Hello Steemian!
It is a pleasure to be here, introduced by my colleagues. My love for science, engineering and mathematics is immeasureable. It always pleases me to post my finding or innovation in this field. My name is Opeodu Abayomi, I'm a graduate of Electrical engineering but that doesn't mean other science field are not worth knowing. This is my first post . It is about the Earth radius. Have ever wonder how the Earth's radius was estimated? Read this article to find out
INTRODUCTION

Earth's radius is the distance from the Earth's centre to the Earth's surface. It is approximately about 6371km or 3959mi. The unit metre (m) is used mostly in astronomy and geophysics. Radius is a term used in circular shapes but it is strictly a property of a sphere. Earth is not completely spherical - reason for its radius being an approximate value between the range of 6353km to 6384km. A length from the center of the Earth to some point on the Earth's surface or idealised surface might be called the Earth's radius at that point. The idealised surface is usually the average sea levels or addition of elevations about 230m above the sea level. Earth's rotation, external tidal forces and internal density variation are the cause of deviation in the Earth's shape from a perfect sphere. As a result, models were created to emulate the characteristic of the Earth's surface, simplest model that suits the purpose of study is used. Each of these models has geometric radius in common.
EARTH MODELS
Some of the models of Earth's surface arranged from exact to more approximate are:
The actual Earth's surface

Actual surface of the Earth
The geoid- defined by the average sea level at any point on the Earth's surface
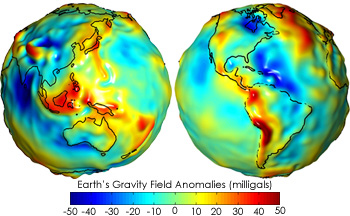
Wikimedia Commons: Earth geoid
The ellipsoid- geocentric to model the earth globally or geodectic for regional Earth
Wikipedia : Earth ellipsodial model
The sphere.

