What is GST?
Goods & Services Tax is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that will be levied on every value addition.
( )
)
To understand this, we need to understand the concepts under this definition. Let us start with the term ‘Multi-stage’. Now, there are multiple steps an item goes through from manufacture or production to the final sale. Buying of raw materials is the first stage. The second stage is production or manufacture. Then, there is the warehousing of materials. Next, comes the sale of the product to the retailer. And in the final stage, the retailer sells you – the end consumer – the product, completing its life cycle.
So, if we had to look at a pictorial description of the various stages, it would look like:
(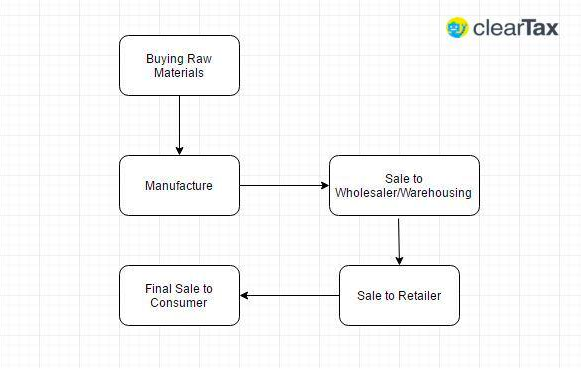 )
)
GST basics
Goods and Services Tax will be levied on each of these stages, which makes it a multi-stage tax. How? We will see that shortly, but before that, let us talk about ‘Value Addition’.
Let us assume that a manufacturer wants to make a shirt. For this he must buy yarn. This gets turned into a shirt after manufacture. So, the value of the yarn is increased when it gets woven into a shirt. Then, the manufacturer sells it to the warehousing agent who attaches labels and tags to each shirt. That is another addition of value after which the warehouse sells it to the retailer who packages each shirt separately and invests in marketing of the shirt thus increasing its value.
( )
)
Value-addition
GST will be levied on these value additions – the monetary worth added at each stage to achieve the final sale to the end customer.
There is one more term we need to talk about in the definition – Destination-Based. Goods and Services Tax will be levied on all transactions happening during the entire manufacturing chain. Earlier, when a product was manufactured, the centre would levy an Excise Duty on the manufacture, and then the state will add a VAT tax when the item is sold to the next stage in the cycle. Then there would be a VAT at the next point of sale.
Why is Goods and Services Tax so Important?
So, now that we have defined GST, let us talk about why it will play such a significant role in transforming the current tax structure, and therefore, the economy.
Currently, the Indian tax structure is divided into two – Direct and Indirect Taxes. Direct Taxes are levies where the liability cannot be passed on to someone else. An example of this is Income Tax where you earn the income and you alone are liable to pay the tax on it.
In the case of Indirect Taxes, the liability of the tax can be passed on to someone else. This means that when the shopkeeper must pay VAT on his sale, he can pass on the liability to the customer. So, in effect, the customer pays the price of the item as well as the VAT on it so the shopkeeper can deposit the VAT to the government. This means that the customer must pay not just the price of the product, but he also pays the tax liability, and therefore, he has a higher outlay when he buys an item.
This happens because the shopkeeper has paid a tax when he bought the item from the wholesaler. To recover that amount, as well as to make up for the VAT he must pay to the government, he passes the liability to the customer who has to pay the additional amount. There is currently no other way for the shopkeeper to recover whatever he pays from his own pocket during transactions and therefore, he has no choice but to pass on the liability to the customer.
Goods and Services Tax will address this issue after it is implemented. It has a system of Input Tax Credit which will allow sellers to claim the tax already paid, so that the final liability on the end consumer is decreased.
(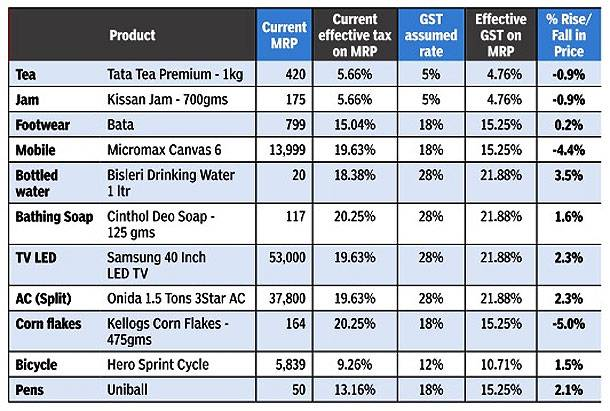 )
)
Let us understand this with a hypothetical numerical example.
Say a shirt manufacturer pays Rs. 100 to buy raw materials. If the rate of taxes is set at 10%, and there is no profit or loss involved, then he has to pay Rs. 10 as tax. So, the final cost of the shirt now becomes Rs (100+10=) 110.
At the next stage, the wholesaler buys the shirt from the manufacturer at Rs. 110, and adds labels to it. When he is adding labels, he is adding value. Therefore, his cost increases by say Rs. 40. On top of this, he has to pay a 10% tax, and the final cost therefore becomes Rs. (110+40=) 150 + 10% tax = Rs. 165.
Now, the retailer pays Rs. 165 to buy the shirt from the wholesaler because the tax liability had passed on to him. He has to package the shirt, and when he does that, he is adding value again. This time, let’s say his value add is Rs. 30. Now when he sells the shirt, he adds this value (plus the VAT he has to pay the government) to the final cost. So, the cost of the shirt becomes Rs. 214.5 Let us see a breakup for this:
Cost = Rs. 165 + Value add = Rs. 30 + 10% tax = Rs. 195 + Rs. 19.5 = Rs. 214.5
So, the customer pays Rs. 214.5 for a shirt the cost price of which was basically only Rs. 170 (Rs 110 + Rs. 40 + Rs. 30). Along the way the tax liability was passed on at every stage of transaction and the final liability comes to rest with the customer. This is called the Cascading Effect of Taxes where a tax is paid on tax and the value of the item keeps increasing every time this happens.
Action Cost 10% Tax Total
Buys Raw Material @ 100 100 10 110
Manufactures @ 40 150 15 165
Adds value @ 30 195 19.5 214.5
Total 170 44.5 214.5
In the case of Goods and Services Tax, there is a way to claim credit for tax paid in acquiring input. What happens in this case is, the individual who has paid a tax already can claim credit for this tax when he submits his taxes.
In our example, when the wholesaler buys from the manufacturer, he pays a 10% tax on his cost price because the liability has been passed on to him. Then he adds value of Rs. 40 on his cost price of Rs. 100 and this brings up his cost to Rs. 140. Now he has to pay 10% of this price to the government as tax. But he has already paid one tax to the manufacturer. So, this time what he does is, instead of paying Rs (10% of 140=) 14 to the government as tax, he subtracts the amount he has paid already. So, he deducts the Rs. 10 he paid on his purchase from his new liability of Rs. 14, and pays only Rs. 4 to the government. So, the Rs. 10 becomes his input credit.
When he pays Rs. 4 to the government, he can pass on its liability to the retailer. So, the retailer pays Rs. (140+14=) 154 to him to buy the shirt. At the next stage, the retailer adds value of Rs. 30 to his cost price and has to pay a 10% tax on it to the government. When he adds value, his price becomes Rs. 170. Now, if he had to pay 10% tax on it, he would pass on the liability to the customer. But he already has input credit because he has paid Rs.14 to the wholesaler as the latter’s tax. So, now he reduces Rs. 14 from his tax liability of Rs. (10% of 170=) 17 and has to pay only Rs. 3 to the government. And therefore, he can now sell the shirt for Rs. (140+30+17) 187 to the customer.
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://cleartax.in/s/gst-law-goods-and-services-tax
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Not indicating that the content you copy/paste (including images) is not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
Some tips to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
Thank You! ⚜
If you are the author, please reply and let us know!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit