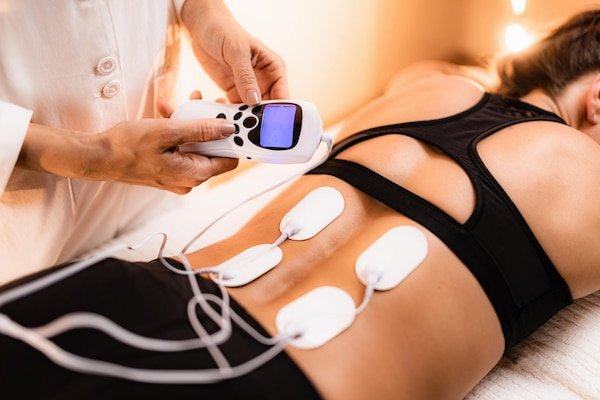
Shockwave therapy (ESWT), or "pain therapy," is a non-invasive medical treatment that uses high-intensity ultrasound to treat various musculoskeletal conditions and speed up the healing process. The therapy involves the transmission of high-energy waves to the affected body area through a portable device. Musculotendinous injuries may require specific treatments for the patient to recover fully. The shockwave treatment works through the skin on tendons or muscles and sometimes on bones through a small, portable device. ESWT works in the affected area by stimulating blood flow, which leads to tissue regeneration and the formation of new blood vessels.
Do You Need a Shockwave Treatment?
The shockwave treatment also triggers an inflammatory response, which can benefit chronic conditions that do not respond well to other therapies. In addition, shock waves can stimulate scar tissue breakdown, helping alleviate pain and improve mobility. That therapy is commonly used to treat musculoskeletal conditions such as plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, rotator cuff injuries, and calcific tendonitis. ESWT may also be beneficial for certain bone fractures and injuries that do not heal as they would typically (delayed healing or pseudarthrosis).
How Shockwave Therapy Works
During a shockwave therapy session , there are usually several steps to follow. First, an orthopaedic specialist will determine whether the therapy suits the patient. In this regard, information related to the medical history is obtained, a physical examination is performed, and, if necessary, various tests are performed. During the therapy, the patient is placed in a comfortable position that allows easy access to the area to be treated. Shock waves are delivered through the skin using a gel applied locally, while a hand-held device emits controlled pulses that will reach the underlying tissues.
The unique applicator transmits much energy, using compressed air, deep into the affected area. The wave creates pressure on the affected tissues, increasing cell permeability and stimulating microcirculation and cell metabolism. As a result of this impact, the formation of blood vessels occurs, collagen production is stimulated, and inflammation decreases. Therefore, the metabolic processes in the tissues are improved, joint mobility is restored, and the feeling of pain disappears. The patient may feel a slight discomfort or pain, the intensity of which varies according to tolerance and the sensitivity of the treated area.
When Is Such Therapy Recommended?
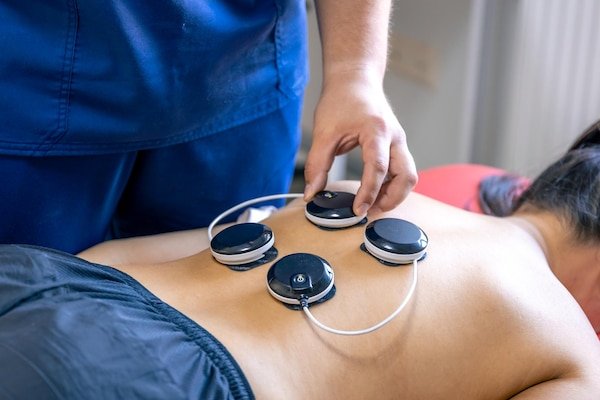
The duration of a shockwave treatment is usually short, about 10-15 minutes. The number of sessions required will depend on the specific condition , severity, and the patient's response to therapy. The intensity of the treatment can be adjusted to ensure an effective and minimally painful treatment. ESWT treatment is not necessarily the first option for patients experiencing various conditions or pain. Such therapy may be recommended for some musculoskeletal problems, but only when the patient has not responded well to other conservative treatments.
ESWT therapy is usually considered when conservative approaches such as rest, physical therapy, medications, or corticosteroid injections have not helped to relieve symptoms and improve health. The decision to recommend shock wave therapy is made by a medical specialist only after a thorough evaluation. Even though shockwave therapy is not new, it appeared half a century ago, and its applications continue to be developed. Also, the benefits of treatment are numerous, including a non-surgical method, allowing the patient to carry out usual activities without needing recovery after the therapy session.
The benefits of this procedure are plenty and include:
• the possibility of combining it with other therapies to facilitate a faster return to daily activities (sports/work);
• ideal for athlete’s injuries;
• less expensive option compared to surgical interventions;
• promotes healing even in complex cases;
• favours the regeneration of soft tissues.
Shockwave treatment is mainly used in the treatment of common musculoskeletal conditions . These include:
• tendinopathies of the upper and lower extremities;
• trochanteric bursitis and tibial stress syndrome;
• patellar tendinopathy, plantar fasciitis, and adhesive capsulitis;
• non-consolidation of bone fractures;
• avascular necrosis of the femoral head;
• osteoarthritis of the knee.
In What Situations Is This Therapy Contraindicated?
Although it does not have side effects, this therapy is not recommended for any injury. One such case is when the soft tissue is completely torn, and the risk of damage from these waves can increase. Such a procedure is also not considered if an injury requires surgery. Also, such treatment should not be an option in these particular situations:
• near the uterus during pregnancy;
• when there are malignant tumours;
• next to the spine or to the brain;
• close to the lungs;
• in cases where any bleeding disorder exists.
Specialists will recommend shockwave therapy treatment to those patients who can benefit from it. Each therapy plan is customized according to individual needs and health status. That treatment is a temporary pressure disturbance that propagates rapidly, three-dimensionally, in space. There is a tension and sudden increase (within nanoseconds) of the pressure, plus the cavitation phenomenon, as a result of the negative wave propagation phase after the initial positive phase. Currently, the essential physics of this treatment is associated with some physical parameters involved in evaluating the amount of energy supplied to the target tissue.
What Does This Therapy Consist of?
The basis of shockwave treatment is, therefore, a release of high energy with a speed more significant than the speed of sound. The main effect consists in triggering microscopic biological effects that include tissue regeneration. Through the pressure it exerts on the treated tissues, the shock waves increase cellular permeability, stimulate microcirculation and cellular metabolism, and increase collagen production, thus stimulating healing and the dissolution of microcalcification deposits in various soft tissues. Doctors apply these waves with the help of a particular applicator head attached to the ultra-modern device in their clinics.
A gel is also necessary to transmit the waves only to the area to be treated; they do not disperse. In the respective area, sometimes you can feel an embarrassment, a discomfort that reduces as the waves take effect. Even at the end of the first session of shockwave therapy, you can see an improvement in pain and a reduction in muscle contracture, allowing greater freedom of movement than at the moment of arrival at the clinic. Benefit: A physical therapy program can be started quickly if this recovery method is also indicated for the patient, so time is gained for recovery as soon as possible!