♕ KEY POINTS ♕
The smart money concept in forex trading involves understanding the behavior of institutional players, such as banks and hedge funds, and analyzing supply and demand dynamics, order blocks, and price patterns.
SMC is often seen as a repackaged version of price action trading with a long history of producing positive results in various asset classes.
Skeptics argue that the liquidity contributed by retail traders is relatively insignificant in the eyes of institutional market makers, making it unlikely that they would specifically target retail traders.
The choice to use SMC trading ultimately depends on individual preferences and the trader’s ability to understand its theory and apply it to the chart.
The Smart Money Concept strategy has gained viral attention over the past few years, and it’s mostly for good reasons: it seems to be working. At least for some people. But what’s unique about this SMC strategy, anyway?
To be accurate, the SMC is not a strategy, per se. But it’s more of a theory or philosophy.
Now, you are probably curious about this new concept. So, here, we reveal everything you need to know about the Smart Money Concept (SMC) strategy. Or theory? Philosophy? Anyway, let’s start.
✓ What is the Smart Money Concept in Trading?
So, what exactly is Smart Money concerned with? Simply put, it’s all about supply, demand, and market structure. Market makers, or the “smart money,” often leave footprints of their trading decisions on the chart, and smart money concept traders are to follow these footprints.
Retail traders tend to believe the market is fair for them to make money, but the SMC might prove otherwise. Here’s how the theory goes:
Market makers such as banks, hedge funds, and other prominent market participants who can move substantial amounts of capital can allegedly manipulate the market against retail traders. While this may sound like a conspiracy theory, it is worth looking into.
These institutions are in the business of making profits or supplying the needs of a country or a big corporation. They are not shy about using their vast resources and market knowledge to their advantage, including setting traps for retail traders to part with their money.
Retail traders, often ignorant of these activities, are more likely to fall victim to the market’s unpredictable swings.
However, that’s not the entire idea of SMC. Very often, these big players enter the market with good intentions. For instance, a government that must purchase large quantities of a commodity, such as wheat, soybeans, or crude oil, can obviously push prices in a specific direction.
So, based on the SMC theory, financial markets are largely controlled by financial institutions, hedge funds, and governments. They significantly impact price movements in the market, and therefore, retail traders must be alert to their intentions to predict where the market is heading.
That, in a nutshell, is what the SMC is all about. If you believe in smart money concepts trading, then you, as an individual trader, should follow smart money.
♕ SMC Key Concepts ♕
- Rather than being just a theory, SMC is a complete trading methodology with its unique terminologies and concepts. Let’s take a closer look at some of SMC’s concepts and trading techniques.
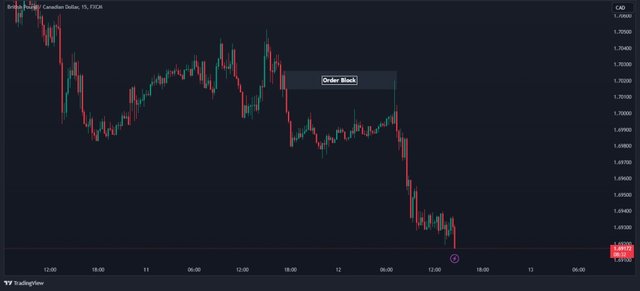
✓ Order Blocks (OB) ✓
This concept is fundamental to understanding SMC. Essentially, order blocks refer to a market condition when central banks, governments, and large financial institutions accumulate or distribute large quantities of an asset through several big orders. They do so to be able to purchase the asset without creating panic and high volatility in the market.
On a price chart, order blocks typically appear as a ranging market (as seen in the chart below). However, to properly identify order blocks in the market, you must use additional tools, such as level 2 market data and volume indicators.
✓ Breaker Blocks ✓
These are order blocks that fail to hold the price level in a given trend. They represent price levels where market makers intentionally break through support or resistance levels to trigger stop-loss orders from retail traders.
On a trading chart, breaker blocks appear as levels where the price breaks above or below a certain level. Based on the SMC theory, most smart money orders are placed at this level.
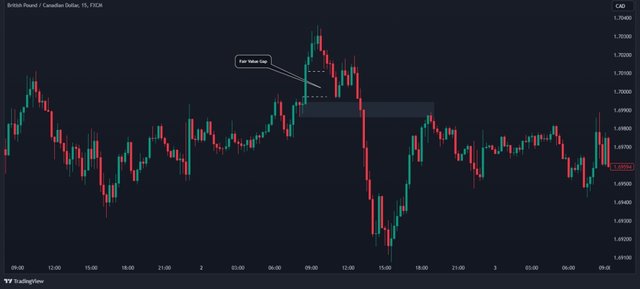
✓ Fair Value Gaps (FVG) ✓
- Fair value gaps, also referred to as FVGs, are a unique trading concept that occurs when the market moves quickly from one price level to another, often leaving gaps on price charts. SMC traders pay close attention to these gaps as they can indicate significant shifts in market sentiment.
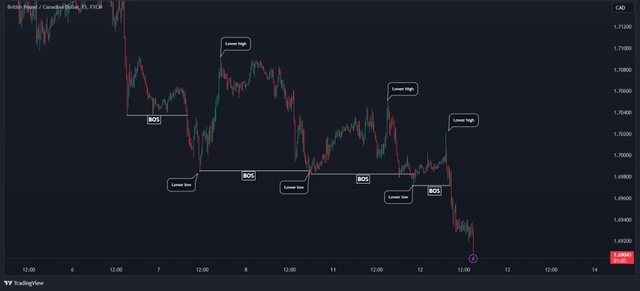
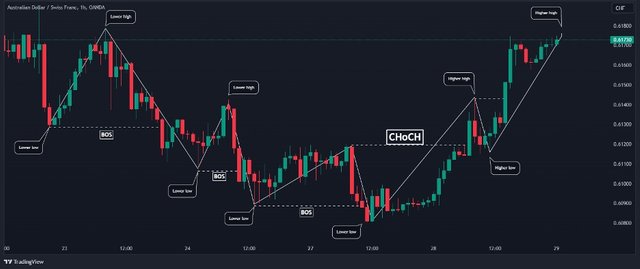
✓ Break of Structure (BOS) ✓
- The break of structure is a concept that focuses on identifying shifts in the market’s overall trend. A break of structure is said to have taken place when the price sets a new high or a new low while breaking the former ones.
✓ Change of Character (Choch) ✓
- Change of Character, often abbreviated as Choch, refers to a situation where the market’s behavior shifts abruptly. It is a sudden change in volatility, volume, or price action, suggesting a weakness in the current trend and a possible reversal.
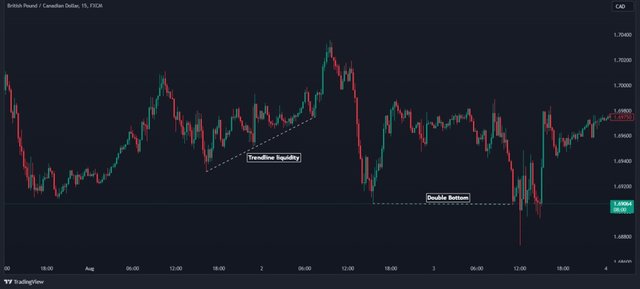
✓ Liquidity ✓
- Liquidity is a crucial factor in SMC trading. It is a point in the price of an asset where orders are either sitting above or below, waiting to be collected. There are different types of liquidity, e.g., trendline liquidity, buy-side liquidity, sell-side liquidity, double tops, and double bottoms, etc.