Friends of steemit, receive my greetings and at the same time wish the best of success to the community and #Steemstem as well as to all my readers.
To begin with the presentation of this clinical case it is important to know a little about the intestinal intussusception is the most common cause of intestinal obstruction in children between 3 months and 3 years of age. Intestinal intussusception occurs when part of the intestine folds like a telescope and one segment penetrates into another. It can occur in the colon, in the small intestine or between the small intestine and the colon. The result can be an obstruction in the small intestine or colon. This obstruction prevents the passage through the intestine of the foods that are being digested.
What is the cause of an intussusception?
The exact cause of the intussusception is not known. It can occur more frequently in people with relatives who also suffered an intussusception.
Although it is rare, there is a higher incidence of intussusception in children with the following characteristics:
• presenting tumors or abdominal or intestinal masses;
• who have appendicitis.
The symptoms:
The most common symptom of intussusception is a sudden loud crying caused by the onset of intermittent abdominal pain in a previously well-functioning child. However, each child may experience the symptoms differently. At first, pain may be confused with colic and may occur at frequent intervals. Babies and children may writhe, bring their knees to their chest, behave irritably and cry loudly. Your child can recover and even be playful between attacks of pain, or can become tired and weak from crying.
Intestinal intussusception can also produce vomiting, which usually begins as soon as the pain has begun.
Your child may defecate normally, but the following stools may look bloody. In addition, gelatinous stools or red mucus are usually seen with intussusception.
The symptoms of intussusception such as fever, lethargy, vomiting of bile, diarrhea, sweating, dehydration and bloating or abdominal bulk, may resemble other disorders or medical problems. Consult your child's doctor to obtain a diagnosis.
How is intussusception diagnosed?
The doctor will obtain the medical history and perform a physical examination of your child. Imaging studies may also be done to examine the abdominal organs, which may include the following:
• Abdominal x-ray. Diagnostic test that can reveal an intestinal obstruction.
• Ultrasound. It is an imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues and organs. The ultrasounds are used to see the functioning of the internal organs and to evaluate the blood flow through different vessels.
• Upper gastrointestinal series. Diagnostic test that examines the organs in the upper part of the digestive system: the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum (the first section of the small intestine). A fluid called barium is ingested (a liquid, metallic chemical substance with a consistency similar to the plaster used to coat the inside of the organs in order to appear on an x-ray). X-rays are taken to evaluate the organs of the digestive system.
• Barium enema (also called lower GI series). It is a procedure performed to examine the large intestine in order to detect abnormalities. Through an enema, a fluid called barium (a liquid, metallic, chemical substance similar in consistency to the plaster used to coat the inside of the organs so that they appear on an x-ray) is introduced through the rectum. An abdominal x-ray shows stenosis (narrowed areas), obstructions (blockages), and other problems. In some cases, the pressure exerted on the intestine while introducing the barium helps the intestine to unfold, which corrects the intussusception.
CLINIC HISTORY
PERSONAL DATA OF THE PATIENT
First and Last Name: F.A.C.C
Natural: Barinas - Venezuela
From: The Town
Service: Pediatric surgery
Age: 1 month and 17 days
Male gender
Updated Medical Diagnosis: intussusception due to plant poisoning
OBJECTIVE DATA
Heart rate: 145 ppm x'.
Breathing: 28 x'.
Temperature: 38.8 ° C
NURSING EVOLUTION
It is an infant younger than 1 and 17 days of age and from the locality which is brought by the mother to this center for presenting continuous crying, vomiting, irritation and fever, is assessed by pediatric surgery diagnosing an intussusception by intoxication by plantain (pasota), tenieOnce an X-ray and an abdominal echo, it is indicated preparation for surgical act. EFFECTIVE PHYSICAL ETHONOMY: active Respiratory: Symmetric Thorax normo expandable without aggregates Abdominal: Abdomen deprehensible, painful to palpation, Hydrous noises present diminished, absolute diet.Genitourinary: Genitals of appearance and normal configuration Tegumentary:. Moist, feverish brown skin. Musculoskeletal: Upper and lower symmetrical extremities with strength and normal muscle tone. Determined surgery surgery. Take a chiropractor for the intervention to resolve the bowel evagination without having to decrease part of the intestine
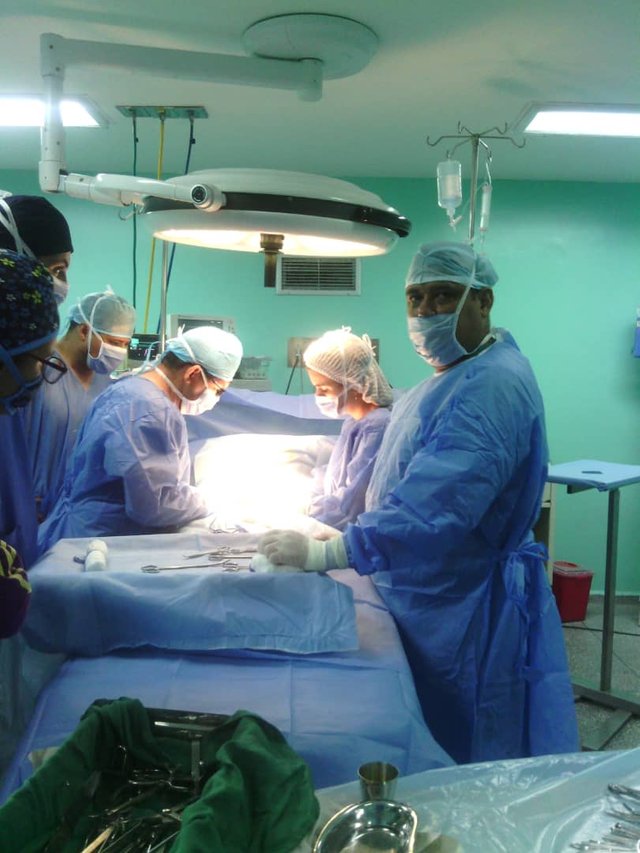
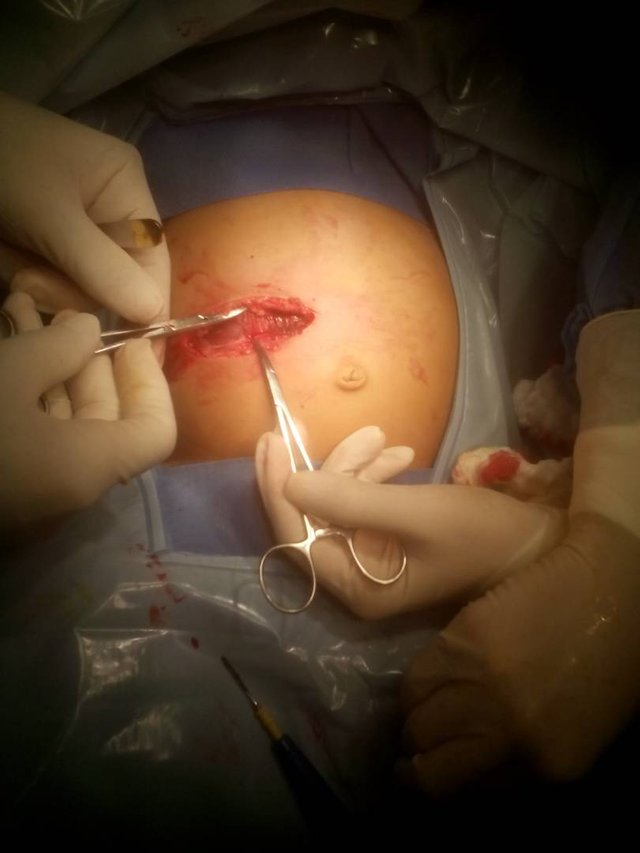
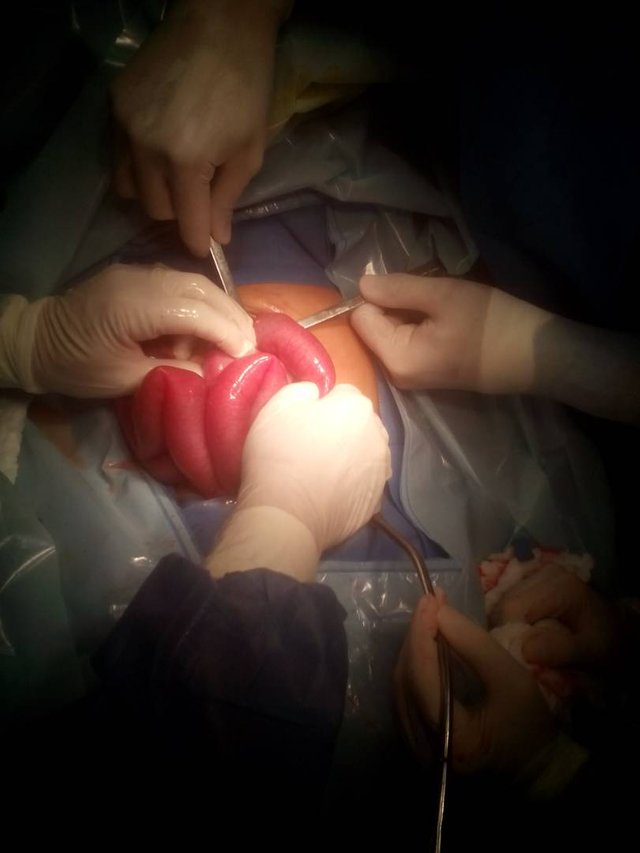
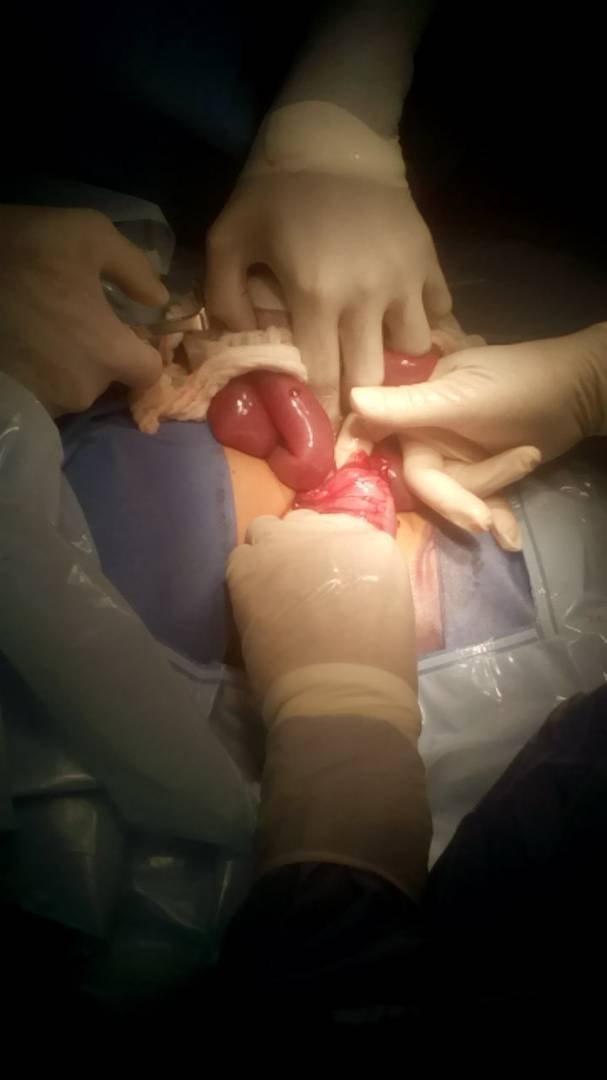
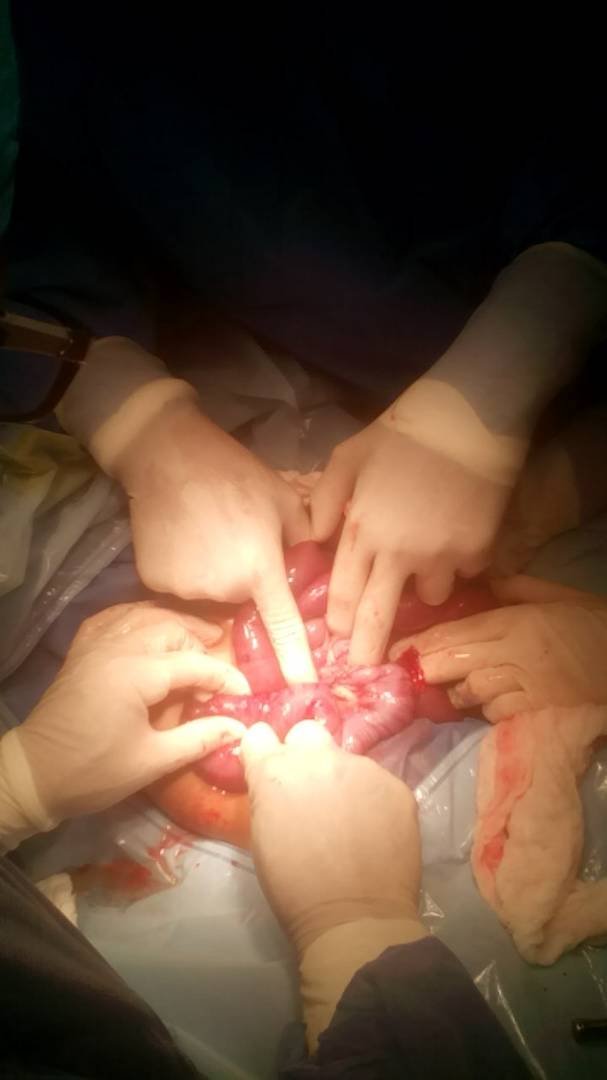
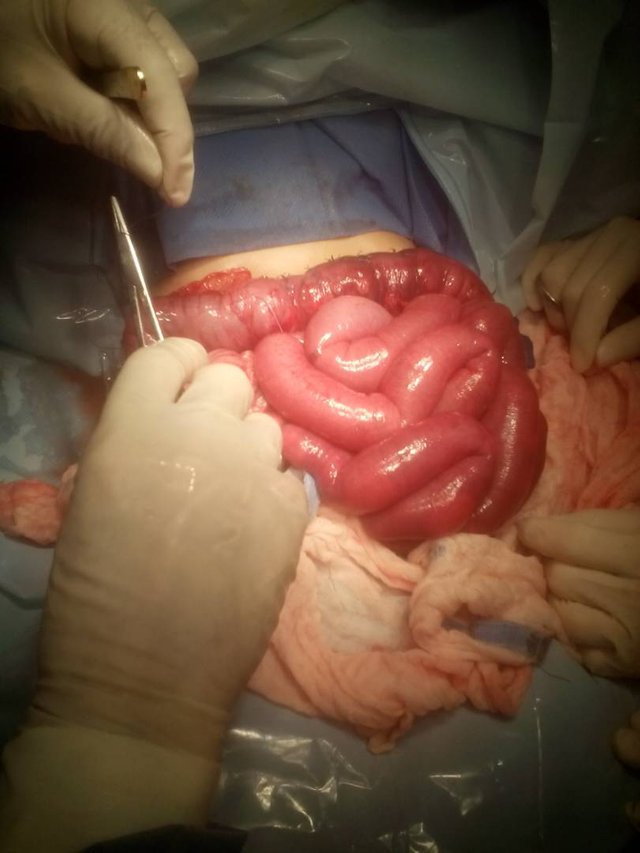
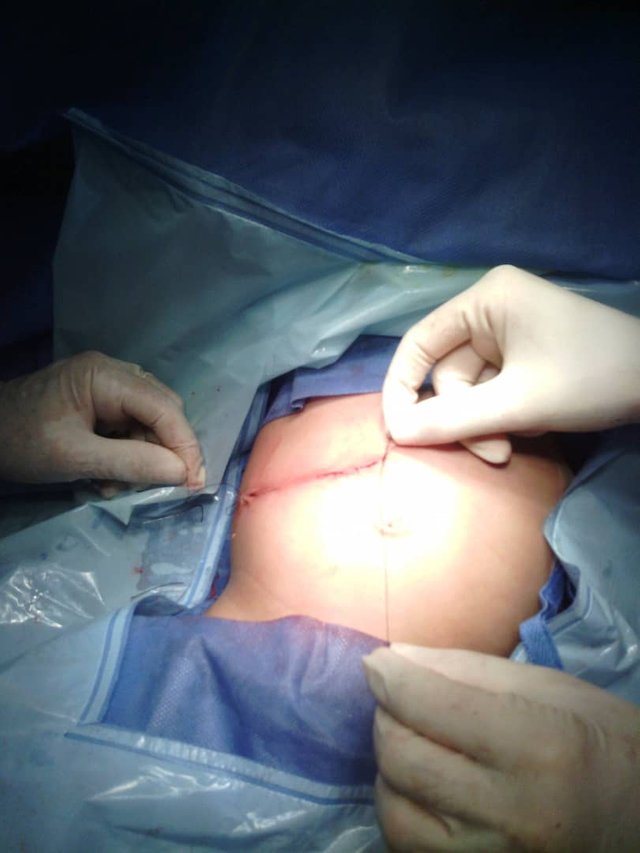
If you loose the intestinal envaginacion plus appendectomy, the infant is transferred to the recovery area until the conditions improve. I hope you like this short experience of mine as an instrumentalist in this surgery.