Friends steemians, today we are going to study a mixture of gases that is vital for life on Earth, it is "Air", which is transparent and manifested by the winds and when some bodies move at high speeds; The air is what surrounds the earth and is known as the atmosphere.
Definition of Air:
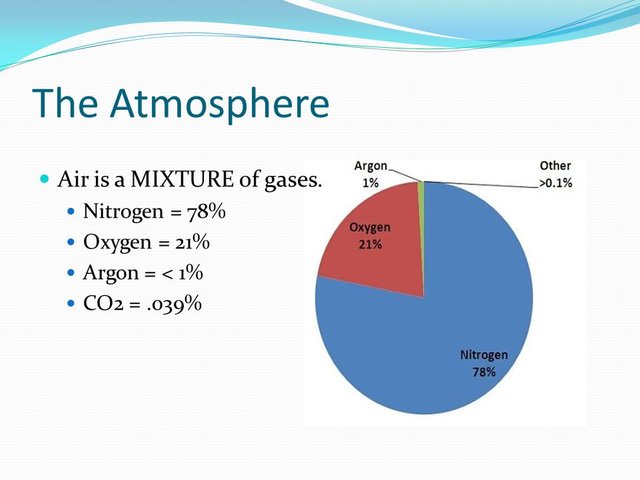
Air is the homogenous mixture of two gases oxygen (symbol O) and nitrogen (symbol N), which constitutes the Earth's atmosphere, which remain around the planet by action of the force of gravity. The air is essential for life on the planet and transparent to the naked eye. FuenteThe air contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and also contains other elements that represent 1%.
Source

Source
Nature of the Air
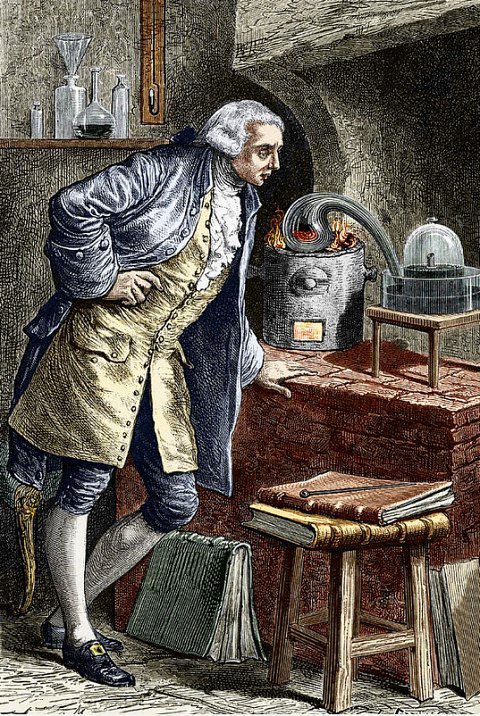
The true nature of Air was only known in 1774, when Lavoisier discovered it during the course of a famous experiment that I will summarize below:

Source
- The mercury in the retort is covered with fine orange-red scales.
- The mercury of the crystallizer rises inside the bell, which proves that a part of the gas contained in said bell has disappeared.
B) If you stop heating the ace that remains in the bell, you can check that it is a gas neither fuel nor oxidizer, of density a little lower than the air that is: Nitrogen.
C) If the orange-red flakes are collected and heated in another retort with a release tube going to a test tube filled with water, mercury will appear in the retort while a gas will be released into the test tube. This gas revives the flame of a match that only has one point of ignition; It is not combustible and is heavier than air, this ace was approximately: Oxygen. The red scales were a combination of oxygen and mercury; mercury oxide (2Hg + O2 ➡ 2HgO). The volume of evolved air represents exactly the volume of gas that disappeared during the first part of the experiment.
Conclusion: Air is a mixture of two gases: Oxygen (O) and Nitrogen (N).
Air analysis
- In volume: Since Lavoisier's experiment is long, delicate and incomplete, a body capable of combining with oxygen faster than mercury can be used, it is said: "That has greater affinity" for the oxygen. You can practice an experiment called "hot match".
- Analysis of the air in weight: The method of analysis of the air in weight, imagined by Dumas and Boussingault, is more precise than the previous one; It consists in principle in the absorption of oxygen from the air by the heated copper. The copper is weighed before the experiment and then the weight of the absorbed oxygen is deducted. The nitrogen that is released from oxygen is also weighed in the following way: vacuum is previously produced in the apparatus and then weighed. The air is let in slowly; loses oxygen when it passes through hot copper and the device fills with nitrogen. Then weigh the device at the end of the experiment and get the weight of the nitrogen.
Atmospheric nitrogen
Nitrogen is an element that together with oxygen is present in the mixture that forms the Air. As Lavoisier demonstrated, in his experiments, the atmospheric nitrogen, is a gas that remains after separating the oxygen from the air.Nitrogen is the gas that Lavoisier obtained during the oxidation of hot mercury. Lavoisier considered that the nitrogen had certain effects, and said that if a bird or a mouse if they were placed under a bell full of this gas, they die immediately. And that a lit candle instantly extinguished in this gas; demonstrating in this way, that it is not suitable for breathing or for combustion.
Other elements present in the air.
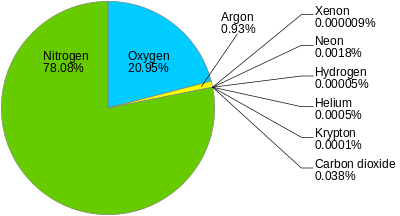
The above analyzes do not take into account other elements and substances that contain air. Because in addition to oxygen and nitrogen, air also contains many solids, such as: mineral dust of various types, such as living microscopic organisms, also organic remains; liquids: as raindrops, haze; gases: water vapor whose proportion varies greatly with temperature, carbon dioxide in an almost constant proportion and equal to 3 / 10,000 in volume, traces of ammonia, ozone, nitrogenous compounds of nitrogen.
Also the air contains some gases which are difficult to isolate, which represent 1% of the air and have applications in the industry; these are: the helium which is a non-combustible light element which is used to inflate balloons; the neon, which is used in luminous advertisements; another is argon and krypton, which are used inside bulbs, and xenon.
Source
Properties of the air
One liter of dry air at 0 ° and normal pressure weighs 1.2935 g; the liquid air boils at 192 °. The chemical properties of air are mainly those contained in oxygen attenuated by the presence of nitrogen.
Posted from my blog with SteemPress : http://oscarcede.vornix.blog/?p=142