Call it legitimate man-in-the-middle, or HTTPS inspection, Re-encryption become crucial in protecting mission critical infrastructures, especially in BYOD environment.
Until recently.
Starting with Android 7, a new policy has been applied allowing apps to ignore user installed root certificates and set their own rules “who to trust”. Shortly after, Firefox joined, blocking custom generated certificates even if trusted on the system level.
While this could make some sense from the point of securing the transmission from hackers, it obviously prevents Layer 7 inspection of SSL traffic - or if you like, forces administrators to switch off SSL re-encryption in order for tons of application to work. Surprising, social media apps was among first to embrace new rules, completely ignoring user level root certificates installed on Android starting version 7.

From the business point of view, if such inspection take place, preventing it, will likely result in ban of such app usage in corporate environment. Security is a lame excuse here, since root certificate deployment is impossible without setting the password, even enforcing it over the swap / pin unlock starting Android 4 making it very hard for hacker to deploy certificate without full device control in order to perform man in the middle.
At least, if full control over the device is already possessed, such attack does not makes much sense.
The whole initiative lead by Android and Mozilla makes not much rationale for improved security. If we can’t inspect the traffic in real time while ensuring all the application works, it gets difficult to protect from breaches.
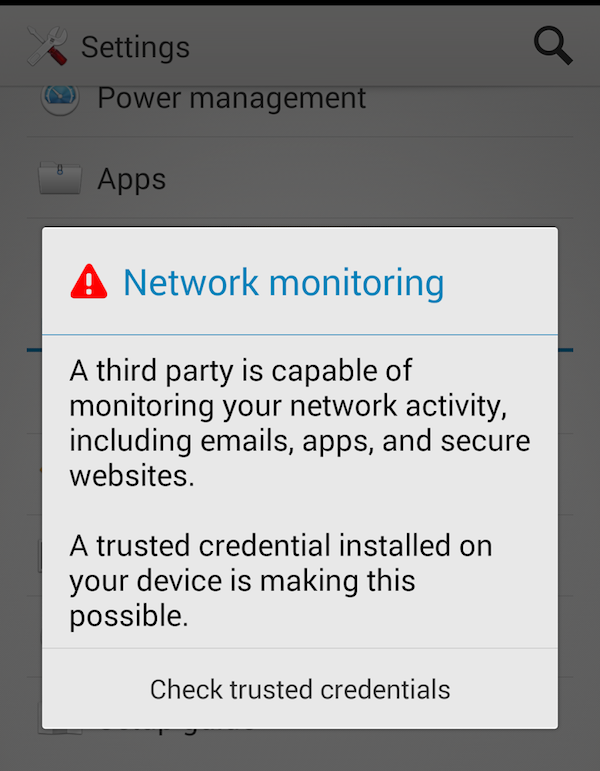
Currently, the only known solution requires Android rooting, installing the re-encryption certificates in kernel space rather then userspace.
openssl x509 -inform PEM -subject_hash_old -in newauthority.crt | head -1
Following by placement into /system/etc/security/cacerts/ using old naming convention.
Re-mounting the system partition is necessity. (root access therefore required)
How do you handle such scenarios in corporate BYOD environment?
Is it an attempt to push-away traditional bare-metal in-house equipment such as Cisco in further pushes to move towards a cloud solution such as GCP. What's your opinion.
Great post brah
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit