Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine. Depending on its location, it can affect the Cervical, Dorsal and Lumbar Spine, and because of its laterality, we can define it as right or left depending on the convexity of the curve.
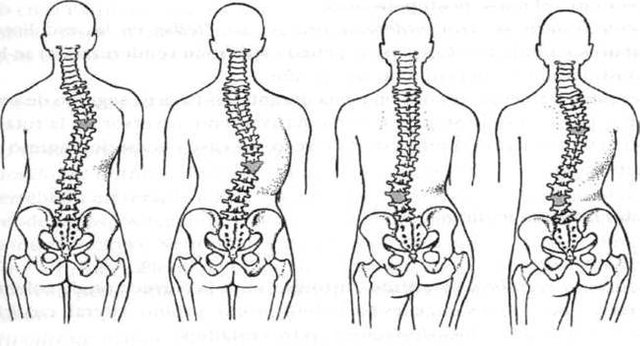
*The exact cause of this curvature is unknown but among the possible reasons we can find:
-Postural: when patients adopt different postures to the anatomy at bedtime, sitting and walking.
-Compensatory: difference in leg length.
-Antalgic: patients trying to relieve back pain with incorrect posture.
*Among the main types of Scoliosis we can find:
- Idiopathic scoliosis: of unknown cause. It is the most numerous type, since it groups 80% of the cases. The age of maximum incidence is between 10 and 14 years. It is more frequent in women (80%) than in men (20%). Its incidence is higher in the white race (6%) than in the black race (2%). It is classified in:
Infant: if diagnosed before 3 years of age
Juvenile: if the diagnosis in children between 4 and 10 years
Adolescent: if diagnosed in older than 10 years.
- Congenital scoliosis: secondary to malformations of the spine due to inadequate development of the vertebrae before birth.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis: associated with a wide variety of neurological or muscular diseases including cerebral palsy, myelomeningocele, spinal muscular atrophy, muscular dystrophies, etcetera.
- Scoliosis due to other causes: traumatisms, tumors, bone infections, neurofibromatosis, connective tissue diseases.
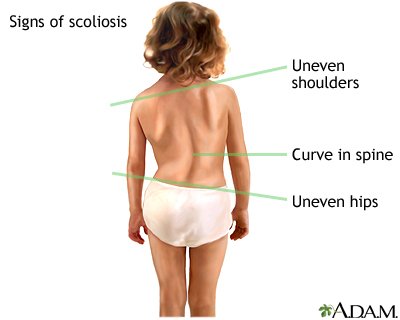
*In most cases there are no symptoms that help us "prevent" scoliosis but there are some, we could define them as:
- Back pain or low back pain that goes down to the legs
- Weakness or tired feeling in the spine after standing or sitting for a long time
- Shoulders or hips that look uneven (one shoulder may be higher than the other)
- Curvature of the column further to one side
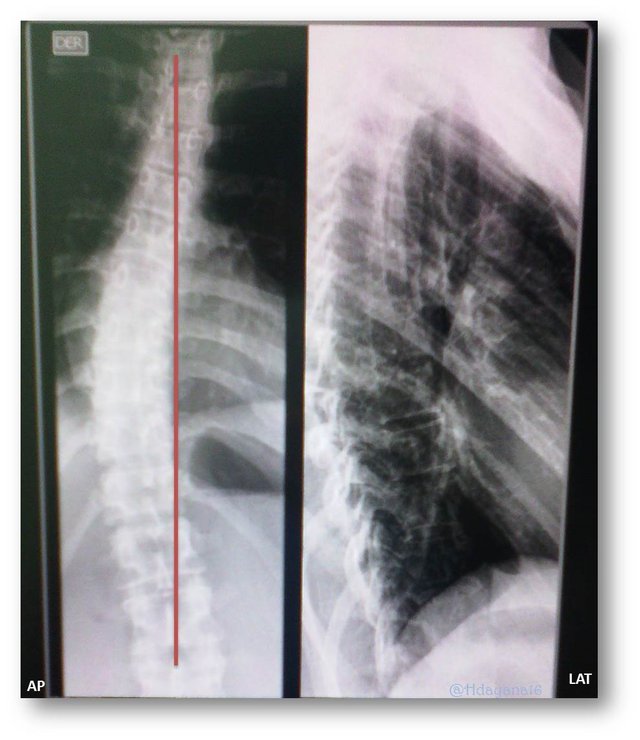
*How can a scoliosis be diagnosed?
with a column x-ray as you can see in the image where we find a Right, Mild Dorsal Scoliosis in a female patient of 24 years.
But you can also perform a physical assessment where the alignments of horses and hips are observed
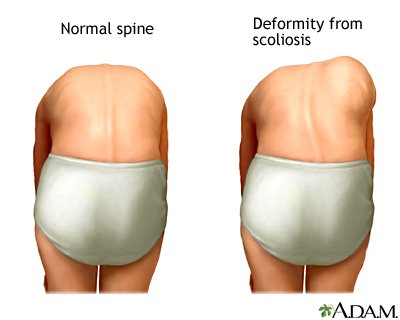
by magnetic resonance or by a CT scan to see the bone changes.