Spread betting is a type of derivative trading in which traders speculate on the future price movement of the underlying instrument. Just like with CFD trading, the trader doesn’t actually own the underlying instrument, but the trader is only betting on the future rise or fall in the price.
Learn More: Complete Spread Betting Guide for Beginners
Each spread bet consists of the spread, the bet size (or bet per point) and the bet duration.
Watch: What is a Spread Bet?
The Spread
The spread is the difference between the buying and selling price of the underlying security and represents the profit of your broker. Nowadays, spreads are usually very tight and depend on the liquidity of the traded instrument – less liquid financial instruments have wider spreads than more liquid ones, and vice-versa.
If you think that a currency, stock or even an entire stock index will rise in value in the coming period, you will deal with the buying price (or offer price) of the spread. On the contrary, if you think that the financial instrument will fall in value, you would deal with the selling price (or bid price) of the spread. A typical spread is shown in the following image.
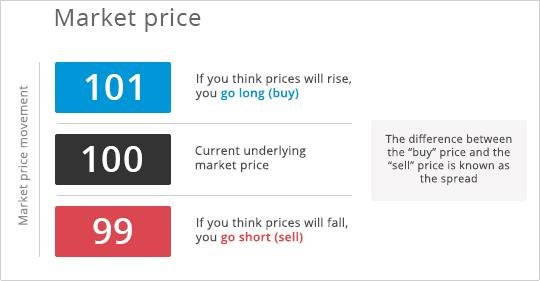
Let’s say that a stock is currently trading at $100. Since the buy or offer price is always higher than the sell or bid price, you would deal with $101 if you want to speculate on a future rise in the stock’s price, or with $99 if you want to speculate on a future fall in the stock’s price.
The Bet Size
The next major building block of a spread bet is the bet size, or bet per point. This represents your position size and directly impacts your profit or loss of the bet, which are calculated as the difference between your opening and closing price multiplied by your bet per point.
Usually, spread betting brokers in the UK measure the price movement of a financial instrument in points, i.e. a movement of one penny in UK equities would equal to a movement of one point. If your bet size is £5 per point, a price movement of one British pound (100 points) will result in a profit or loss of £500.
The Bet Duration
Finally, the bet duration is the period of time before your bet expires. Daily funded bets are the most commonly used bet duration for short-term market speculation. With these bets, your broker will automatically adjust your balance to reflect the daily funding costs of your bet until you decide to close it.
The second bet duration type is a quarterly bet which is usually used when betting on futures contracts and expires by the end of a quarterly period.
Origins of Spread Betting
Charles K. McNeil, a mathematics professor who later became a trader, has been widely considered as the inventor of the spread betting concept in the 1940s, but it was not until the 70s that spread betting increased in popularity. While the first offered spread bet was on gold as it was extremely difficult to participate in the gold market at that time, traders can spread bet on almost all financial markets nowadays.
A spread betting scenario
Let’s say that the stock ABC trades at $50, with the offer price set at $50.50 and the bid price set at $49.50. If you expect that price of the stock to rise, you could place a bet at the buying price of $50.50 and make a profit from the difference between the buying and selling price if your analysis proves correct.
With a bet size of $1 per point and the price rising to $55, you would make a profit of $400 by closing your position (selling) at $54.50, assuming that the spread is unchanged.
Spread Betting vs Stock Trade
There are certain benefits of spread betting compared with a usual stock trade. Besides the lower taxes (the UK has no taxes at all on spread betting profits), commissions are also usually lower and the availability of leverage can significantly magnify your profits (and losses.)
Commissions – With spread betting, usually the only trading cost you’ll face is the spread, i.e. the difference between the offer and bid price. A stock trade typically has additional trading fees and commissions.
Leverage and Margin – The availability of leverage and margin trading makes spread betting extremely attractive to many traders. Trading on leverage requires a significantly lower cash outlay to get the same market exposure compared with trading without leverage.
Spreads – Most spread betting brokers feature very tight spreads which depend on the liquidity of the underlying instrument. Liquid instruments, such as Amazon stocks, for example, have tighter spreads than exotic instruments.
Spread Betting and Risk Management
Unlike its name might suggest, you should not consider spread betting as a betting activity. By having a sound analysis and strict risk management rules, you can significantly improve your odds of winning. Always use stop-loss orders when you spread bet and don’t overtrade.
Stop-Loss Orders – A stop loss order automatically closes your position at the best possible price once the market price reaches a pre-specified threshold. However, certain market conditions may cause that your stop-loss order gets filled at a more unfavourable price than specified.
Guaranteed Stop-Loss Orders – Unlike normal stop-loss orders, guaranteed stop-losses are always executed at the pre-specified price, regardless of the current market conditions. These types of stop-losses usually carry an additional charge from your broker.
In summary
Spread betting is a popular type of derivative trading in which the trader doesn’t own the underlying instrument. Instead, the trader only speculates on the future price movements of the instrument. The profit of a spread bet is calculated as the difference between the opening and closing price, multiplied by the bet size (bet per point).
A point usually refers to one penny in equities, or to the fourth decimal place in currency exchange rates. Traders who believe that the price will rise in the future are buying at the buy (or offer) price, while traders who believe that the price will fall in the future are selling at the sell (or bid) price.
Bio: Phillip Konchar is the Head Tutor providing spread betting education at My Trading Skills. Over the past 10 years he has provided trading education and market analysis to a range of financial institutions and specialises in the application of technical analysis in margin trading.
Hello @joeflanagan! This is a friendly reminder that you have 3000 Partiko Points unclaimed in your Partiko account!
Partiko is a fast and beautiful mobile app for Steem, and it’s the most popular Steem mobile app out there! Download Partiko using the link below and login using SteemConnect to claim your 3000 Partiko points! You can easily convert them into Steem token!
https://partiko.app/referral/partiko
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Overall, it's a very good article but I'd like to add some points so even spread betting novices can understand it.
Financial spread betting is very different from all other derivatives as it's made as simple as possible and removes the charade of the currency fluctuations.
On top of it we can compare spread betting against many trading instruments but CFDs come the closest but for an average person spread betting is more beneficial.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit