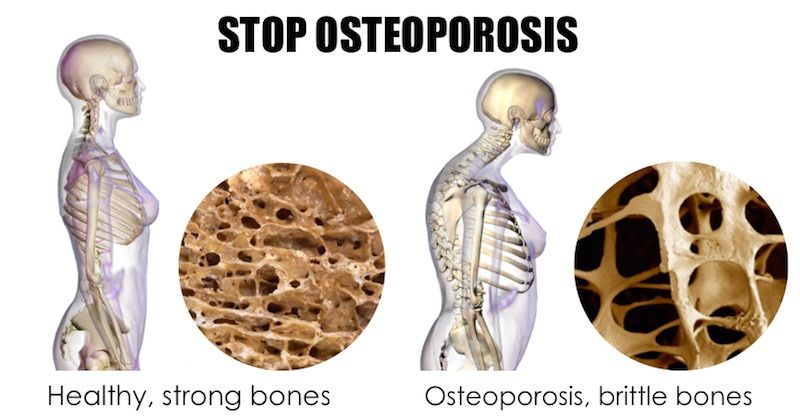
Osteoporosis is a disease where there are low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue. Osteoporosis will increase the fragility of bones and thus increase the risk of fracture. As you may know, female, especially postmenopausal women tend to be at a greater risk of getting osteoporosis.
Classification of osteoporosis
Primary osteoporosis
There are two types of primary osteoporosis:
Type 1: Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Women have a drastic increase in bone resorption in 3-6 years after menopause.
Type 2: Senile osteoporosis. Both men and women aged 75 years old and above are at a higher risk of getting it.
Secondary osteoporosis
Secondary osteoporosis happens when the osteoporosis is caused by an underlying disease or a particular drug. In this case, the management of underlying cause is more essential. The following are some of the disease states which may lead to secondary osteoporosis.
- Cushing’s syndrome: It is a disease state characterized by buffalo hump, moon face, pink or purple stretch marks on the skin due to prolonged exposure to hormone cortisol.
- Thyrotoxicosis: It is a condition where thyroid glands in the body overproduce thyroid hormones, resulting in other conditions.
- Hyperparathyroidism: Hyperparathyroidism happens when parathyroid gland in the body overproduce too much parathyroid hormones.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: It happens when there is a gradual loss of kidney function over a long period of time.
- Liver Cirrhosis: It is an abnormal condition of liver where there is irreversible fibrosis (scarring) of the liver.
Drugs which may cause secondary osteoporosis are:
- Glucocorticoids
- Heparin
- Phenytoin
- Immunosuppressants
- Aromatase inhibitors
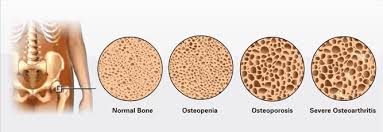
According to World Health Organization, osteoporosis can be classified as below:
- Normal – Bone mineral density > -1.0 SD of young adult reference range (T-score >-1.0)
- Osteopenia - Bone mineral density between -1.0 SD and -2.5 SD below the young adult mean (-1/0> T-score > -2.5)
- Osteoporosis – Bone mineral density < -2.5 SD of the young adult mean (T-score < -2.5)
- Established osteoporosis - Bone mineral density < -2.5 SD of the young adult mean with the presence of at least one fragility fracture.
For your information, osteopenia is referring to a condition where the bone mineral density is lower than normal peak but it is not low enough to be classified as osteoporosis. Precautionary measures should be taken once osteopenia happen.
Risk factors of osteoporosis
It is classified into modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors as below:
Non-modifiable risk factors are:
- Advanced age
- Female
- Ethnicity (Causasian or Asian)
- Family history of bone fracture
- Personal history of previous fracture as adult
- Small stature
On the other hand, modifiable risk factors are:
- Low intake of Calcium or Vitamin D
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Cigarette smoking
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Excessive caffeine intake
- Oestrogen deficiency
- Low Body Mass Index (BMI < 19)
.jpg)
Image Source

.jpg)

It is great to find articles in your expertise since you deal with many medical conditions and prescribe the suitable medication for the sick. Keep posting!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This post has received a 2.61 % upvote from @drotto thanks to: @fun2learn.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Your Post Has Been Featured on @Resteemable!
Feature any Steemit post using resteemit.com!
How It Works:
1. Take Any Steemit URL
2. Erase
https://3. Type
reGet Featured Instantly – Featured Posts are voted every 2.4hrs
Join the Curation Team Here
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Hello, I really liked your publication, I followed you, I hope to see more articles like this one. Greetings.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit