The most popular and widely accepted theory about the origin of universe is the Big Bang Theory.
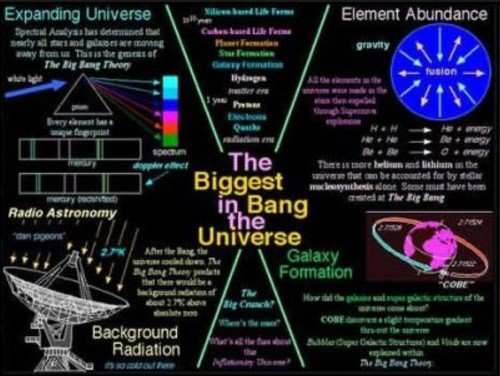
The Big Bang Theory states that the universe began in a state of extremely high density and a volume approaching just a point. Then the universe has been expanding since some particular instant that marked the origin of the universe. Tracing the expansion of the universe back in time shows that the universe would have been compressed to infinite density approximately 10-20 × 109 years ago. The universe began at the time as the big bang began the expansion. The Big Bang was the origin of space and time. It is tempting to think of the Big Bang as something like the explosion of an artillery shell. But it is more correctly an expansion of space, filled with hot radiation and matter.
Scientists have been trying to visualize the creation of the universe implying properties of energy and matter and by the experiments in nuclear reactors. Nuclear reactors are used to study the elementary sub-atomic particles and fundamental forces. In attempt to extrapolate the universe back to its origin or the big bang, different stages of the life of universe have been discussed. The time of the Big Bang is takes as time Zero. At time 10-43 seconds after the Big Bang the universe was as simple as it could possibly be. At the present time many kinds of particles make up matter, and four different forces govern the behavior of matter: electromagnetic force, gravitational force, strong force (attraction between sub-atomic particles in the nucleus) and weak force (which contribute to radio-active decay). In the first fraction of second after the Big Bang, all the particles were fundamentally similar and only one force (the grand unifying force) was functioning.
Between 10-43 and 10-35 seconds after the Big Bang, the universe was extremely hot and the particles were exerting upon one another the single, strong weak electromagnetic force. Due to high energy, quarks and electrons present at that time were interchangeable. Quarks are the most fundamental particles discovered which combines to form protons and neutrons. The temperature of the universe at that time was 100,000 million degree centigrade (°C). From 10-35 to 10-10 seconds of the Big Bang, the universe was cooling and the strong and electromagnetic weak forces were functional distinctly between quarks. Quarks and electrons were no longer interchangeable. String like concentrations appeared around which future galaxies were to be formed.
After 10-10 to 10-5 seconds of the moment of creation, the hot radiations continued to cool and three forces, electromagnetic, strong and weak, became differentiated. After the end of this era, quarks started coming together to form protons, neutrons and other sub-atomic particles. Then starting from 10-5 seconds, the commonly known sub-atomic particles were formed. Quarks had combined to form protons and neutrons. However, the universe was too hot to allow the particles to combine in the form of atoms and atomic nuclei. The collections of high energy particles would have knocked any nucleus trying to assemble. Electrons, protons, neutrons, neutrinos, and anti-neutrons were involved in atomic activity characteristics of particles.
By about three minutes after the Big Bang, the temperature of the universe dropped enough that the protons and the neutrons were able to collect to form atomic nuclei. The temperature was, however, too high for the formation of atoms or elements. The electrons going around the atomic nuclei would have been knocked to go astray, leaving the orbit. By about 500,000 years after the Big Bang, the temperature was low enough to form complete atoms. Radiations were, however, so strong that they were preventing the particles to assemble in the form of galaxies and stars. After the formation of atoms, the the matter started condensing to form early planetary bodies. These cosmic bodies could interact with one another through force of gravity. More matter was condensed to make nuclei for the formation of galaxies.
Is The Universe Expanding, Contracting Or Static?
Scientists have known since the 1920s that the universe is expanding. Most of the earth's galactic neighbors are receding and the farther away they are, the higher is their velocity.
Edwin P. Hubble, who was the pioneer of modern astronomy, analyzed the red shift of galaxies. He discovered that the speed at which a galaxy is receding (moving away from us) is proportional to its relative distance. It means that the more distant a galaxy, the faster it is moving away. The principle was named as Hubble's Law. This law can be represented as:
Speed = H × Distance
Where "H" is the Hubble's constant.
A generally accepted value of "H" is 56 Km per second per megaparsecs (a megaparsec is equals to 3.26 million light years).
Source: http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:VVXO_O141cIJ:www.business-science-articles.com/articles/science/item/237-the-big-bang-theory+&cd=1&hl=en&ct=clnk&gl=us
Not indicating that the content you copy/paste is not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
Some tips to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
Creative Commons: If you are posting content under a Creative Commons license, please attribute and link according to the specific license. If you are posting content under CC0 or Public Domain please consider noting that at the end of your post.
If you are actually the original author, please do reply to let us know!
Thank You!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit