
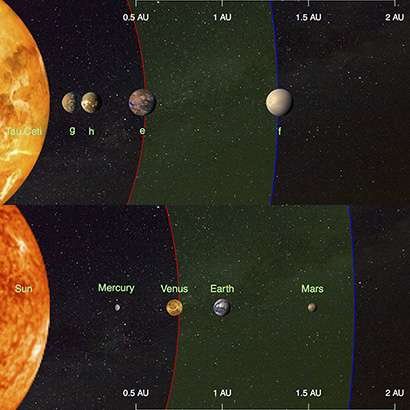
Recently, a team of international astronomers revealed that they found four Earth-sized planets orbiting the star "Tau Ceti". That is a star similar to our sun. the star is located at a distance of 12 light years from Earth and can be seen with the naked eye. These planets have a mass of 1.7 Earth masses, which is included in the smallest planet list ever detected around the Tau Ceti.
Two of them are Super Earth, the exoplanet with a higher mass of Earth and is in the massive ice giants of the Solar System, Uranus, and Neptune. The planet is located in a habitable star zone. That means, their condition allows for water on the surface.
These planets are detected by observing the movement of "tau Ceti" movement. The technique used is sensitive enough to detect variations in star movements as small as 30 centimeters per second.
"Through the highly sophisticated data set modeling of some independent observers, we can eliminate noise due to the star surface activity of very small signals. The signal is generated by the gravitational pull of the Earth-sized planets, "said Steven Vogt, one of the authors of the journal as well as professor of astronomy and astrophysics at UC Santa Cruz. His journalists' journals have now been published in the Astrophysical Journal.
According to lead author Fabo Feng from the University of Hertfordshire, UK, researchers are closer to the 10 centimeters per second limit needed to detect Earth's analogs. "Through this analogue comparison, our detection of such weak wobbles becomes a milestone in the earth's analogue search and understanding of the sustainability of the earth," Feng said.
The two outermost planets around Tau Ceti tend to be habitable planet candidates, although the large debris disks around the star are less supportive because of the explosion of asteroids and intense comets.
In 2013, the same team also investigated the Tau Ceti. Mikko Tuomi from the University of Hertfordshire led the effort in developing data analysis techniques and using the star as a benchmark.
"We came up with a clever way to distinguish between signals caused by planets and those caused by star activity. We look at how different the star activity is at different wavelengths and use that information to separate this activity from planetary signals, "explains Tuomi.
With great difficulty, the researchers increased their engineering sensitivity and were able to get rid of two signals that the 2013 team identified as a planet. "No matter how we look at the star, there are at least four rocky planets orbiting it," Tuomi said.
"We are slowly learning to distinguish between the rocking caused by planets and those caused by the star's active surface, enabling us to essentially verify the existence of two potentially inhabitable outermost planets within the system," he added.
Sun-like stars are considered the best targets in search of a habitable planet because of their similarity to the sun. Unlike small stars in general, like the red dwarf Proxima Centauri and Trappist-1, they are not so dim.
With such conditions, they will be locked together, showing the same side with the star at any time. Tau Ceti is very similar to the sun in size and brightness, and the two stars host a multi-planetary system.
Reference :
- https://phys.org/news/2017-08-earth-sized-planets-orbiting-nearest-sun-like.html
- https://news.ucsc.edu/2017/08/tau-ceti-planets.html
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/08/170817095549.htm
- http://www.dailygalaxy.com/my_weblog/2017/08/12-light-years-away-four-rocky-earth-like-planets-detected-orbiting-our-nearest-sun-like-star-tau-ceti-sun-like-star.html
- http://www.astrobiology.com/2017/08/four-earth-sized-planets-detected-orbiting-tau-ceti.html
- https://www.herts.ac.uk/about-us/news/2017/august/two-potentially-habitable-planets-detected-orbiting-the-nearest-sun-like-star



wonderful post
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit