
1. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence exhibited by machines. In computer science, the field of AI research defines itself as the study of "intelligent agents": any device that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chance of success at some goal. Colloquially, the term "artificial intelligence" is applied when a machine mimics "cognitive" functions that humans associate with other human minds, such as "learning" and "problem solving".
2. Recent developments
The implications of recent advances in AI have spurred heated the global debate. As science fiction starts to become reality, AI products are slowly infiltrating homes and workplaces. This is raising concerns about the potential detrimental effects of AI on the job market, or even about the dangers of an AI singularity, where sentient robots take over the world and destroy humans.
You might have heard of these concerns before …

3. What good does come with AI?
Besides these valid concerns, AI can first and foremost be used to fundamentally rethink how we solve the world’s problems.
AI has the potential to greatly improve things like healthcare, education, poverty and security. AI machines can do some very beneficial things already today that humans will simply never be able to. If we leverage that to augment what humans do well, AI could positively impact society, business, and culture on the order of magnitude of the internet itself.
AI is meant to scale the human mind, not replace it. The human brain is the most elegant computer in existence. We process millions of sensory inputs automatically and constantly, allowing us to learn and respond to our environment. But the human brain only contains about 300 million pattern processors that are responsible for human thought. What if we could complement all of our amazing ideas with not just more data, but also orders of magnitude more data processing capability?
Imagine how we would rethink every single problem that exists today. Let’s have a look into the (near) future of AI.
a)Personalized medicine

AI is driving the adoption and implementation of precision medicine: an emerging approach for disease treatment and prevention that takes into account individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle for each person. Think of it as a type of personalized medicine. For example, around 25,000 people in the US are diagnosed with brain tumors every year. Traditionally, they might all be given the same course of treatment to see what might work in a one-size-fits-all approach. Personalized medicine will allow doctors and researchers to predict more accurately which treatment and prevention strategies for a particular disease will work in which groups of people.
Many of the answers lie in the vast amount of medical data already collected. AI algorithms like deep learning are already used to enable doctors and hospitals to better analyse their data. Through their work, medical practitioners have been able to identify previously unknown diabetes sub-types that could lead to better understanding of therapies that could work better for certain types of patients. AI algorithms are also used to detect tumors in radiology scans more accurately and efficiently, and even potentially accelerate finding a cure for cancer.
AI combined with new groundbreaking medical breakthroughs like CRISPR genome editing offers unexpected opportunities.
Recommended articles for CRISPR:
https://steemit.com/science/@meisi51/hpv-about-to-be-cured-by-crispr-very-soon
b)Cybersecurity

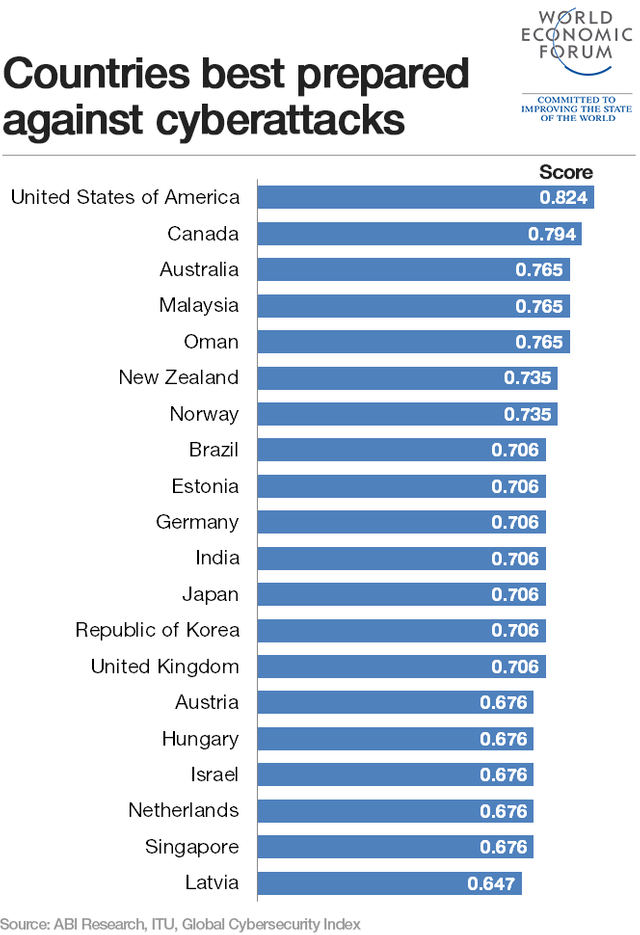
There were around 2 billion cybersecurity breaches in 2015 and 2016. Security teams struggle today to work through the increasing number of alerts generated by traditional tools. The self-learning and automation capabilities enabled by AI can increase effectiveness and reduce costs, keeping us much safer from terrorism or even smaller scale identity theft.
AI-based solutions already in the market can be more proactive and can preempt attacks in the pre-execution state by identifying patterns and anomalies associated with malicious content. There are already predictive capabilities of AI used for advanced threat detection on a global scale. Further AI is used for fraud preventions and for endpoint security, like smartphones and laptops. These technologies will dramatically expand the scope and scale of security professionals and allow them to detect threats hopefully well before they actually attack.
c)Precision Farming

The world's population is expected to increase significantly over the next three decades, but our capacity for food production will struggle to keep pace. AI is driving efficiency in our current farming methods to increase production and reduce wastage without adversely affecting the environment.
AI enables huge machines to plant crops in a far more uniform and accurate way and can reduce overlap in agricultural processes such as tilling, planting and fertilising, which in turn reduces the use of chemicals and increases productivity.
AI's deep learning has created a facial recognition system than can identify individual cows by their facial features in just six seconds, enabling huge herds to be monitored with minimal human involvement. Soon, they will be able to detect early signs of lameness in a cow based on its body shape, and alert the farmer accordingly.
As sensors proliferate on farms and drones capture real-time images of the condition of vast amounts of farmland, AI machines will be able to help farmers foresee what their crops and farms are going to need potentially over a year in advance, giving them more time to react to adverse conditions.
d)Further applications
AI can be applied to many more problems and markets. In fact, it should be thought of as a fundamentally new approach to every problem. Those decisions will be made by humans who want to change and improve the world, and who now can scale their minds to address ever-expanding frontiers.
Don’t fear the future my friends, be excited and interested in it.
For further information:
http://reports.weforum.org/global-risks-2017/executive-summary/
https://futureoflife.org/ai-open-letter/
https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/primer/precisionmedicine/definition
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/05/artificial-intelligence-will-change-the-world-heres-how/
Welcome to Steemit @meisi51 :)
Make sure to participate in this weeks giveaway to get known in the community!
Here are some helpful tips to get you started:
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/05/artificial-intelligence-will-change-the-world-heres-how/
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Yeah thanks - that is what I already cited in my article ... ;)
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
That's just normal computational power as well, check out DWave a company Alphabet (google parent company) bought that specialise in quantum computing. Can you imagine that computational power combined with this kind of AI? I'm so excited for what the future will bring!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Haven't heard of DWave before. Just know Google's deepmind and alphaGo. However, I also considered to dig deeper into quantum computing - this stuff is so freaking exciting and could be the next breakthrough
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Looking forward to it!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit