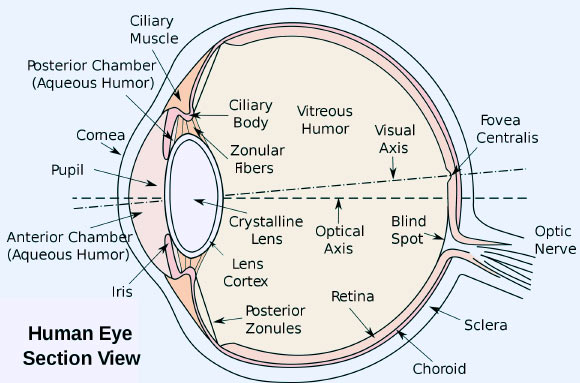
The crystalline lens is a transparent, biconvex structure in the eye, which is located behind the iris and in front of the vitreous humor, as shown in Figure 1. Its main purpose is to allow focusing on objects located at different distances. The lens is characterized by its high concentration of proteins, which give it a higher refractive index than the fluids that surround it. This fact is what gives it its ability to refract light, helping the cornea to form the images on the retina. The radiation is invisible to our eyes, by making contact with them, we can add structural damage to the DNA of the lens cells. This organ is one of the most radiosensitive tissues in the body (tissue that is highly sensitive to ionizing radiation), noting detectable changes in the lens that are observed in doses between 0.2 and 0.5 Gy, while other eye diseases in other tissues they occur in acute or fractionated exposures between 5 and 20 Gy [1].
Radiation protection standards, formulated by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), indicate that tissue damage will occur when a dose threshold is exceeded. For the lens, opacities are detected from 0.5 to 2 Gy for acute exposures and 5 Gy for chronic exposures. For cataracts to occur, the values are higher, with a threshold dose between 2 and 10 Gy for acute exposures and 8 Gy for chronic exposures [1].
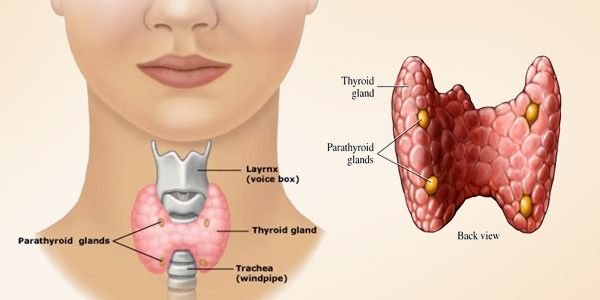
On the other hand, the thyroid gland is shaped like a butterfly and is located in the anterior part of the neck, as shown in Figure 2. Its job is to form the thyroid hormones, dump them into the bloodstream and deliver it to all tissues of the body. Thyroid hormones help the body use energy, maintain body temperature, and allow the brain, heart, muscles, and other organs to function normally [2].
Thyroid disorders are commonly found after radiotherapy for cancer, either secondary to an alteration of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis or after direct damage to the thyroid gland itself. The abnormalities of the thyroid gland among which stand out, thyroid dysfunction, nodules and, rarely, thyroid cancer. This gland is radioresistant, for low doses there is no record but if direct damage to the thyroid gland arises through radiation, at a fractional dose greater than 18 Gy, hypothyroidism is commonly present, with low thyroxine (T4) and thyrotropin (TSH) elevated, being able to see the effects 5 years after the irradiation [1].
The cristalline lens and thyroid are exposed in a mammography study, although the dose they receive is not from the direct beam, as it could receive scattered or secondary radiation. As we know, the primary beam goes directly to the woman's breast. This type of study is also done in men with pathologies.
Mechanisms of cellular damage by ionizing radiation
The biological effects of ionizing radiation derive from the damage they cause in the chemical structure of cells, mainly in the DNA molecule (deoxyribonucleic acid). In DNA is all the information necessary to control cellular functions such as growth, proliferation and differentiation. In addition, this information is transmitted to offspring cells [3].
The radiation trajectories can deposit energy directly into the DNA, ionizing molecules (direct effect) or they can ionize other molecules of the cell, especially water molecules, to form free radicals that can damage the DNA (indirect effect). Understand as free radical that unstable molecule that has an unpaired electron, its mission is to remove an electron from another molecule to achieve its stability, triggering multiple free radicals in the body. In this case, the final result of the process of absorption of radiation by a water molecule, is concreted in the creation of both ions (H + and OH-), and free radicals (H • and OH •).
Emphasizing that the human body is composed of 80% water and that there is a high probability that the effects will occur indirectly.
Repair mechanisms
One of the most interesting biological factors to consider in understanding the response of a cell to radiation is its ability to repair the damage produced in the DNA molecule. When potentially lethal damage occurs, only if the cell is able to repair it can it survive. Said repair is especially effective when the cells are in a resting state of proliferation [3]. Thus, if an irradiated cell is stimulated proliferatively, it is unlikely that it can repair the potentially lethal damage induced. Although most of the damage produced by ionizing radiation is repaired, what has consequences for the cell and its offspring is the remaining damage not repaired or badly repaired, being the result in these cases a viable cell but genetically modified (mutant cell) or cell death.
In the event that cell death occurs, deterministic effects are generated, as a result of tissue death or loss of functional capacity of the tissue when it exceeds the threshold limits of the organ. If mutant cells are produced, it means that the radiation affected reproductive cells, those that are in constant cell division, producing stochastic or hereditary effects. If the mutant cells interact with other cells, they generate a cancer after a period of latency, which over time also causes hereditary effects.
REFERENCE
[1] ICRP 118. "Statement on Tissue Reactions and Early and Late Effects of Radiation in Normal Tissues and Organs - Threshold Doses for Tissue Reactions in a Radiation Protection Context". P.116-161.
[2] The American Thyroid Association. (2014). Consulted: September 13, 2016. Available at: http://www.thyroid.org/cancer-de-tiroides/.
[3] Nuclear Safety Council (2013). "General aspects of the interaction of radiation with the biological environment". Course of Supervisors of radioactive facilities (IR) BASIC MODULE