Measles is an acute and highly infectious disease accompanied by fever, maculopapular rash, and respiratory. Complications of measles are very serious and common type. The introduction of an effective live-virus vaccine has dramatically reduced the incidence of measles occurrence in the United State of America, but in Africa, measles has been the major cause of deaths of the young ones in many parts of Africa.
Humans is known to be the only hosts for measles virus, though other species of animals like dogs, monkeys, and mice, can be experimentally infected.
Rubeola Virus gains access into the human system through the respiratory tract, where the virus begins to reproduce and multiply rapidly. This viral infection then spread over to regional lymphoid tissue where it can further its reproduction activities. The primary viremia disseminates the virus, which then replicates in the reticuloendothelial system. A secondary viremia seeds the epithelial surfaces of the body which includes the respiratory tract, skin, and conjunctiva where focal replication take place.
Measles have the ability to replicates in certain lymphocytes, which aids in dissemination all through the body system. The multinucleated giants’ cells with intranuclear inclusions are seen in lymphoid tissues throughout the body (tonsils, lymph nodes and appendix). 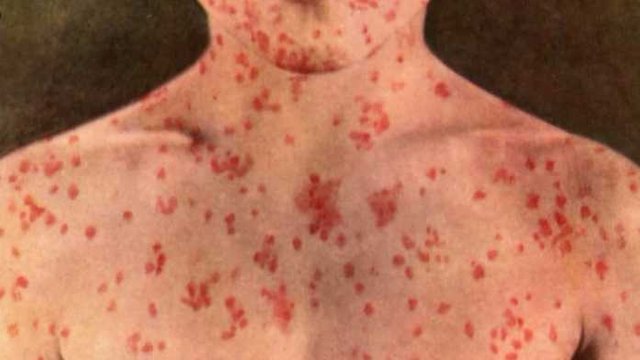 source
source
The describe events occur during the incubation period, which typically last for the period of 8 to 12 days but may sometimes last up to three (3) weeks in adults.
During the prodromal phase which is going to last for about two to four days and the first two to five days of rash that develop on the skin, Measles virus is then present in mucous, nasal, saliva, blood, body sweat and urine. The features maculopapular rash shows on the fourteenth day as circulating antibodies become detectable, the viremia then disappears, and the fever drops. The rash develops and multiply as a result of communication of immune T cells with virus-infected cells in the small blood vessels which should lasts about a week. In a person with defective cell- mediated immunity no rash will developed.
Rubella is one of the major causes of birth defects. Measles is highly contagious and can be communicated to another person through body contact of infected person, also can be transmitted through body fluids, cough sneezing. It is highly infectious to the extent that the majority of the people the victim come close in body contact will be infected if they have not received the measles immunization (Measles Vaccination). A person can also be immune if such person has previously contacted the infection and has been treated and gone, such a person cannot be infected with measles again.
In many developing countries in Africa and Asia, where people living in rural communities, villages, do not have access to measles vaccinations due to some predisposing factor like poor health systems, ignorance, poverty, poor knowledge about the virus, traditions that makes it very difficult for the environments to get vaccinated, it has claimed many lives of children in such area.
The involvement of the central nervous system is common in measles. Symptomatic encephalitis develops in about 1:1 cases. Reason been that infectious virus is rarely recovered from the brain, it has been suggested that an autoimmune reaction is the mechanism responsible for this complication. In contrast, progressive measles inclusion body encephalitis may develop in patients with defective cell-mediated immunity. Actively replicating virus is present in the brain in this usually fatal form of disease.
A rare late complication of measles is subacute slcerosing panencephalitis. This fatal disease develops years after the initial measles infection and is caused by virus that remains in the body after acute measles infection. Large amounts of measles antigens are presents within inclusion bodies in infected brain cells, but only a few virus particles mature. Viral replication is defective owing particles mature. Viral replication is defective owing to lack of production of one or more viral gene products, often the matrix protein.
Manifestation
Measles infections in nonimmune hosts are almost always symptomatic. After an incubation period of 8 to 12 days, measles is typically a 7 to 11 days illness with a prodromal phase of 2 to 4 days then accompany by an eruptive phase of 5 to 8 days.
The prodromal phase is characterized by sneezing, running nose, redness of eyes, coughing, fever, spots, and lymphopenia. The coryza and cough reflect an intense inflammatory reaction involving the mucosa of the respiratory tract. The conjunctivitis is commonly associated with photophobia. Koplik’s spots – pathognomonic for measles are small, bluish-white ulcerations on the buccal mucosa opposite the lower molars. These spots contain giant cells and viral antigens and appear about two days before the rash.
The fever and cough persist until the rash appears and then subside within 1- 2 days. The rash, which starts on the head and then spreads progressively to the chest, the trunk, and down the limbs, appears as light pink, discrete maculopapular that coalesce to form blotches, becoming brownish in 5 to 10 days. The fading rash resolves with desquamation. Symptoms are most marked when the rash is at its peak but subside rapidly thereafter.
Modified measles occurs in partially immune persons, such as infants with residual maternal antibody. The most common complication of measles is otitis media.
Pneumonia is the most common life-threatening complication of measles, caused by secondary bacterial infections.
Treatment, Prevention and Control
1.Vitamin A treatment in developing countries has decreased mortality and morbidity. Measles virus is susceptible in vitro to inhibition by ribavirin, but clinical benefits have not been proved. A highly effective and safe attenuated live measles virus vaccine is available. Measles vaccine is available in monovalent form and in combination with live attenuated rubella Vaccine and live attenuated rubella and mumps vaccines.
Antibiotic therapy is also set apart for bacterial complications. It involves prompt antibiotic for infected person. Contraindications to vaccination include pregnancy, allergy to eggs or neomycin, immune compromise, and recent administration of immunoglobulin.
Quarantine is not effective as a control measure because transmission of measles occurs during the prodromal phase.
Measles infection could be prevented by the administration of human immunoglobulin early in the incubation period.
References
Measles(Rubeola): Epidemiology, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment & Prevention
Measles: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment-Healthline
Top 4 Things Parents Need to Know about Measles
Unfortunately, there is an epidemic of measles in Serbia right now, because people refuse to vaccinate their children...
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@scienceangel, that is what ignorance can cause. People is such part of the country needs proper orientation about measles and the importance of vaccination before bringing vaccines to the communities. Thanks for your contribution!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hi @polaleye50, is there any difference in terms of physical manifestation between an adult which has been infected with measles and a child?
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@n4zriofficial adults are more likely to have complications than healthy children that are older than age of 5 years.
Some of the physical manifestation in adults are: vomiting, eye infection, laryngitis, bronchitis, seizure and permanent hearing loss among other symptoms. Prevention. is better than cure(Vaccination).
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Indeed prevention is better. Thanks for the explanation.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
My pleasure!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I never thought of it - but after reading the story above, I came to think that the western "anti-vac"-movement is perhaps contributing insignificantly to the spread of Measles compared to the situation in Africa.
The Measles is a disease that can be eradicated through the usage of vaccines if there just is a sufficient political will for it.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
@tobixen, yes, measles was eradicated in America long years ago through vaccination, it can also be done in Africa too. Thanks too Bill Gate, WHO, UNICEF and other supporting bodies for supporting measles eradication in Africa in one way or the other.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by polaleye50 from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit