Cyclotron-
Q ) What is a Cyclotron and its derivation] with principle,working construction,Uses and its Limitations ?
Principle-
A charged particle accelerates to very high speed when kept in a the moderate electric field and in uniform,perpendicular magnetic field.
The frequency of revolution open charged particle a magnetic field is independent of speed and radius of the Earth .
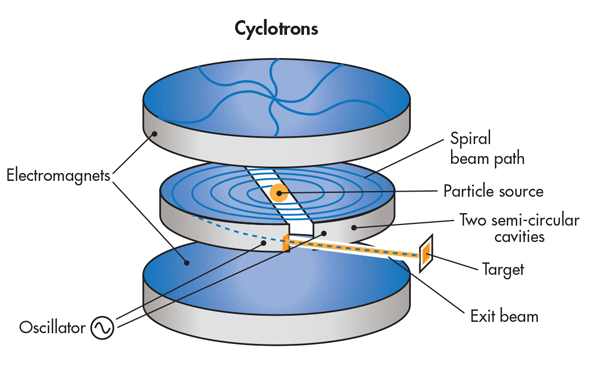
Construction :-
It consists of 2- D shapes dees made up of metals arrange parallel and enclosed under a steel chamber.
To electromagnet with opposite polarity North and South are applied perpendicular to the dees and does are connected to a high frequency oscillator.
Working :-
I. Suppose a positive iron presence in the gap between hollow metallic d's D1 and D2 at the point P.
II. Supposed even is negative then the positive Ion is accelerated towards D1 and with a velocity V.
III. On entering D1 it does not experience any electric field (due to shielding effect of metallic
dees) but follows a circular path due to perpendicular magnetic field.
IV. when it comes out of D1 it finds D2 nagative due to polarity change caused by HF
oscillator,hence It is now accelerated towards D2 .
V. The electric field polarity gets reverse every time it reaches the gap and hence it gets
accelerated.
VI. The particle follows a spiral path and when the radius of regulation of the positive ion
becomes maximum it is ejected out through the window buy a defective electric field.
Theory :-
The regulation of the positive ion is balanced by the magnetic field therefore ;
Now,
Centripetal force, mv^2/r = Bqv
=> mv/r = Bq
=> V = Bqr/m
and , r = mv/Bq
Now, we find maximum kinetic energy :-
1) Maximum K.E. is :-
K.E. = 1/2 mv^2
K.E. = 1/2 m [Bqr/m]^2
K.E. = 1/2 B^2q^2r^2/m------------(2)
2) Frequency:-
Let "t" is the time taken to cover semicircle D1 or D2 then,
Total time (T) = 2t,
=> T = 2 * [Pie r/m] ------ (pie means mathematical symbol)
=> T = 2 Pie r/(Bqr/m)
=> T = 2 pie /[B(q/m)] = constant;
Frequency, (meu) = 1/T
= B(q/m)/2 pie
=> w = 2 pie meu ----- , where w= angular velocity;
=> w = qB/m
Note - " W " is also called magnetic resonance frequency.
# Magnetic resonance frequency is independent of the radius and velocity of the
# moving ion.
Uses :-
⦁ To bombard nuclei with energetic particles and study the resulting nuclear reaction.
⦁ The implants iron into solid and modify their party properties or even synthesis new materials.
⦁ In hospital to produce radioactive substance which can be used in diagnosis and treatment.
Limitations :-
⦁ The elementary particle such as electron requires unusually high frequencies (GHz).
⦁ Maintaining the uniformity of the magnetic field over the extended reason of the dees can also be a problem .