"C" is a general-purpose programming language that was developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs. It was designed to be a low-level language, allowing direct access to computer hardware while still providing the high-level programming constructs necessary for writing complex programs.
C has since become one of the most popular programming languages in the world, and is used in a wide range of applications, including operating systems, embedded systems, game development, and scientific computing.
One of the key features of C is its efficiency and speed, making it a popular choice for applications that require high-performance computing. It is also known for its simplicity and versatility, allowing programmers to write concise and elegant code that is easy to read and understand.
C has a rich library of functions and data types, and supports many programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. It is also a standardized language, with a well-defined syntax and semantics that allow code written in one implementation of C to run on any platform that supports the language.
Some of the most popular tools used for C programming include the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), the Clang compiler, and the Microsoft Visual C++ compiler. These tools provide developers with a comprehensive set of features for compiling, debugging, and optimizing C code, and are available on a wide range of platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS.
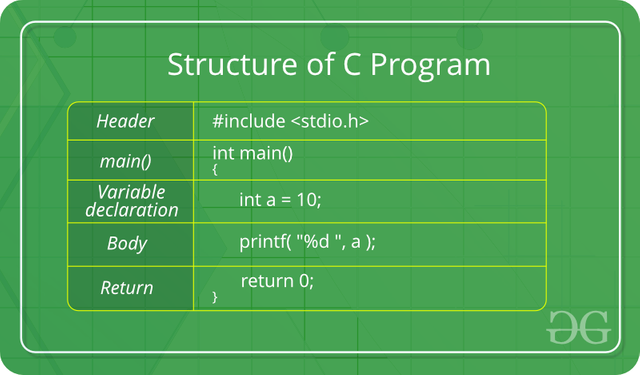
General Structure of "C"