Bitcoin is the first-ever currency to usher the era of the peer-to-peer transfer. It is not like that previously it was not attempted, but Bitcoin established the legacy of digital currencies, p2p transfer by solving the long-standing issues like double-spending which is one of the major challenges in digital currencies as a medium of exchange.
Bitcoin is also known to have redefined privacy in a way that privacy is respected, yet auditable by a third party.
In this publication, I will detail both the wonderful features of Bitcoin.

Bitcoin redefines Privacy: Making it private yet auditable by a third party
In the traditional banking system, the transactions or the business between two parties happens through a third party or a trusted entity which is the Bank. The access to the business or transaction is very limited, not available for a third-party audit, it requires permission to conduct an audit, which is a time-consuming process.
Further, the business between two parties in the traditional system is not that private as the intermediary(Bank) still has all the information about the business, so the corrupt individuals of a Bank can still have that sensitive information of the businesses between two individuals/entities.
Bitcoin redefines privacy.
First off, it does not require any trusted entity for the transaction to happen between two peers. Second, all the transactions are publicly available in the distributed ledger (making it auditable by any third party without seeking permission from anyone), yet making it anonymous, respecting the privacy of the peers, as the public keys are not attached to the identity of any person, they are anonymous.
So you have the flow of business information, but you won't be able to know who the person behind the public key is. However, repeated transactions from the same address could help to establish the owner of the public key by little social engineering. To shield you from that probability, it enables you to create a new key pair for each new transaction you go for.
Put simply, with Bitcoin, you get to know the time of a trade, size of a trade, but not who the parties behind the trade, unless the parties reveal that to you.

Bitcoin solves the biggest ever problem of digital currencies: "Double-spending"
One of the three functions(Store of Value, Medium of Exchange & Unit of Account) of money is Medium of Exchange. The biggest challenge with the Medium of Exchange in the case of digital currency is double-spending.
For a centralized digital currency, it is not an issue, as a central authority always gets to check the transaction. But for a trustless network, it is not that straight forward to prevent double-spending. However, Bitcoin solves it and that is how it has gained recognition all across.
Bitcoin is a trust-less network that is run by the nodes, nodes are simply the computers that run the software of the Bitcoin chain. All the transactions that happen in this network are broadcasted to all the nodes, then the nodes verify the transaction & confirm it.
Unlike a bank or centralized authority, each node has the same copy of the Blockchain. That is why it is decentralized and it is also difficult to corrupt all the nodes at any given time.
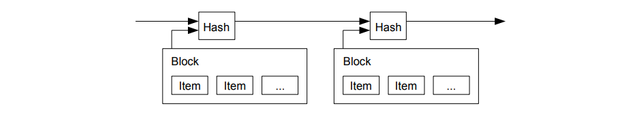
The ones that validate the transactions in the network are called miners, they are put into this task of validating the transaction through the Proof-of-work mechanism, they are incentivized for the computing effort. The block producing time in Bitcoin is 10 mins. So the miners are tasked to validate the transaction, record them on the public ledger, which also becomes a part of the "chain of blocks", it is append-only, means only blocks can be added, can not be erased.
Now how does it prevent double-spending?
Double-spending means you try to spend the same asset more than once. For example, you have 1 BTC and you try to send the same 1 BTC to both A & B.
Bitcoin is the first-ever digital currency to solve this problem of double-spending. It does so by Order & Timestamping.
As said earlier, it has a distributed public ledger in which all the transactions are added after mined by the miners through the PoW mechanism. But the most important thing that prevents double-spending is that the Blockchain is in order and append-only. That means an unordered blockchain is not all possible.
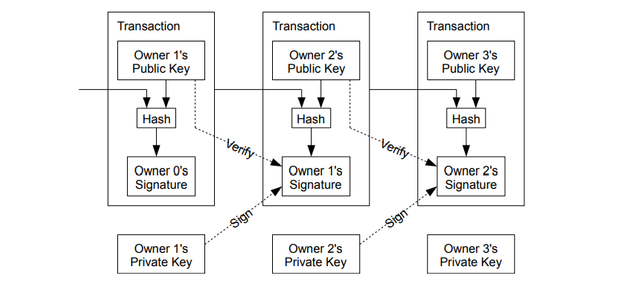
Each time a transaction happens in Bitcoin, the sender has to sign the hash of the previous transaction & public key of the next owner, that is why it is known as the chain of digital signatures.
Further, it employs timestamping of the hash of a Block. The cryptographic hash function takes all the input of the data to produce a unique output that we call hash. So with each transaction, a hash will be added to it. Bitcoin prevents double-spending by time-stamping this hash.
Timestamping of the hash proves that the data which is included in the hash is not created previously, so when this hash is broadcasted to the nodes, they will get to know which hash is created first and which one later(to prevent double-spending). Further, it also includes the previous timestamp. That means it will be in a chronological sequence, the chain of the events/transactions.
- It has a public distributed ledger.
- All the nodes agree to a single history.
- The longest chain is the valid chain.
- In the event of the double-spending, the nodes will get to agree, which one is the valid one.
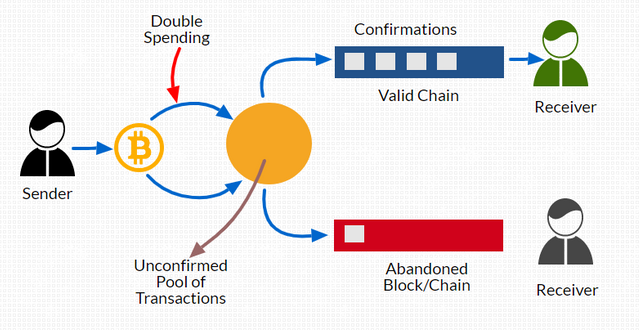.png)
Whenever a transaction in the Bitcoin network is initiated it will go into the unconfirmed pool, then Bitcoin miners are tasked to solve the cryptographic puzzle(PoW mechanism) to verify and validate the transaction. The one that is validated is added in the Block (along with a timestamp and its previous timestamp). That way any second attempt to spend the same amount will be invalidated and pulled out from the network.
In case both the transactions are taken simultaneously from the unconfirmed pool, the one which got the first confirmation will be considered valid.
Thank you.

Cc:-
@steemitblog
@steemcurator01
@steemcurator02