Net refers to the thousands of topic–specific search engines on the Internet, including those that are inaccessible to traditional crawler–based search engines like Google or Yahoo.
Turbo 10 is a metasearch engine that provides a universal interface to these Deep Net engines. Turbo 10 also pulls out information from database sources that are not web–based (e.g., peer to peer networks). The service offered by Turbo 10 is free and you can:
Find more quality information from specialist, topic–specific engines.
Directly access online government, business and university databases.
Search these databases in real–time, the moment you enter a search.
Save time, you can search up to 10 Deep Net engines simultaneously.
Turbo 10 also lets you add more engines to the collection on which your search query is executed.
I came back with this to share what I know.
Hope you all enjoyed reading!
X0A0