Preface

Photo Credit: Tallsay
The Porphyria is a group of diseases caused by an abnormality in the iron ions in the blood. The Iron ion is responsible for the red coloring in the blood. These ions are a part of the hemoglobin, a protein that enables the red blood cells to transport oxygen to the lungs and to all parts of the human body. The same ion plays a major role in the kidney function and assists with the breaking down of chemical fabrics. The accumulation of porphyrins who are harmful when exposed to light is the most important symptom of the disease.
The iron ion is a product of the bone marrow and the liver through a complex process induced by eight different enzymes. When the ion formation is developed, they combine with intermediary newly formed components. The damage of one of the essential enzymes can result in the production of different substances in the liver, the spinal cord, and the blood circulation before leaving the body through the natural way. Porphyria is the result of a defective enzyme in this process.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Porphyria can differ from patient to patient. The most known symptoms are high sensitiveness to sunlight. Skin exposed to sunlight is itching, in some case, there is the formation of blisters, scars and extreme redness of the skin. A hypersensitivity for bruising all over the body and damage to the skin with multiple wounds is also a distinctive symptom. In some cases, a dark coloring of the urine and extreme facial hair growth can appear.
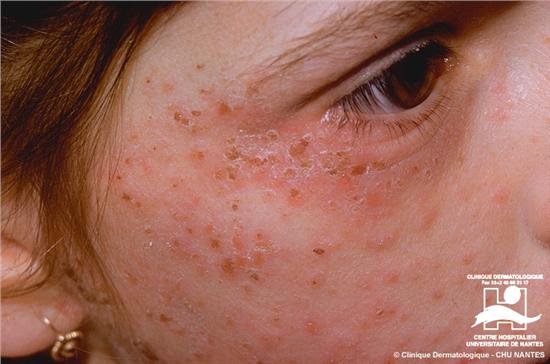
Photo Credit: SlidePlayer
Some forms of Porphyria damage the nervous system. Most common symptoms are in those cases: chest pain, abdominal spasms, heave psychological disorders, serious muscle weakness, and contractions. These symptoms appear unexpectedly and can last for weeks at a time. Porphyria can also be a combination of all those symptoms together.
External factors can trigger or induce the symptoms, such as:
- Nicotine.
- Drugs.
- Hormones.
- Alcohol.
- Exposure to sunlight.
- Stress.
- Diet.
- Fasting.
Pathological Determination
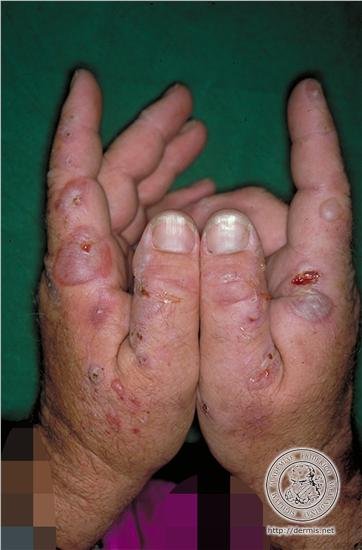
Photo Credit: foto-basa.com
Determination of Porphyria is possible by samples of blood, urine, and feces during the presence of the symptoms. The results of the determination are highly complexed because many of the symptoms occur in the pattern of other diseases. The test is multiple but not always reliable because of lab mistakes or the wrong interpretation by the doctors.
Treatment

Photo Credit:dermis.net
Each patient gets a treatment in accordance with his own pathology. Possibly iron ions are added with chemical suppression of the symptoms or blood transfusions. Hospitalization is a possibility with high-risk symptoms.
Heredity
Most kinds of Porphyria are hereditary. The disease is a result of the passing on of defaulted genes from one of the parents to the children. The chance that the disease is hereditary depends on a number of facts and are unpredictable.
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) is mostly not hereditary. Eight out of ten patients got the disease through external factors such as H.I.V., hepatitis B, alcohol, cancer treatment, nicotine and other drugs mostly in combination with a failing liver. Of the twenty percent of the genetic carriers, only a few will develop the disease.
Disease Classification
Porphyria falls under the classification as an enzyme disease. In some medical terminology, it gets a place under neurological symptoms. Liver disease is the third classification if the illness found its origin in the liver or the spine. Some cases fall under more than one or all classifications.
Cultural Relevance
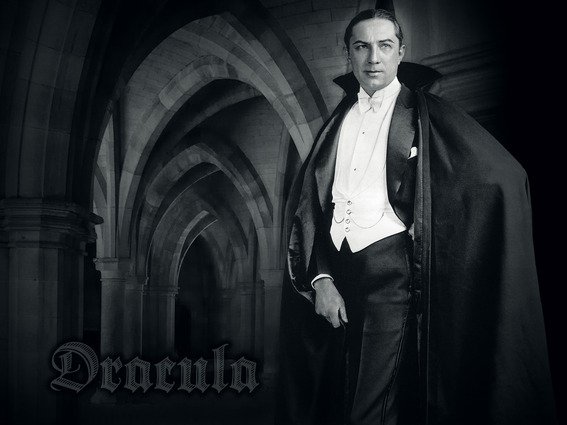

Photo Credit:doctormacro.com
The symptoms of those diseases can explain a lot of the myths and folk legends about vampires. The idea of a vampire is not that far stretched as many people think; the base is a human medical condition. It is always interesting to search for the origins of myths and legends; in the case of vampirism, it is obvious. Bram Stoker will have found his inspiration for his epic novel ‘Dracula’ in the disease.
Modern science dismisses all reference to the myths and legends of vampires, although it is clear that there is a connection between the legend and the symptoms of the disease. The fact that the vampires feed on blood is important because even today blood transfusions are a means to treat the disease.
Another strange association is the reference in the legend of garlic. Science has proven that garlic contains an enzyme that destroys hemoglobin by removing the iron in the molecule. In some cases of the disease, patients have serious jaw- and teeth malformations, facts we find back in the folk legends of werewolves and vampires. Until now, there are some 200 documented cases.
The origin of the disease is the forming of porphyrin and not the lack of hemoglobin. The myth only copied the symptoms but there is no scientific relevance.
The illness Porphyria gets his name from the old Greek language: ‘The Purple Pigmentation’.
Statistics

Photo Credit:tallsay.com
- The chance of being born with Porphyria is 1 in 10.000.
- The chance of getting Acute Intermittent Porphyria is 1 in 20.000.
- The chance of getting hereditary Porphyria is 1 in 1.000.000.
In the United States, the disease is still under active investigation and research. The scientists believe that there are 200.000 patients with the disease. There are no significant statistics in Europe or the rest of the world.

Photo Credit:buzzymag.com
Porphyria is a rare case where medicine and myths get an overlap, it is important to continue the research for this illness, it may be a threat in the future and to stop investigating it would be a mistake. Knowledge is will always be the safeguard for tomorrow.
Enjoyed this content? Feel free to upvote and follow @Thalmaray!

@originalworks
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
The @OriginalWorks bot has determined this post by @thalmaray to be original material and upvoted it!
To call @OriginalWorks, simply reply to any post with @originalworks or !originalworks in your message!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit