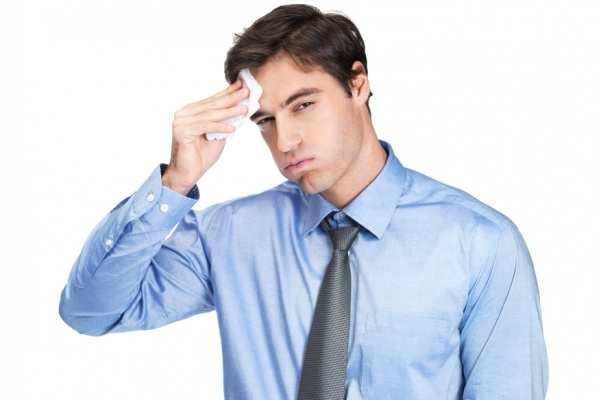

Hyperhidrosis is the exaggerated and uncontrollable production of sweat by the ecrine sweat glands. This excess sweating can be observed in different parts of the body, although hands, feet, armpits and pubic region are the areas that register a greater degree of perspiration, due to their concentration of sweat glands.
Hyperhidrosis is a common pathology that can affect 2% of the white population.
It is observed with greater frequency in patients between 25 and 64 years old.
In 40% of cases, there is usually one more relative who suffers from it, which shows its hereditary character.
Causes
Sweating helps the body stay cool. In most cases, it's perfectly natural. People sweat more in warm temperatures, when exercising, or in response to situations that make them feel nervous, angry, embarrassed, or scared.
When excessive sweating affects the hands, feet, and armpits, it is called primary or focal hyperhidrosis. In most cases, the cause cannot be found. It appears to be hereditary.
If sweating happens as a result of another medical condition, it is called secondary hyperhidrosis. Sweating may occur throughout the body or only in one area. Conditions that cause secondary hyperhidrosis include:
- Acromegaly
- Anxiety disorders
- Cancer
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Certain drug and substance abuse
- Glucose control disorders
- Heart disease, such as heart attack
Characteristics of hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis can be localized or generalized (depending on the affected area), or primary or secondary (depending on its cause).
Localised hyperhidrosis: mainly affects the armpits, palms of the hands, soles of the feet and face.
Generalized hyperhidrosis -affects most or all of the body.
Primary hyperhidrosis:
It begins in childhood or adolescence. Its cause is unknown.
It may persist throughout life, or improve with age.
He may have a family history.
It tends to involve the same parts as localized hyperhidrosis.
It tends to shrink during the night and disappear during sleep.
Secondary hyperhidrosis:
Less common than primary hyperhidrosis.
This is often due to underlying clinical situations.
It is more likely to be asymmetrical and generalized.
It can occur at night and during sleep.
It may be caused by endocrine or neurological causes.
Treatment
Treatment
- Antiperspirants. Excessive sweating can be controlled with strong antiperspirants, which block sweat ducts. Products containing 10% to 20% aluminum chloride hexahydrate are the first treatment for armpit sweating. Some people may be prescribed a product containing higher doses of aluminum chloride, which is applied at night to the affected area. Antiperspirants can cause skin irritation, and large doses of aluminum chloride can damage clothing.
Note: Deodorants do not prevent sweating, but they help reduce body odor.
Medications. Certain medications can prevent the sweat glands from stimulating. These are prescribed for certain types of hyperhidrosis such as excessive sweating in the face. Medications have side effects and are not suitable for everyone.
Iontophoresis. This procedure uses electricity to temporarily disable the sweat glands. It is most effective for sweating of hands and feet. Hands or feet get into water and then a soft electrical current is passed through it. Electricity is gradually increased until you feel a slight tingling sensation. Therapy lasts about 10 to 30 minutes and several sessions are needed. Although side effects are rare, they include skin cracking and blisters.
Botox. Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) is used to treat intense sweating in the armpits, feet, and hands. This condition is called primary axillary hyperhidrosis. Botulinum toxin is injected into the armpit to temporarily block nerves that stimulate sweating. Side effects include pain at the injection site and flu-like symptoms. Botox used for sweating on the palms of the hands can cause mild, but temporary weakness and severe pain.Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS). In some severe cases, a minimally invasive surgical procedure called sympathectomy may be recommended if other treatments have not worked. During the procedure, a nerve is cut, which turns off the signal that tells the body to sweat excessively. This procedure is usually performed on people whose palms sweat much more than normal. It can also be used to treat extreme sweating of the face. ETS does not work as well for people with excessive sweating in the armpits.
Armpit surgery. This is surgery to remove sweat glands in the armpits. The methods employed
.gif)

Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
http://www.scripps.org/articles/1612-hyperhidrosis
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit