Self-regulation is understood as situational which learners are not expecting to engage

Image Source
Learners must see how to adjust procedures to particular domains and must feel efficacious about doing as such. This situational specificity is caught in Zimmerman's calculated system including six areas in which one can utilize self-regulatory procedures, for example, techniques, thought processes, time, physical condition, results, and social condition.
Self-regulation is conceivable to the degree that learners have some decision in one or more of these areas. At the point when all parts of an undertaking are foreordained, students may learn, however the wellspring of control is outer Human functioning includes equal interactions between practices, environmental factors, and perceptions and other personal factors.
This reciprocity is exemplified with a critical build in Bandura's theory, seen self-efficacy, or convictions about one's capacities to learn or perform practices at assigned levels. Research demonstrates that students' self-efficacy convictions impact such actions as selection of undertakings, ingenuity, exertion, and accomplishment.

Image Source
Students' practices adjust their efficacy
As students take a shot at errands they take note of their advance toward their learning objectives. Advance markers pass on to students that they are fit for performing admirably, which improves self-efficacy for kept learning. The cooperation between self-efficacy and environmental factors has been exhibited in look into on students with learning inabilities, a significant number of whom hold low self-efficacy for performing admirably.
People in students' social environments may respond to them in view of traits commonly connected with them as opposed to in light of what students really do. Teachers may judge such students as less fit than average learners and hold lower scholarly desires for them, even in content areas in which students with learning inabilities are performing enough.
Convincing proclamations can raise self-efficacy
Instructor's criticism can influence self-efficacy. Students' practices and classroom environments impact one another. Consider a common instructional grouping in which the educator presents data and requests that students guide their regard for an overhead.
Environmental impact on conduct happens when students stop people in their tracks without much cognizant pondering. Students' practices frequently modify the instructional condition. In the event that the educator makes inquiries and students give inaccurate answers, the instructor may reteach a few focuses as opposed to proceed with the lesson.
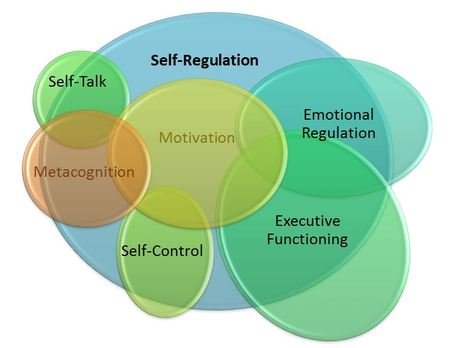
Image Source
3 Subprocesses of Self-regulation
- Self-observation
- Self-judgment
- Self-reaction
These subprocesses are not fundamentally unrelated, they cooperate. While watching parts of one's conduct, one may judge them against norms and respond positively or negatively. One's assessments and reactions set the phase for extra observations of the same behavioral angles. These subprocesses additionally don't work freely of the learning condition. Environmental factors can help the advancement of self-regulation.
Self-observation is simply a similar checking
Self-judgment
Self-judgment alludes to contrasting present execution and one's objective. The conviction that one is gaining objective ground upgrades self-efficacy and maintains motivation. Students who observe an undertaking to be simple may feel that they set their objective too low and may set it higher whenever.
Realizing that comparative others played out an undertaking can advance self-efficacy and motivation, students are able to trust that on the off chance that others can succeed, they can also. Students who trust they have not gained worthy ground won't wind up disheartened on the off chance that they feel efficacious about succeeding and trust that an alternate methodology will deliver better outcomes.
Image Source
Self-reactions
Self-reactions to objective advance apply motivational impacts. Students who judge objective advance as adequate and who foresee fulfillment from objective achievement will feel efficacious about proceeding to enhance and roused to finish the errand. Negative assessments won't really diminish motivation if students trust they are fit for enhancing, for example, by working harder.
Motivation won't increment if students trust they do not have the capacity to succeed or to move forward. Guidelines to individuals to react evaluatively to their exhibitions can influence motivation. Individuals who trust they can perform better hold on longer and work harder. Assessments are not personally attached to level of execution.
Image Source
References:
https://study.com/academy/lesson/self-regulation-theory-definition-strategies.html
http://faculty.washington.edu/jdb/452/452_chapter_06.pdf
http://homepages.rpi.edu/~verwyc/bandura.htm
Self regulation is key in our human development. It helps regulate and make our body systems function properly
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This part here. This should be a must to all teacher..hmmmm I think I will let someone read this post quick!
This is a very enlightening post!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit