Sugar Processing
Hello Dear Steemian.....
A few days ago I had discussed generally how an engineer established a chemical industry, Now I will explain a little more detail about glucose processing from the corn. Can a corn processed as glucose ?? How can it be ? Lets read post below !!
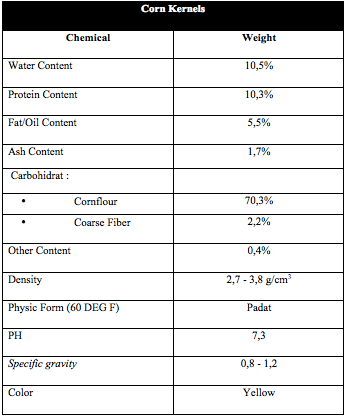
Corn Kernels
The Corn kernels have rich carbohydrates. Most of endospermium. Carbohydrate content reach about 80% of all dry seeds. Carbohydrates in starch generally is mixture both of amylose and amylopectin. The most of sticky corn is amylopectin. This difference does not have much effect of nutrient content, but more processing as food.
Sweet corn is unable to produce starch till the seeds taste sweeter when it young.
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharides are single sugars such as glucose, fructose and dextrose with having same formula C6H12O6. Glucose and fructose are also called as reducing sugars. In the composition of corn, reducing sugar occupies second order of the most components. This reduction sugar is a monosaccharide group consisting of glucose combined with fructose. Sucrose can be broke to glucose and fructose, but the glucose and fructose can't be resolved by dilute acid solution. The basic solution turns out of glucose and fructose convert to reducing sugars into various organic acids that can be salt base. At temperatures below 550C, this solution not very meaningful because the solving results of low temperatures only produce substances with old colors will affect of sugar.
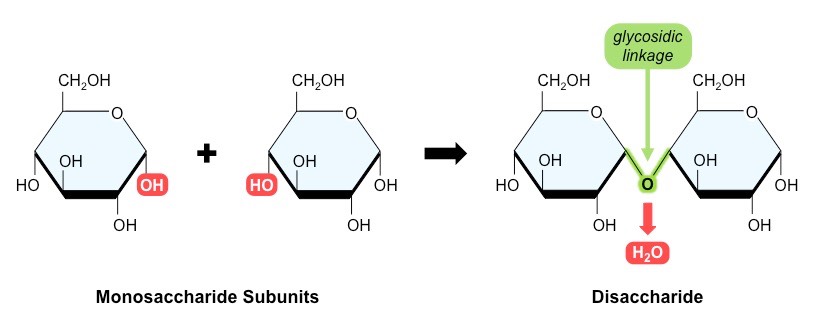
Disaccharide
Two or more sugar molecules can bind each other to glycoside group, forming a new substance called polysaccharides. If the simple sugar molecules bonded each other less than 10, the substance formed called as oligosaccharides. The simplest oligosaccharide is a disaccharide composed of two monosaccharide molecules.
The first glucose and the second sugar bind each other through C1 and C4 in the aglyone-O group. Such as disaccharides still possess properties of glucose, since second group still has free of hemiasetal group (C1) which can readily be exposed of aldehyde form, for example weakly basic suits of Fehling and Tollens oxidators.
Both simple sugar molecules interlock as glycosides and aglycons (C1-C1). Since two simple sugar molecules bonding together are coupled through their respective acetal groups, the molecule of disaccharide is no longer free of hemiasetal group, so, it can not reducing sugar. It is only hydrolysis of reducing sugar properties of each components recur. In general, disaccharides can't possess of reducing properties, or cant to be carbonyl reactions such as glucose, for example in osason formation, mutarotation, etc.
Illustration of Reaction
source
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides are composed of single sugar molecules, most importantly disaccharides are celluloses which have formulas (C12H22O11) and starch (C6H10O5)8. Cellulose molecule is composed of glucose more than 1000 molecules linked with oxygen. Starch is a complex carbohydrate that water insoluble, tangible white powder, tasteless and odorless. Starch is main of ingredient produced by plants to store excess glucose (as a photo synthesis product).
Cellulose (C6H10O5)n is a carbohydrate polysaccharide consisting of a beta-glucose monomer. Cellulose is a major structural component of plants and can not be digested by humans. Cellulose form is crystalline. These cellulose crystals coexist through kind of sugar (not glucose) forming a long chain called misela. The misela of cellulose is highly resistant of chemical or enzyme influences. Amount of molds and bacteria who live from substrate of agricultural can produce a kind of cellulose enzyme can hydrolyze cellulose into simpler compounds.
Process Engneering
In enzyme conversion can produce glucose with 95% dextrose content, higher of dextrose content can be obtained by using lower substrate concentration. Dextrose levels can be reduced by trans-glucose, because the enzyme used is not pure. High doses of enzymes and long conversion times in polymerization can form maltose which be formed due to non ideal conversion.
At 60°C, the solubility of dextrose is same as sucrose. Solubility of sucrose is higher than dextrose at temperatures below 60 oC s, otherwise at temperatures above 60 oC higher dextrose solubility. The dextrose transition temperature is at 50 ° C, at the temperature below this glucose monohydrate forms a solid phase. Dextrose is not easy to be crystallize as sucrose. The crystal nucleus does not form until dextrose solution reaches 75% of saturation. But at high temperatures glucose syrup can crystallize.
Blue Line is Cooling Water Inlet
Red Line is Steam Inlet
R-01 is A Rector to React Corn Starch and T-01 is HCl Tank pumped to reactor, HCl is as Catalyst
More Reference :
Support Scientist By Use #science tag or join @steemSTEM
Follow Me @jamhuery



Nice post...
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This post has received a 0.45 % upvote from @drotto thanks to: @banjo.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
sweet lol, that's how herbivores survive, cellulose lol
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Exactly sweet, hehehe
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit