#303 Information: April 17, 1996

“The Helix nebula (New General Catalog number 7293) is estimated to be a mere 450 light-years from the Sun, in the direction of the constellation Aquarius. At that distance it may well be the closest planetary nebula, offering a dramatic snapshot of a brief final evolutionary stage in the life of a solar-type star. In this color image the nebula glows red in the light of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms energized by the ultraviolet radiation from the central star. The main rings themselves, though faint, have an angular size about half that of the full moon and span about 1.5 light-years. Because it is so close, it is a prime subject for study by astronomers. When the Hubble Space Telescope was focused near the inner edge of the main ring, at about the 12 o'clock position in the above image, it resolved some of the spoke like radial structures visible into intriguing cometary knots. Information: The Scale of the Universe Debate in April 1996"
Copyright: Anglo-Australian Telescope
Board
#304 Latest Comet Hyakutake images: April 18, 1996

“Can you find Comet Hyakutake in the above picture? In this gorgeous photo, the starry night sky of April 9th is pictured with its new comet visitor. In the foreground is a pond with the lights of Kansas City, Missouri on the western horizon. On the upper left, the constellation of Orion is visible. At the center, the brightest object in the picture is the planet Venus. Venus's reflection can be seen in the pond. On the right - halfway between Venus and the photograph's edge - can be seen two bright objects fairly close to each other. Of these two, look closely at lower right object. See the tail? Comet Hyakutake is still visible for Northern observers in the Western sky and now has begun to brighten again as it nears the Sun. Latest Comet Hyakutake images: APOD Hyakutake Archive, JPL, Fayetteville Observer-Times, NASA's Night of the Comet, ICSTARS, Jerry Lodriguss, ScienceWeb, Crni Vrh Obs.,"
Copyright: Vic
WinterICSTARS
#305 Information: April 19, 1996
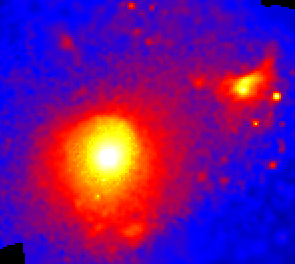
“This ROSAT image of the Virgo cluster of galaxies reveals a hot X-ray emitting plasma or gas with a temperature of 10-100 million degrees pervading the cluster. False colors have been used to represent the intensity of X-ray emission. The large area of X-ray emission, just below and left of center, is about 1 million light-years across. The giant elliptical galaxy M87, the biggest member of the cluster, is centered in that area while other cluster members are scattered around it. By adding up the amount of X-ray emitting gas astronomers have found that its total mass is up to 5 times the total mass of the cluster galaxies themselves - yet all this matter still does not produce nearly enough gravity to keep the cluster from flying apart! Where is the unseen mass? Because galaxy clusters are the largest structures in the Universe, this mysterious Dark Matter must dominate the cosmos but its nature is still an open question. Information: The Scale of the Universe Debate in April 1996"
Copyright: Public domain
#306 Information: April 20, 1996
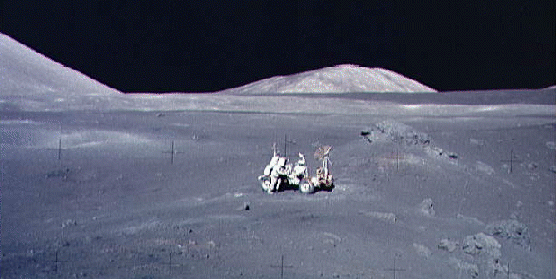
“Buzz Aldrin, Apollo 11 Lunar Module pilot and the second human to walk on the Moon described the lunar landscape as "a magnificent desolation". Dramatic pictures from the Apollo missions to the moon's surface testify to this apt turn of phrase. Near the Apollo 17 landing site, Family Mountain (center background) and the edge of South Massif (left) frame the lunarscape in this photo of astronaut Harrison Schmitt working alongside the lunar roving vehicle. Schmitt and fellow astronaut Eugene Cernan were the last to walk on this magnificent desolation. Information: The Scale of the Universe Debate in April 1996"
Copyright: Public domain
#307 Tomorrow's picture: April 21, 1996
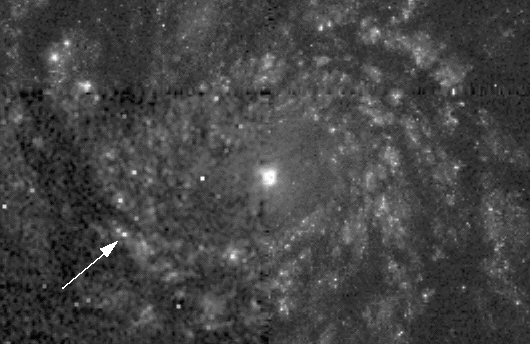
“In 1994, a new star in a distant galaxy was seen by amateur astronomers, who alerted the world to their discovery of a supernova. Near the nucleus of spiral galaxy M51, popularly known as the Whirlpool, this supernova (1994I) is identified as the bright spot indicated by the arrow in the lower left of this Hubble Space Telescope image. Supernovae are violent death explosions of stars that eject radioactive debri clouds. They are often discovered by amateur observers dedicated to systematic searches of the sky and are of intense interest to astronomers who hope to learn what kind of stars generate these explosions and what chemical elements are produced and mixed into space. Distances to these these intrinsically bright events can also be determined, providing crucial yardsticks for measuring the Scale of the Universe."
Copyright: Public domain
#308 Tomorrow's picture: April 22, 1996

“While exploring the inner edge of the Helix Nebula with the Hubble Space Telescope's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, astronomers were able to produce this striking image - rich in details of an exotic environment. This planetary nebula, created near the final phase of a sun-like star's life, is composed of tenuous shells of gas ejected by the hot central star. The atoms of gas, stripped of electrons by ultraviolet radiation from the central star, radiate light at characteristic energies allowing specific chemical elements to be identified. In this image, emission from nitrogen is represented as red, hydrogen emission as green, and oxygen as blue. The inner edge of the nebula (the direction to the central star) is toward the bottom right. Clearly visible close to the inner edge are finger shaped "cometary knots"."
Copyright: Public domain
#309 Latest Comet Hyakutake images: April 23, 1996

“It was a starry night in April (April 9th, 1996, 9:32 pm CDT to be exact) near Lone Jack, Missouri when Comet Hyakutake graced this astronomically rich field. Making an appearance as the brilliant evening star, Venus is overexposed at the far left. Just below Venus and slightly to the right, the Pleiades star cluster (M45) glistens. On the right hand side of the image, the comet itself shows a bright blue tail extending upwards past the nearby star cluster in the constellation Perseus (top right, the Alpha Persei Group). Hyakutake, receding from the Earth and appoaching the Sun, will sink into the western horizon at sunset in late April, disappearing from Northern Hemisphere skies. Latest Comet Hyakutake images: APOD Hyakutake Archive, JPL, Fayetteville Observer-Times, NASA's Night of the Comet, ICSTARS, Jerry Lodriguss, ScienceWeb, Crni Vrh Obs.,"
Copyright: Vic
WinterICSTARS
#310 Congratulations: April 24, 1996

“What are those strange blue objects? Many are images of a single, unusual, beaded, blue, ring-like galaxy which just happens to line-up behind a giant cluster of galaxies. Cluster galaxies here appear yellow and -- together with the cluster's dark matter -- act as a gravitational lens. A gravitational lens can create several images of background galaxies, analogous to the many points of light one would see while looking through a wine glass at a distant street light. The distinctive shape of this background galaxy -- which is probably just forming -- has allowed astronomers to deduce that it has separate images at 4, 8, 9 and 10 o'clock, from the center of the cluster. Possibly even the blue smudge just left of center is yet another image! This spectacular photo from HST was taken in October 1994. The first cluster lens was found unexpectedly by Roger Lynds (NOAO) and Vahe Petrosian (Stanford) in 1986 while testing a new type of imaging device. Lensed arcs around this cluster, CL0024+1654, were first discovered from the ground by David Koo (UCO Lick) in 1988. Congratulations: Hubble Space Telescope is six years old today!"
Copyright: Public domain
#311 Tomorrow's picture: April 25, 1996

“In the center of M51, a spiral galaxy 23 million light-years away, astronomers have identified a dense region of young stars. The graceful swirling arcs of this galaxy's spiral arms have inspired its popular name, "The Whirlpool Galaxy". This Hubble Space Telescope image of its nucleus reveals the light from millions of stars, perhaps one tenth the age of the Sun, packed into the bright central region. This area is a mere 80 light-years across -- the stars are so crowded here that the view from a hypothetical planet orbiting one of these distant suns would be of a continuously bright sky! The dark "Y" shape visible within this region is an indication that lanes of dust are present, partially blocking the intense starlight."
Copyright: Public domain
#312 Tomorrow's picture: April 26, 1996

“G1, pictured above, is the brightest known globular cluster in the whole Local Group of galaxies. Also called Mayall II, it orbits the center of the largest nearby galaxy: M31. G1 contains over 300,000 stars and is almost as old as the entire universe. In fact, observations of this globular cluster show stars as old as the oldest of the roughly 250 known globular clusters in our own Milky Way Galaxy. This image was taken with the Hubble Space Telescope in July of 1994. It shows, for the first time, the same fine detail in a distant globular cluster as can be discerned from a ground-based telescope of a globular cluster in our own Galaxy."
Copyright: Public domain
Upvote! Resteem! Comment! As you like it! Thank you for attention!