Earth Globe
The geoid and the ellipsoid model assumed the Earth's radius to be a fixed distance from any point on the model to specific center. These models referred to the Earth's radius as the "the radius of the earth at that point" or "the radius of the earth". The actual earth surface model on the other hand assumed the radius to be a pseudonym since the Earth is not practically a sphere. Rather, elevation above or below sea levels is more helpful when estimating the radius.
Irrespective of the model, any radius of each model falls between 6357km (polar minimum) and 6378km (equatorial maximum). Hence, the Earth's deviates from a perfect sphere by three percent, which buttresses the spherical model in many contexts and support the term "radius of the earth".
TYPES OF EARTH RADIUS
Earth's radius can be classified into three, namely the fixed radii, location-dependent radii and the global average radii.
The fixed radii are constant in value and they are independent of various location. WGS (World Geodetic System-1984) standard ellipsoid served as its basis. Equatorial radius and polar radius are the types of fixed earth radius. The Earth's equatorial radius or the semi-major axis, is the distance from its center to the equator and its value is 6,378.1370km while the Earth's polar radius or semi-minor axis is the distance from its centre to the poles (North and South poles) and equals 6,356.7523km. The equatorial radius is used to compare Earth with other planetary bodies.
Location-dependent radii is the radius of the Earth at specific latitude or noticeable locations on the Earth's surface. Such radii are geocentric radius - the distance between the Earth's centre to a point on the spheroid surface at geodectic latitude; radii of curvature - which include meridonal radius (Earth;s radius of curvature in the North - South) and prime vertical radius (radius that appears due east of the other, it is perpendicular to meridonal radius at the same latitude); directional radius - the Earth's radius of curvature along a course measured from north at a given latitude; and combination radius - it is the mean of the meridonal and prime vertical radius.
Global average radii use the notation and dimensions for the Earth as derived from WGS-84 ellipsoid namely the equatorial radius and the polar radius. Subdivision of the global radii are the mean radius, authalic radius, volumetric radius, rectifying radius and the average distance from the centre to surface. IUGG (International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics) calculated the mean radius to be 6,371.0088km while IAU (International Astronomical Union) subdivided the mean radius into the nominal equatorial Earth radius and nominal polar Earth radius with values of 6378.1km and 6356.8km respectively. Authalic radius is the radius of the Earth assumed to be a perfect sphere that has the same surface area as the reference ellipsoid. The authalic radius for the Earth is 6371.0072km.
Volumetric radius is the radius of a sphere of volume equal to the ellipsoid, volumetric radius equals 6,371.0008km. Rectifying radius is the radius at which the circumference of the Earth's sphere equals the perimeter of the ellipse. The rectifying radius is equivalent to the meridonal mean. For Earth, the rectifying radius is 6397.4491km. Average distance from center to surface is based on the reference ellipsoid, closely related to a geoid, but geoid has no relationship with the surface topography.
Alternatively, average elevations everywhere, resulting in a mean radius of 230m larger than authalic radius, the volumetric radius or the IUGG radius. This average is 6,371.230km with tolerance of 10m.
HOW THE EARTH'S RADIUS WAS ESTIMATED
How was these radii calculated? Was there a super-long measuring instrument used to estimate the radius? What an intellectual question. The first published paper about the Earth's size is written by Aristotle in his book titled "On the Heavens" around 350BC. He reported that mathematicians had predicted the circumference of the Earth to be 400,000 stadia, but scholars were critical about Aristotle's figure to be inaccurate and almost twice the true value. Eratosthenes is the first known scientist to measure and calculate the radius of the Earth in about 240BC.
Eratosthenes was a Greek geographer, poet, mathematician, astronomer and music theorist. He is best known for being the first person to estimate the Earth's circumference, other laudable works are invention of leap year, first map of the the world and the calculation of the Sun's radius amongst others. How did Eratosthenes calculated the Earth's radius? Eratosthenes estimated the circumference of the Earth without leaving Egypt. He observed that at local noon on the summer solstice in Syene, the Sun was directly overhead. He discovered this due to the blockage of Sun reflection by someone shadow when looking down a deep well at that time in Syene.
He measured the Sun's angle of elevation at noon in Alexandria by using a gnomon ( a vertical rod ) and measuring the length of the rod's shadow on the ground. The angle of the Sun's ray was calculated using the length of the rod and the length of the shadow, as the legs of the triangle. Elevation angle turned out to be 7 degrees. Taking the Earth to be spherical and knowing the distance between Alexandria and Syene, he finalised that the Earth's circumference was fifty times the distance between Alexandria and Syene. Eratosthenes had the distance between the two cities (Alexandria and Syene) to be 5000 stadia - a common distance unit of the time.
The unit stadia was not a universal standard length, so it is vague to know which version Eratosthenes used. However, the errors were not more than 16 percent resulting to the actual polar circumference of the Earth to be over 40 thousand km. With the knowledge of the circumference of the Earth, he estimated the radius of the Earth using convectional formula between the radius and the circumference by assuming its shape to be spherical.
Later on, efficient and easy method to calculate the Earth's radius was discovered by Al-Biruni.
Al-Biruni is regarded as one of the greatest scholar of muslim meideval. He was versed in mathematics, physics, astronomy and natural sciences. Abbasid Caliphate needed to calculate the Earth's size due to their increasing population from Spain till Indus river in Pakistan. Also, Muslims are required to face the direction of the Kaaba while praying, determination of the Kaaba exact position poses as a challenge because they needed to know the curvature of the Earth and the Earth's size. To solve this directional issue, Ablasid Caliph Al-Mamum employed a team of well-known scholars of that era and assigned them to calculate the Earth's size. The team first found the distance covered when the Sun's angle changed by 1 degree at noon and multiply it by 360 to arrived at circumference from which the size was gotten. The shortcomings of this method was the difficulty to measure large straight line in the desert due to intense heat, error of this method is 4 percent of the actual value. Al-Biruni devised a more advanced and reliable method to measure the Earth's radius. He used three things. An astrolabe- an early form of sextant, a suitable mountain with a flat horizon and the knowledge of trigonometry. He calculated the height of the mountain first, by measuring angle of elevation at two different points lying on a straight line using astrolabe and the distance between the two points using paces. Simple trigonometric techniques was then used to estimate the height of mountain. The next step was by measuring the ange of dip or depression of the flat horizon from the mountain top using the astrolabe the same way. He made sure the line of sight from the mountain top to the horizon to make an angle of 90 degrees with the radius.
Finally he figured out that the figure linking the Earth's center, the mountain top and the horizon was a large right angle triangle on which the law of sines was used to yield the Earth's radius. Biruni's stated radius of 6335.725km, with error less than 1 percent.
To avoid confusion and non-uniformity of different values of the Earth's radius, it is advisable to round up the Earth's radius to two significant figure, that is 6400km.
REFERENCES
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details.




I never thought of it for once. Thanks for this eye opening post.. What a way to have you here mate.
Just keep doing your thing. Good job
But don't forget to always comment on other people's post. That is the best way to survive in this large community..
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Dear friend, you do not appear to be following @wafrica. Follow @wafrica to get a valuable upvote on your quality post!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
You welcome on board @opeodu
Good write up for a start..Engage more in the STEM community and explore! Happy writing...!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Scientists of old didn't have it easy at all... a lot to be discovered but litte imstruments available. Kudos to them all. Nice post @opeodu, keep it up
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Wow... I never really thought about how this was done but now i know. Welcome to the steemSTEM community. Do well to engage on posts in the community.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
wow... i never thought of this forehand.
Nice digging Sire
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
This is a nicely researched and well written post. Nice one brother.
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit
Congratulations @opeodu! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Downvoting a post can decrease pending rewards and make it less visible. Common reasons:
Submit