Hi there!
This is the second part of my post of endocrine system. Let's keep talking about this, I know you'll enjoy it.
As we were talking in the past post, we find out that the endocrine system is one of the most important in the human body, which it helps to regulate all the functions in our bodies.
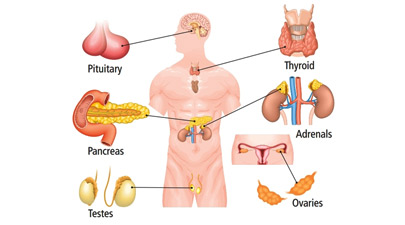
Pineal gland
The pineal gland, also called epiphysis, is a small endocrine gland found in the brain and produces melatonin, a hormone that regulates the biorhythms of the organism. The gland is shaped like a fruit or pine pineapple, so its name. It is located in the vicinity of the midline and binds to the third ventricle.
You will also find a series of nuclei that correspond:
- Pinealocitos
- Interstitial cells
The pineal gland has calcium deposits called pineal acérvuloss. They begin to appear after the birth
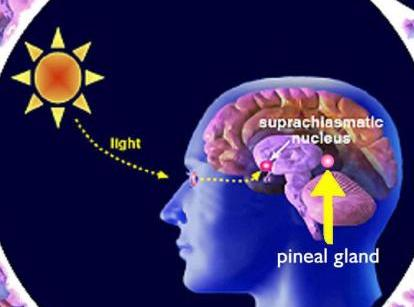
Pineal gland function
- It is related to the sleep-wake cycle, through the influence of light and darkness, and the hormone.
- The jetlag is treated with melatonin, because the jetlag itself is generated by an imbalance that has the hormone.
- In other species, it inhibits the secretion of GNRH and therefore the activity of the gonads (ovaries and testicles)
When species hibernate, their reproductive capacity and sexual desire are diminished. This is because when the species is in winter, food and hydration become very difficult to achieve, so they do not bring offspring during that period.
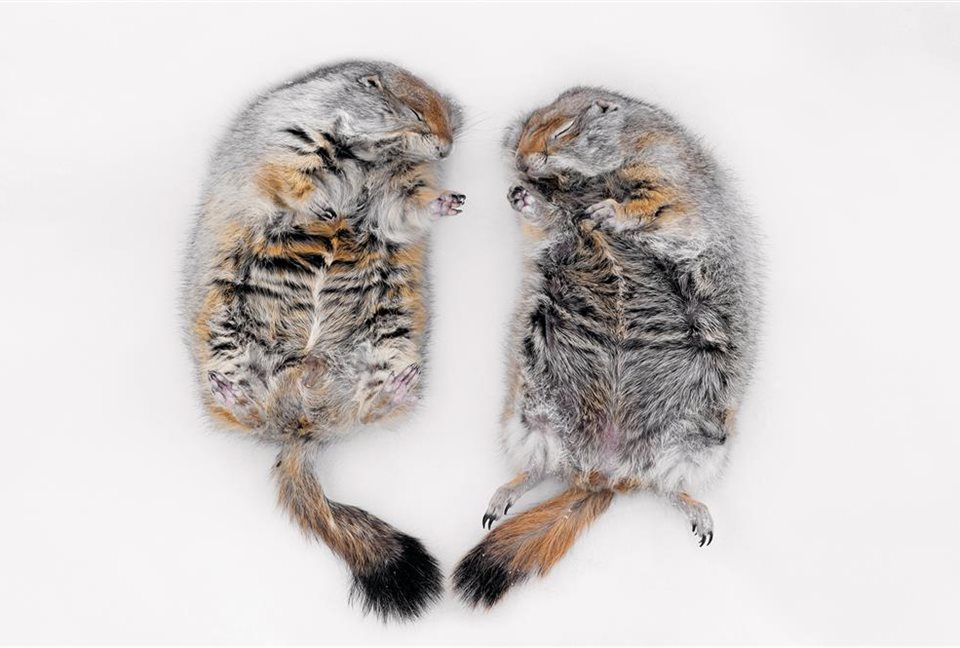 Arctic squirrels must contend with very adverse environments that offer long, cold winters with strong winds, a short cropping season, permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil), poor drainage, and limited vegetation. The temperature of their bodies reached-2.9 °c (26,8 °f). The squirrels pass, by necessity, seven months a year in a dormant state. Newborns have to grow in adult size during the short spring and summer period in the Arctic. When they are six weeks old they are ready to leave the underground nest. They reach eighty percent of their adult weight a month after they have surfaced and by mid-September they reach the prehibernation weight between six hundred and seven ounces.
Arctic squirrels must contend with very adverse environments that offer long, cold winters with strong winds, a short cropping season, permafrost (permanently frozen subsoil), poor drainage, and limited vegetation. The temperature of their bodies reached-2.9 °c (26,8 °f). The squirrels pass, by necessity, seven months a year in a dormant state. Newborns have to grow in adult size during the short spring and summer period in the Arctic. When they are six weeks old they are ready to leave the underground nest. They reach eighty percent of their adult weight a month after they have surfaced and by mid-September they reach the prehibernation weight between six hundred and seven ounces.
CURIOUS FACTS!
As a curious fact, pineal gland is related to the mystical area of the
Human being. The pineal gándula is at the brow level, midway between the forehead and nape, ie, exactly in the middle of the brain, so it is a kind of third eye, directly related to the seventh Chakra.
For all this, it is believed that the pineal gland can "activate" to open the door to new experiences. But this is not for anyone; It is indicated for those who are in deep spiritual pursuit and trying to understand things that go beyond human nature.
When the pineal gland is activated:
-Opens a portal to universal energy and divine Essence
-Develop the perception and extrasensory faculties
-Creativity is enhanced
-The person feels more happiness, well-being, optimism and joy
-Reduces stress
-it regulates the absorption of free radicals
-Aging is delayed
-Consciousness expands
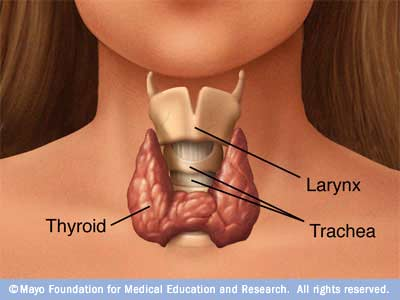
Thyroid gland
It is located in the anterior part of the neck, inferior to the larynx and superior to the trachea. of soft consistency and a form of "butterfly", where the gland is formed by two lateral lobes joined in the midline.
Thyroid hormones
- regulate the basal metabolism and the production of heat by all the cells of the organism.
They practically regulate the energy machinery of all cells so that the cells can meet or stop a certain function. - participates in the growth of tissues.
- influences the development of the CNS, especially in the fetus and children.
The deficiency of thyroid hormones at birth generates congenital hypothyroidism or cretinism. If this abnormality is not corrected in time, mental retardation may result.
The characteristics of congenital hypothyroidism are:
- Prominent language
- Hypotonic (umbilical hernias, constipation)
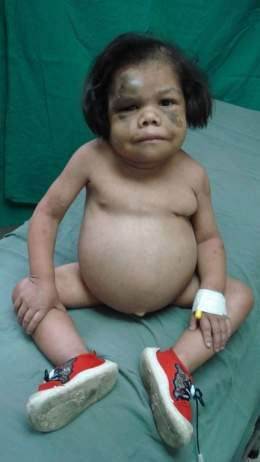
- Ronco Plain
- are "slow" babies
- can lead to serious Mental retardation
Hyperthyroidism
It is based on the excessive production and release to the bloodstream of hormones produced in the thyroid gland--the especially thyroxine--which leads directly to an acceleration of thyroid-regulated functions, especially metabolic. Visually, this hyperactivity is associated with the onset of goiter, i.e., widening of the anterior part of the neck due to inflammation of tumor origin of the thyroid.
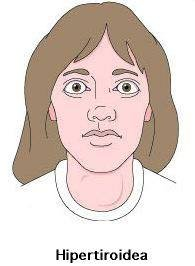
Symptoms
- Hypertension
- Exalted Osteotendon reflexes
- diarrhea (excessive increase in intestinal transit)
- tachycardia, arrhythmia, palpitations
- Sweating
- feeling of heat (intolerance to heat). The skin looks shiny (sweat) and the patient is usually hot.
- goiter.
- Bright Look, palpebral retraction.
Parathyroid glands
Are four glands that are located posterior to the thyroid gland
Parathormone hormone
increases the calcium in the blood
Bone: Increase bone resorption to increase calcium levels.
Digestive tract: increases intestinal absorption of calcium.
Kidney: They act at the level of the tubules, and increase the absorption of calcium. They activate the Alfahidroxilasa enzyme, which allows active vitamin D to form. Transforms vitamin D3 into 1.25-dihydroxy-Vitamin-D3 (Calcitrol – Active vitamin D). This vitamin D acts on the digestive tract to increase the absorption of calcium.Increases Bone resorption
Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is an electrolytic imbalance with a low level of calcium in the blood. The normal value of calcium in adults is 4.5 to 5.5 MEq/L.
Calcium is important for having healthy bones and teeth, as well as for the normal functioning of the muscles and nerves. Normal levels of blood calcium are maintained through the action of parathyroid hormone (HPT), kidneys, and intestines.
Symptoms
- Paresthesia
- Dry and scaly skin
- Muscular Cramps
- Neurological or psychic disorders
- Convulsions
- Lethargy
- Cardiac arrest.
- Arrhythmias.
- They present a flexion of the wrist, and another flexion in the Metatarsofalangica joint. Interfalangicas joints are usually hyperextended. It's called a Crusoe sign.

Hypersecretion of PTH.
It is derived from a tumor at the level of the parathyroid, so there is an abnormal amount of PTH, which causes greater bone resorption for a longer period, which causes a wear and secondary osteoporosis originates. This osteoporosis translates into fractures.
Adrenal glands
They are located in the upper pole of the kidney, with a triangular shape.
They have two areas that are macroscopically differentiated, the crust (brownish-yellow coloration) and the medulla (reddish-brown coloration).
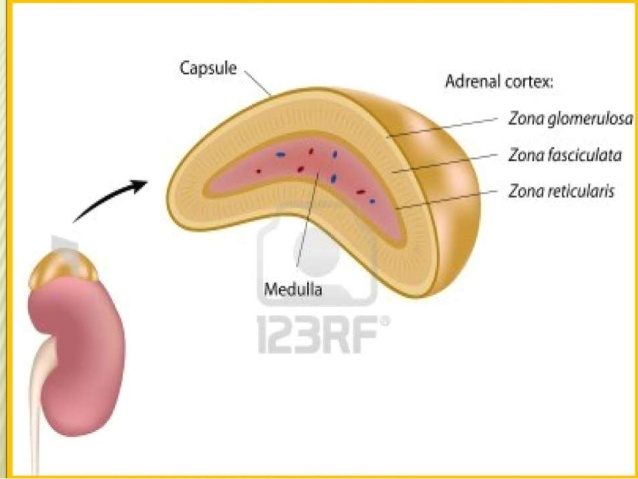
- Adrenal Cortex
It is the area of the adrenal gland that surrounds the medulla. Cells located in this region secrete steroid hormones.
has three parts
- Glomerular zone: represents 15%
Mineralocorticoid: Aldosterone is produced.
Aldosterone: Is the hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, aldosterone is a hormone that inhibits the level of sodium excreted in the urine, maintaining volume and blood pressure.
The increase of this hormone can cause some diseases such as Bartter syndrome, people with this syndrome present a loss of potassium (Hypokalemic alkalosis) and an increase in the hormone aldosterone.
- Fasciculation zone: represents 75%
Glucocorticoids occur: Cortisol
In Adenohypophysis, Corticotropas cells release ACTH (ACTH) and stimulate the fascicle area, and consequently, cortisol is produced.
Cortisol: Anti-stress hormone. You can't live without this one.
• Carbohydrate metabolism
• lipolysis
• Neoglucogenesis
• Decreases protein synthesis and muscle mass
• immunosuppressants
• Inflammation Regulator
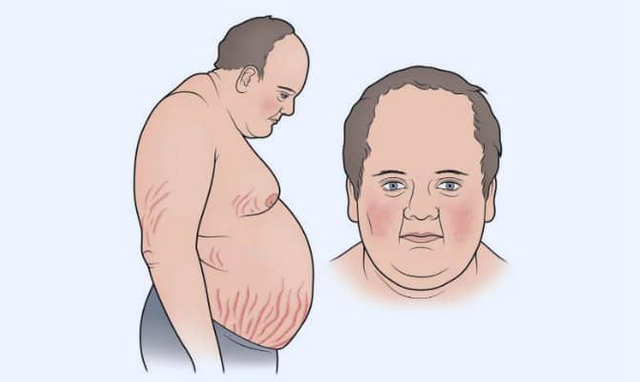
Cushing's syndrome, also known as Hypercortisolism
It can occur when the pituitary gland produces too much acth hormone (ACTH). This later sends signals to the adrenal glands to produce excess cortisol. A tumor of the pituitary gland may cause this condition and a tumor in the adrenal gland can generate excess cortisol.
Symptoms:
A. Full Moon face
B. Central obesity (only the belly grows, the arms remain skinny)-> derived from the decrease in protein synthesis.
C. Collagen is not synthesized, so the skin is weak and striations of 1 cm thick purpurea are generated.
D. ACTH stimulates the ANDROGENOS of the adrenal gland, so that women can leave them bigothic.
- Reticular zone: represents 10%
Adrenal androgens are produced: Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
- Adrenal medulla
It is located in the center of the adrenal gland.
Adrenaline-> Stress hormone
- prepares the individual to flee
- increases respiratory rate and cardiac volume.
- increases the blood flow to the skeletal muscle
- Activates the glycolysis.
We can live without adrenaline, because thanks to the nervous system can produce noradrenaline, which is enough to live.
Español
Glándula Pineal
La glándula pineal, también llamada epífisis, es una pequeña glándula endócrina que se encuentra en el cerebro y produce melatonina, hormona que regula los biorritmos del organismo. La glándula tiene forma de fruto o piña de pino, por eso su nombre. Se ubica en las proximidades de la línea media y se une al tercer ventrículo.
También se van a encontrar una serie de núcleos que corresponden:
- Pinealocitos
- Células intersticiales
La glándula pineal cuenta con depósitos de calcio denominados acérvulos pineales. Comienzan a aparecer luego del nacimiento

Función de la glándula pineal
- Está relacionada con el ciclo sueño-vigilia, a través de la influencia de la luz y oscuridad, y la hormona.
- El jetlag se trata con melatonina, debido a que el jetlag propiamente dicho, se genera por un desbalance que tiene la hormona.
- En otras especies, inhibe la secreción del GNRH y por lo tanto, la actividad de las gónadas (ovarios y testículos)
Cuando las especies hibernan, se disminuye su capacidad reproductiva y su deseo sexual. Esto se da gracias a que cuando la especie se encuentra en invierno, el alimento e hidratación se vuelven muy difíciles de conseguir, por lo que no traen crías durante ese periodo.

Las ardillas del Ártico deben lidiar con ambientes muy adversos que ofrecen inviernos largos y fríos, con fuertes vientos, una corta temporada de cultivo, permafrost (subsuelo permanentemente congelado), drenaje deficiente y vegetación limitada. La temperatura de sus cuerpos llegó a los -2,9°C (26,8°F). Las ardillas pasan, por necesidad, siete meses al año en estado latente. Los recién nacidos tienen que crecer a tamaño adulto durante el corto periodo de primavera y verano en el Ártico. Cuando cumplen seis semanas de nacidos están listos para salir del nido subterráneo. Llegan al ochenta porciento de su peso adulto al mes de haber surgido a la superficie y para mediados de septiembre alcanzan el peso de prehibernación que es entre seiscientos a setecientos gramos.
CURIOSIDADES
Como un hecho curioso,la glandula pineal está relacionada al area mistica del ser humano. La gándula pineal está a la altura del entrecejo, a mitad de camino entre la frente y la nuca, es decir, exactamente en la mitad del cerebro, por eso es una especie de tercer ojo, relacionado directamente con el séptimo chakra.
Por todo esto, se cree que la glándula pineal puede "activarse" para abrir la puerta a nuevas experiencias. Pero esto no es para cualquiera; está indicado para quienes están en una búsqueda espiritual profunda e intentando comprender cosas que van más allá de la naturaleza humana.
Cuando la glándula pineal se activa:
- Se abre una portal hacia la energía universal y esencia divina
- Se desarrollan la percepción y las facultades extrasensoriales
- Se potencia la creatividad
- La persona siente más felicidad, bienestar, optimismo y alegría
- Disminuye el estrés
- Se regula la absorción de radicales libres
- Se retrasa el envejecimiento
- La conciencia se expande

Glándula Tiroides
Se ubica en la parte anterior del cuello, inferior a la laringe y superior a la tráquea. De consistencia blanda y una forma de “mariposa”, donde la glándula está formada por dos lóbulos laterales unidos en la línea media.

Hormonas Tiroideas
- Regulan el metabolismo basal y la producción de calor por todas las células del organismo.
Prácticamente, regulan la maquinaria energética de todas las células para que las células puedan cumplir o detener determinada función. - Participa en el crecimiento de los tejidos.
- Influye en el desarrollo del SNC, especialmente en el feto y en los niños.
La deficiencia de hormonas tiroideas en el nacimiento genera el Hipotiroidismo Congénito o cretinismo. Si no se corrige a tiempo esta anormalidad, se puede generar retraso mental.
Las características del hipotiroidismo congénito son: - Lengua prominente
- Hipotónicos (hernias umbilicales, estreñimiento)
- Llano ronco
- Son bebes “lentos”
- Puede derivar en un Retraso Mental Grave

Hipertiroidismo
Se basa en la producción excesiva y lanzamiento al torrente sanguíneo de las hormonas producidas en la glándula tiroides -la tiroxina especialmente- que lleva directamente a una aceleración de las funciones reguladas por el tiroides, en especial la metabólica. Visualmente, esta hiperactividad está asociada a la aparición del bocio, es decir, ensanchamiento de la parte anterior del cuello debido a una inflamación de origen tumoral del tiroides.

Síntomas
- Hipertensión
- Reflejos osteotendinosos exaltados
- Diarrea (aumento excesivo del tránsito intestinal)
- Taquicardia, arritmia, palpitaciones
- Sudoración
- Sensación de calor (intolerancia al calor). La piel luce brillante (sudor) y el paciente generalmente está caliente.
- Bocio.
- Mirada brillante, retracción palpebral.
Glándulas Paratiroides
Son cuatro glándulas que se ubican posterior a la glándula tiroides
Hormona Paratohormona
Aumenta el calcio en la sangre
Hueso: aumentan la resorción ósea para aumentar los niveles de calcio.
Tubo digestivo: aumentan la absorción intestinal de calcio.
Riñón: actúan a nivel de los túbulos, y aumentan la absorción de calcio. Activan la enzima alfahidroxilasa, la cual permite que se forme la vitamina D activa. Transforma la Vitamina D3 en 1,25-dihidroxi-vitamina-D3 (calcitrol – vitamina D activa). Esta vitamina D actúa sobre el tubo digestivo para que aumente la absorción de calcio.Aumenta la resorción ósea
Hipocalcemia
La hipocalcemia es un desequilibrio electrolítico con un nivel bajo de calcio en la sangre. El valor normal del calcio en los adultos es de 4,5 a 5,5 mEq/L.
El calcio es importante para tener huesos y dientes saludables, así como para el normal funcionamiento de los músculos y nervios. Los niveles normales de calcio en sangre se mantienen a través de la acción de la hormona paratiroidea (HPT), los riñones y los intestinos.
Síntomas
- Parestesia
- Piel seca y escamosa
- Calambres musculares
- Trastornos neurológicos o psíquicos
- Convulsiones
- Letargia
- Paro cardiaco.
- Arritmias.
- Presentan una flexión de la muñeca, y otra flexión en la articulación metatarsofalangica. En las articulaciones interfalangicas generalmente se encuentran hiperextendidas. Se denomina Signo de Crusoe.

Hipersecreción de PTH.
Se deriva gracias a un tumor a nivel de la paratiroides, por lo que existe una cantidad anormal de PTH, lo que origina mayor resorción ósea por un mayor tiempo, lo que origina un desgaste y se origina una osteoporosis secundaria. Esta osteoporosis se traduce en fracturas.
Glándulas Suprarrenales

Se ubican en el polo superior del riñón, con una forma triangular.
Cuentan con dos zonas que se distinguen macroscópicamente, la corteza (coloración pardo-amarilla) y la medula (coloración pardo-rojiza)
1 Corteza suprarrenal
Es la zona de la glándula suprarrenal que rodea a la medula. Las células ubicadas en esta región secretan hormonas esteroideas.
Cuenta con tres partes
- Zona glomerular: representa el 15%
Se producen mineralocorticoides: aldosterona.
Aldosterona: Es la hormona producida por la corteza adrenal, la aldosterona es una hormona que inhibe el nivel de sodio excretado en la orina, manteniendo el volumen y la presión sanguínea.
El aumento de esta hormona puede causar algunas enfermedades como el síndrome de Bartter, las personas con este síndrome presentan una pérdida de potasio (alcalosis hipocaliémica) y un aumento en la hormona aldosterona.
Zona fascicular: representa el 75%
Se producen glucocorticoides: cortisol
En la Adenohipófisis, las células corticotropas liberan ACTH (Corticotropina) y estimulan la zona fascículo, y por consecuencia, se produce cortisol.
Cortisol: hormona anti estrés. No se puede vivir sin esta.
• Metabolismo de Carbohidratos
• Lipolisis
• Neoglucogenesis
• Disminuye la síntesis de proteínas y masa muscular
• Inmunosupresora
• Reguladora de la inflamadora
Síndrome de Cushing, también conocido como hipercortisolismo,
Puede ocurrir cuando la hipófisis produce demasiada hormona corticotropina (ACTH, por sus siglas en inglés). Esta posteriormente envía señales a las glándulas suprarrenales para producir cortisol en exceso. Un tumor de la hipófisis puede causar esta afección y un tumor en la glándula suprarrenal puede generar cortisol en exceso.
Síntomas:
a. Cara de luna llena
b. Obesidad central (solo crece la panza, los brazos se quedan delgaditos) -> derivado de la disminución de la síntesis proteica.
c. No se sintetiza colágeno, por lo que la piel es débil y se generan estrías purpureas de 1 cm de grosor aproximadamente.
d. La ACTH ESTIMULA LOS ANDROGENOS DE LA GLANDULA SUPRARRENAL, por lo que a las mujeres les puede salir bigotico.

- Zona reticular: representa el 10%
Se producen andrógenos adrenales: dehidroepiandrosterona (DHEA)
- Medula Suprarrenal
Se encuentra en el centro de la glándula suprarrenal.
Adrenalina -> Hormona del Estrés
- Prepara al individuo para huir
- Aumenta la frecuencia respiratoria y el volumen cardiaco.
Aumenta el flujo sanguíneo al musculo esquelético- Activa la glucolisis.
Podemos vivir sin adrenalina, ya que gracias al sistema nervioso se puede producir noradrenalina, que es suficiente para vivir.

Congratulations @cariosjavier! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDownvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @cariosjavier! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @cariosjavier! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit