"In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat.[1] An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking or over-specification voids any warranty, however there are an increasing number of manufacturers that will allow overclocking as long as performed (relatively) safely."
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overclocking
"Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about −195.8 °C (−320 °F; 77 K). It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is widely used as a coolant.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liquid_nitrogen
"The ROBOCLOCKER was designed by KINGPIN and Illya "TiN" Tsemenko, and adopts some ideas from the liquid (water) cooling realm for LN2 cooling. The cooling process is automated through a closed loop system and requires no human intervention for pouring the LN2; it is instead drawn from a primary tank. Software is used to keep both the CPU and GPU(s) cooled to the desired temperature while leaving the operator/overclocker free to focus on other activities. And since this is a closed loop solution, it "uses a lot less LN2" according to KINGPIN."
https://hothardware.com/news/evga-closed-loop-liquid-nitrogen-cooling-system
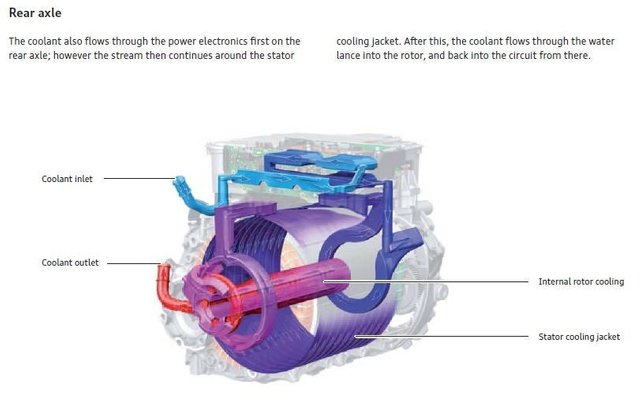
"Electric motors can generate considerable heat, thereby making motor cooling difficult, especially in the traction motor of a vehicle where size and weight constraints are coupled with the need for high output. Additionally, in order to avoid excessive wear due to differential thermal expansion, it is important to cool the internal motor components (e.g., rotor) as well as the outer motor components (e.g., casing, stator). Lastly, the means used to cool the motor must not be susceptible to large variations in the operating environment as such a motor can be expected to be subjected to a wide range of ambient temperatures, humidity levels and dust/dirt levels.
A number of different approaches have been taken to meeting the cooling demands placed on a vehicle's electric motor. For example, U.S. Pat. No. 6,191,511 discloses using a closed loop, liquid cooling circuit to try and achieve a temperature balance within the motor, the cooling circuit passing the coolant through both the stator and a hollow rotor shaft. Within the hollow rotor shaft is a stationary injection tube, the injection tube fixed to the stator flange. The coolant is pumped through the injection tube to the end of the rotor shaft where it is driven back between the injection tube and the hollow rotor. The coolant then passes through a cylindrical cooling chamber extending over the length and periphery of the stator before cooling the stator structure and being returned to the injection tube."
https://patents.google.com/patent/US7489057B2/en
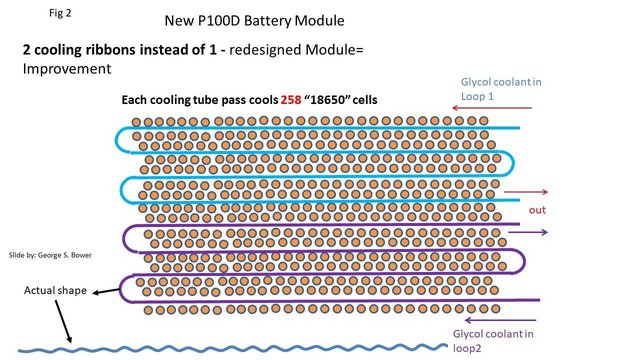
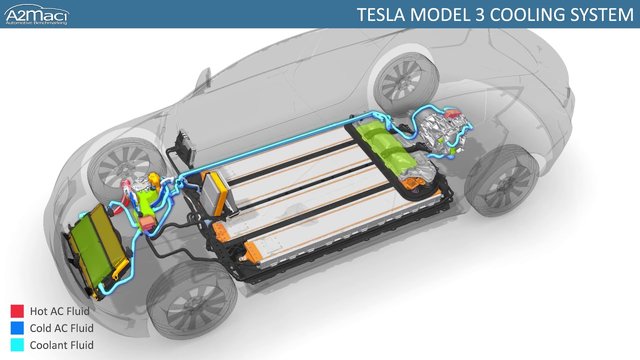
"Tesla's Liquid Cooling System Is State of The Art
The BMS Tesla patent has every battery cell against the coolant pipe. This provides better thermal management because the pipes snake around the cells to provide more area for the heat to transfer."
https://electrictransportab.com/qa/are-tesla-motors-liquid-cooled.html
Tesla Motor the Secret of high Efficiency
"Batteries are the most important element in electric vehicles. Tesla cars have long-range partially thanks to their superior battery cooling system."
https://aircondlounge.com/how-tesla-battery-cooling-system-works/