Anonymity: Tails vs Whonix vs Qubes OS
Tor and VPNs often get compared side-by-side, while a VPN may be more suitable in one context, Tor may be more suitable in another context. This guide will break down Tor and VPNs so that you know when to use which. This post doesn't have much to do with anonymity, but it doesn't hurt to do the best possible when we need.
Tor
Tor works somewhat differently. Instead of directly connecting to a server of your choice, your connection is encrypted, bounced around three other servers (usually called 'relays' or 'nodes'), before being decrypted and sent to your destination. Now Google sees your request coming for the last of three nodes (also called ‘exit node’). Tor Overview page explains how Tor works.
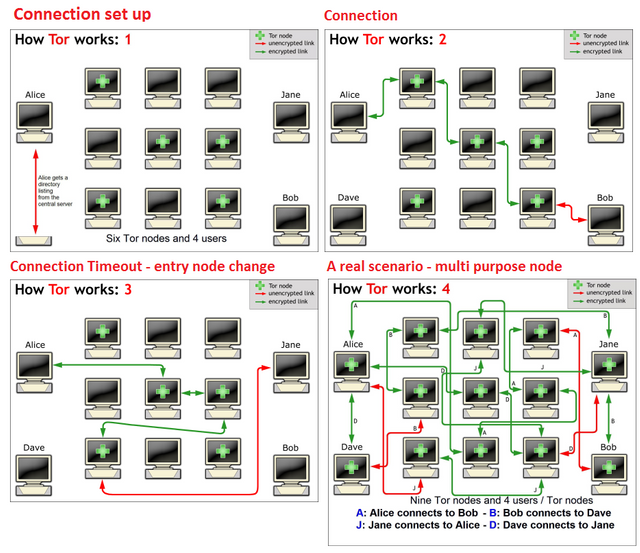
VPN
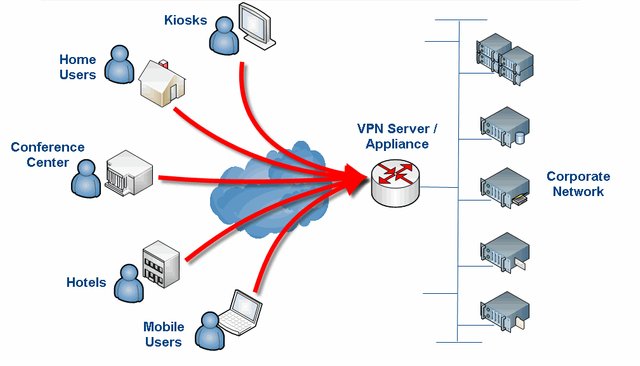
What VPNs do is take your connection, encrypt it, and pass it through a server. This means that instead of your computer directly contacting Google.com, it first goes to a server, and then to Google.com. Google sees your IP as VPN provider’s, not your own. But, anything that you do through a VPN is also known by the operator of the VPN and without your knowing, it may be logging all or some of your online activities.
Tor softwares
Softwares that enable using the Tor network include: Tor Browser, Tails, Whonix and Qubes OS, listed by least to most complicated to use. While studying the subject, I encountered this great post. Comparison is taken mostly from that post.
Tor Browser Bundle
It's a Firefox based browser targeted at casual users, and anonymity (all users looking alike, and preventing tracking) is its main goal.Tails – The Amnesic Incognito Live System
Tails is a live operating system built off Debian GNU/Linux. There is no installation process. You boot your computer with it, and it runs from the temporary media you booted from. When you shut it down, it forgets (amnesic) and helps keep you anonymous while using it (incognito). All network connections are routed through the Tor network and applications attempting to access the internet directly are blocked.
Tails download page has a detailed, easy-to-follow installation tutorial. Tails ISO file can directly be loaded it into VirtualBox. If you’re going to use Tails properly you will need to burn that ISO to some media that you can boot from; usually a CD/DVD or a USB stick.- Tails pros
Live CDs in general are very easy to use. You can burn once, use anywhere which is very handy if you’re on multiple untrusted computers. The default configuration to use Tor provides out-of-the-box anonymity, to the extent that Tor provides it. - Tails cons
Tails does not encrypt documents created during its session by default, but has an encrypted persistent volume feature you can use for this. All Live CDs don’t address the monolith problem; the operating system has no segregation so risky activities in one application can affect others.
- Tails pros
Whonix - anonymity in two parts
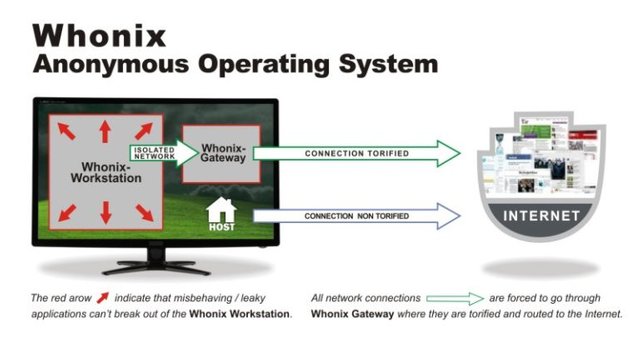
Whonix is designed specifically to provide anonymity while using the internet. It consists of two virtual machines, the gateway and the workstation. The workstation can only talk to the gateway and the gateway connects to the internet via Tor. Both are VirtualBox virtual machine appliances, so you can run it on any operating system that runs VirtualBox.
The Whonix workstation and gateway are configured to use a private network on your host computer. The workstation routes all of its traffic to the gateway, which uses the Tor network to access the internet. All network activity performed on the workstation is done through Tor.
The host machine does not participate in the Whonix private network and therefore continues to use its normal internet connection. See Whonix wiki for more.- Whonix pros
Using the VirtualBox technology ensures that the widest range of people can use Whonix. VirtualBox is available for every major operating system and is free. The default installation and use is extremely easy. No special knowledge or configuration is required to get to work. - Whonix cons
While the Whonix workstation is separated from the host computer, there is no further separation. Performing both risky and non-risky behaviours in the workstation is just as dangerous as doing both on the host computer. Since the anonymity is provided only in the workstation virtual machine, it can be easy to forget to use it, and end up using the host machine by accident.
- Whonix pros
Qubes OS
Qubes OS is best described as a Xen distribution running virtual Linux instances (domains, cubes in Xen parlance). Xen is a very stable and mature bare-metal type 1 hypervisor. This type of virtualization is analogous to what you may be picturing when using a product like VirtualBox with one important difference. A type 1 hypervisor has no operating system running below it which can be compromised. Xen is installed on the bare metal and can then create and manage virtual machines.
This architecture allows Qubes to create separate virtual machines in which to run applications. This ensures that risky applications can’t affect trusted applications, or even write to the underlying file system. This degree of separation doesn’t provide much anonymity in itself, but it does provide a significant degree of protection from malware spread. If you end up being infected with malware from a bad website, or by falling prey to an email phishing scam, it would be hard for that malware to spread outside of the domain it is in.
Qubes calls these Xen domains qubes. It creates a number of qubes in which to assign application instances. For example, surfing miscellaneous websites that you have no reason to trust is probably best done in the untrusted qube. Work related activities on trusted websites and applications may be done in the trusted zone. The point being that each qube only has the potential to affect applications in the same qube.- QubesOS pros
Application separation through the use of sandboxed virtual machines ensures that an exploited app, or malicious javascript, can’t be passed to other applications or to the host operating system. The use of Whonix within QubesOS provides a further level of separation from the internet by forcing all your internet traffic through the Whonix Tor gateway - QubesOS cons
Qubes OS is difficult to test because it does not perform well, or at all, in a virtual machine. There is an unsupported Live CD on the download page. It may or may not work for your system. And, since it is unsupported, it doesn’t really fulfill the job of a Live CD by allowing you to use it to gain confidence as to how a full installation will work. Therefore, you’re pretty much stuck with an all-or-nothing install of Qubes onto your machine to see how it fares.
- QubesOS pros
Now this what I call a professional post. High 5!
Tails is good, but Whonix is the best. Will be happy to follow you, Maybe I see more posts like this.
Linux > VPN > Whonix Tor > AnonSurf
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Steemit is such a great platform to exchange knowledge and experience. I hope to share more useful experiences.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
I can't agree more with you. It seems like byebye Facebook for me :)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit